- Types of Sailboats
- Parts of a Sailboat
- Cruising Boats
- Small Sailboats
- Design Basics
- Sailboats under 30'
- Sailboats 30'-35
- Sailboats 35'-40'
- Sailboats 40'-45'
- Sailboats 45'-50'
- Sailboats 50'-55'
- Sailboats over 55'
- Masts & Spars
- Knots, Bends & Hitches
- The 12v Energy Equation
- Electronics & Instrumentation
- Build Your Own Boat
- Buying a Used Boat
- Choosing Accessories
- Living on a Boat
- Cruising Offshore
- Sailing in the Caribbean
- Anchoring Skills
- Sailing Authors & Their Writings
- Mary's Journal
- Nautical Terms
- Cruising Sailboats for Sale
- List your Boat for Sale Here!
- Used Sailing Equipment for Sale
- Sell Your Unwanted Gear
- Sailing eBooks: Download them here!
- Your Sailboats
- Your Sailing Stories
- Your Fishing Stories
- Advertising
- What's New?
- Chartering a Sailboat
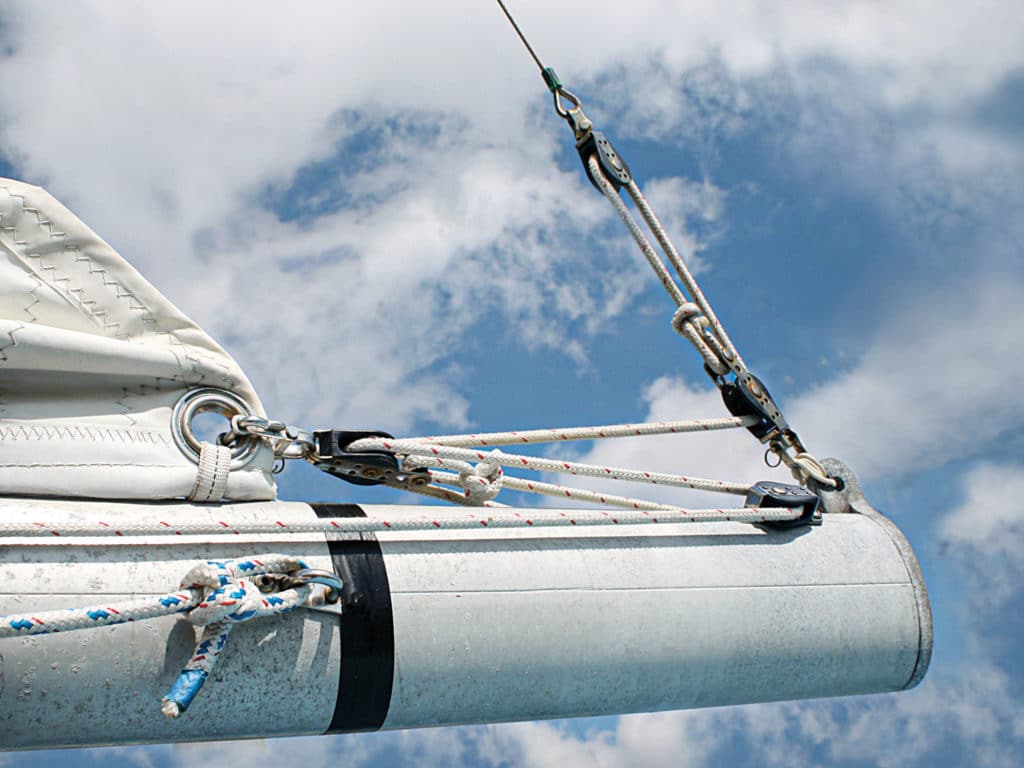
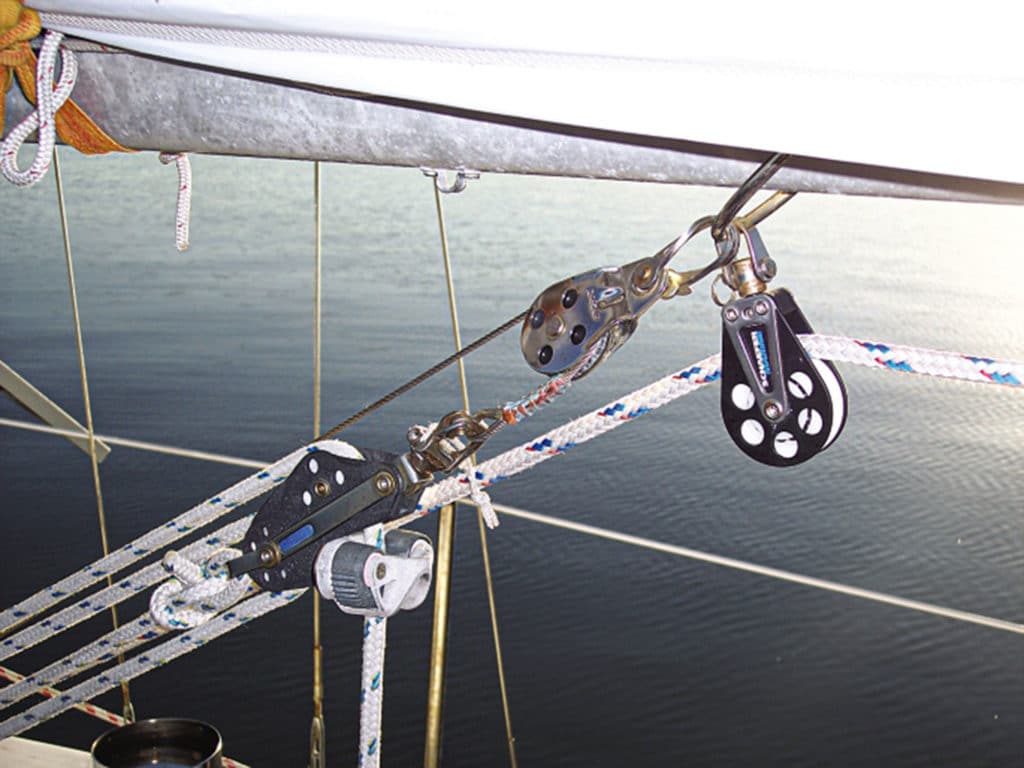
- Running Rigging

Sailboat Rigging: Part 2 - Running Rigging
Sailboat rigging can be described as being either running rigging which is adjustable and controls the sails - or standing rigging, which fixed and is there to support the mast. And there's a huge amount of it on the average cruising boat...

- Port and starboard sheets for the jib, plus two more for the staysail (in the case of a cutter rig) plus a halyard for each - that's 6 separate lines;
- In the case of a cutter you'll need port and starboard runners - that's 2 more;
- A jib furling line - 1 more;
- An up-haul, down-haul and a guy for the whisker pole - 3 more;
- A tackline, sheet and halyard for the cruising chute if you have one - another 3;
- A mainsheet, halyard, kicker, clew outhaul, topping lift and probably three reefing pennants for the mainsail (unless you have an in-mast or in-boom furling system) - 8 more.
Total? 23 separate lines for a cutter-rigged boat, 18 for a sloop. Either way, that's a lot of string for setting and trimming the sails.

Many skippers prefer to have all running rigging brought back to the cockpit - clearly a safer option than having to operate halyards and reefing lines at the mast. The downside is that the turning blocks at the mast cause friction and associated wear and tear on the lines.
The Essential Properties of Lines for Running Rigging
It's often under high load, so it needs to have a high tensile strength and minimal stretch.
It will run around blocks, be secured in jammers and self-tailing winches and be wrapped around cleats, so good chafe resistance is essential.
Finally it needs to be kind to the hands so a soft pliable line will be much more pleasant to use than a hard rough one.
Not all running rigging is highly stressed of course; lines for headsail roller reefing and mainsail furling systems are comparatively lightly loaded, as are mainsail jiffy reefing pennants, single-line reefing systems and lazy jacks .
But a fully cranked-up sail puts its halyard under enormous load. Any stretch in the halyard would allow the sail to sag and loose its shape.
It used to be that wire halyards with spliced-on rope tails to ease handling were the only way of providing the necessary stress/strain properties for halyards.
Thankfully those days are astern of us - running rigging has moved on a great deal in recent years, as have the winches, jammers and other hardware associated with it.
Modern Materials
Ropes made from modern hi-tech fibres such as Spectra or Dyneema are as strong as wire, lighter than polyester ropes and are virtually stretch free. It's only the core that is made from the hi-tech material; the outer covering is abrasion and UV resistant braided polyester.
But there are a few issues with them:~
- They don't like being bent through a tight radius. A bowline or any other knot will reduce their strength significantly;
- For the same reason, sheaves must have a diameter of at least eight times the diameter of the line;
- Splicing securely to shackles or other rigging hardware is difficult to achieve, as it's slippery stuff. Best to get these done by a professional rigger...
- As you may have guessed, it's expensive stuff!
My approach on Alacazam is to use Dyneema cored line for all applications that are under load for long periods of time - the jib halyard, staysail halyard, main halyard, spinnaker halyard, kicking strap and checkstays - and pre-stretched polyester braid-on-braid line for all other running rigging applications.
Approximate Line Diameters for Running Rigging
But note the word 'approximate'. More precise diameters can only be determined when additional data regarding line material, sail areas, boat type and safety factors are taken into consideration.
Length of boat
Spinnaker guys
Boom Vang and preventers
Spinnaker sheet
Genoa sheet
Main halyard
Genoa / Jib halyard
Spinnaker halyard
Pole uphaul
Pole downhaul
Reefing pennants
Lengthwise it will of course depend on the layout of the boat, the height of the mast and whether it's a fractional or masthead rig - and if you want to bring everything back to the cockpit...
Read more about Reefing and Sail Handling...

Headsail Roller Reefing Systems Can Jam If Not Set Up Correctly
When headsail roller reefing systems jam there's usually just one reason for it. This is what it is, and here's how to prevent it from happening...

Single Line Reefing; the Simplest Way to Pull a Slab in the Mainsail
Before going to the expense of installing an in-mast or in-boom mainsail roller reefing systems, you should take a look at the simple, dependable and inexpensive single line reefing system

Is Jiffy Reefing the simplest way to reef your boat's mainsail?
Nothing beats the jiffy reefing system for simplicity and reliability. It may have lost some of its popularity due to expensive in mast and in boom reefing systems, but it still works!
Recent Articles
Westerly Discus 33 Sailboat Specs & Key Performance Indicators
Aug 28, 24 02:14 AM
Beneteau Oceanis 400 Specs & Key Performance Indicators
Aug 27, 24 05:09 AM
Grand Soleil 37 Sailboat Specs & Key Performance Indicators
Aug 27, 24 01:19 AM
Here's where to:
- Find Used Sailboats for Sale...
- Find Used Sailing Gear for Sale...
- List your Sailboat for Sale...
- List your Used Sailing Gear...
Our eBooks...

A few of our Most Popular Pages...

Copyright © 2024 Dick McClary Sailboat-Cruising.com
- AROUND THE SAILING WORLD
- BOAT OF THE YEAR
- Email Newsletters
- America’s Cup
- St. Petersburg
- Caribbean Championship
- Boating Safety
- Ultimate Boat Giveaway

Simple Ways to Optimize Running Rigging
- By Erik Shampain
- December 6, 2022

It’s easy to underestimate the benefits of good running rigging. There are many rope products on the market, and there is a time and a place for most of them. Let’s take a look at lines that need the most attention and why, as well as basic rules for using low-stretch line, using lightweight or tapered line where most beneficial and using rope that is easy to work with.
Let’s start up front with the headsail halyard. Luff tension greatly affects shape and thus performance of the jib or genoa, so having a halyard that is as low-stretch as possible is paramount. Saving a little weight aloft is also key, so find a lightweight rope as well. It’s a little against the norm, but for club racing boats that aren’t tapering their halyards, I really like some of the Vectran-cored ropes. Products like Samson’s Validator and New England Ropes V-100 are easy on the hands and easy to splice. For a little more grand-prixed tapered halyard, talk to our local rigger about using a DUX core, or other heat-set Dyneema, with a Technora-based cover. Lately, I’ve been using a lot of Marlow’s D12 MAX 78 and 99. Tapering the halyard saves weight aloft as well. I like soft shackles for jib halyards. There, weight savings aloft generally outweighs the little extra time a bowman needs to attach the sail. This is especially true in sprit boats where the jib is rarely removed from the headstay.
Pro Tip: When not racing, use a halyard leader to pull the halyards to the top of the mast, getting the tapered section out of the sun. For extra protection, put all the halyard tails into an old duffle bag at the base of the mast when not in use.
For jib sheets, I follow the same low-stretch rule as the jib halyard. I don’t want the jib sheet to stretch at all when a puff hits. On boats with overlapping genoas, I don’t generally recommend tapering the line because by the time the genoa is trimmed all the way in, the clew is really close to the block. On boats with non-overlapping jibs, tapering is an easy way to save a little weigh. Plus, the smaller core size runs through across the boat more easily in tacks. I’ve been using soft shackles on the jib or genoa sheets for a while now, mostly because they don’t beat the mast up during tacks. There also a bit “softer” when they hit you.
What about jib lead adjusters? There are a couple of approaches here. Some believe a little stretch is okay, as it allows the lead to rock aft a couple of millimeters in puffs, which twists the top of the jib off slightly. This can be fast as it helps the boat transition through puffs and lulls. I am a fan of this as long as it isn’t too stretchy. I use low-stretch Dyneema for the gross part of the purchase and then a friendlier-on-the-hands rope for the fine tune side, the part that is being handled. Samson Warpspeed or New England Enduro Braid work well.
Spinnaker sheets are a fun one. They should be relatively low-stretch but not necessarily the lowest stretch. I’ve found that near-zero stretch lines can wreak havoc on people and hardware when flogging or when the chute is collapsing. They have to be easy on the hands, as they are the most moved sheets on the boat, and they should be tapered as far as you can get away with. Tapering saves weigh, which is very important in keeping the spinnaker clew lifting up, especially in light air when sails want to droop. Again, Samson Warpseed and New England Enduro braid are good. For boats with grinders or even small boats with no winches, a cover that is a little grippier or stronger is good. Most Technora-based covers work well for this purpose.
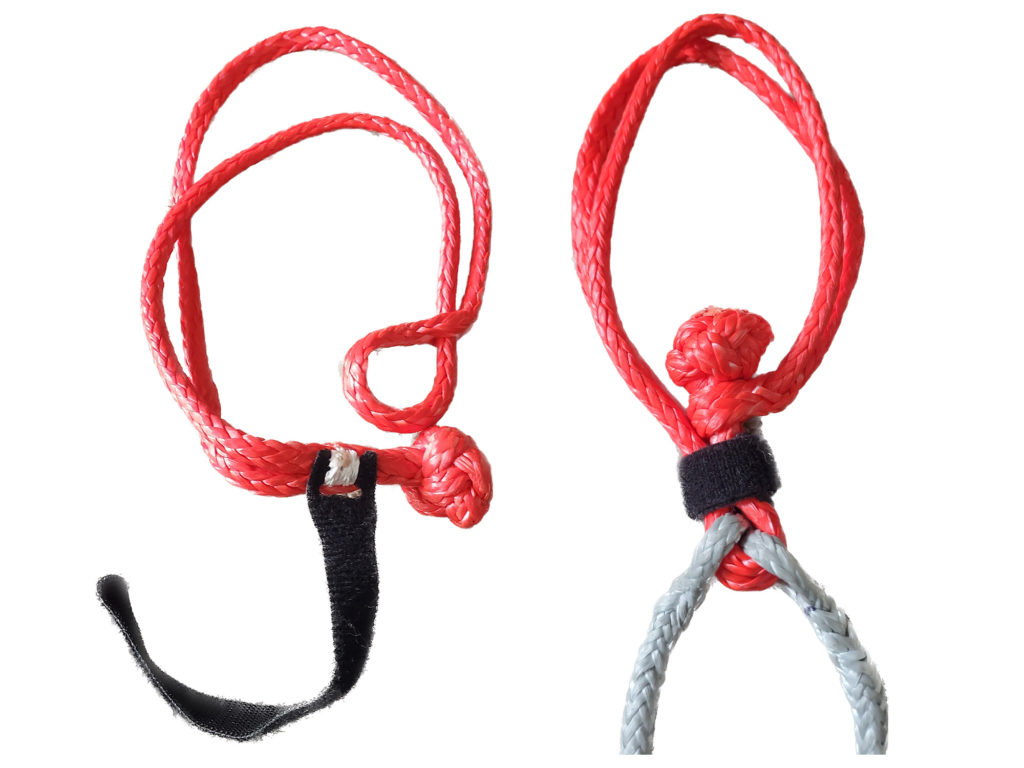
Pro Tip No. 2: On boats with asymmetric spinnakers I like to connect the ‘Y’ sheet with a soft shackle that also goes to the spinnaker. This saves weight. I sew a Velcro strip around one part of the shackle (see picture) so that the soft shackle stays with the ‘Y’ sheet when open. This is beneficial when you have to quickly disconnect or re-run a sheet, replace one sheet, or even quickly replace a soft shackle. On most boats I will keep one spare spinnaker sheet with soft shackle down below as a spare side, changing sheet, or code zero sheet. On boats with a symmetric spinnaker, we’ll splice the spinnaker sheet to the afterguy shackle to save weight in the clew.

The spinnaker halyard has a couple of more options. For halyards supporting code zeros, zero stretch is important. The same principals we used when talking about the jib halyard apply here. For boats without code zeros, I like a little softer halyard with a touch of give. Those tend to run though sheaves better without kinking. Enduro and Warpseed are good for these applications. Most bowmen prefer a shackle that is quick and easy to open. Since a happy bowman is a good thing, I will generally use an appropriately sized Tylaska shackle or dogbone style shackle for those halyards
For symmetric spinnaker boats, the afterguy must be very low stretch line. I go back to products like covered Vectran for club-level sheets. I also find that afterguys generally last longer if I don’t taper them. When the pole is squared back, the afterguys often run pretty hard across the lifelines, producing a fair amount of chafe. Covered lines help minimize that.
For tack lines on asymmetric boats, I like matching spinnaker halyard material on club-level boats and using low-stretch heat-set Dyneema cores with a chafe resistant cover for grand prix and sportboats.
Like the headsail halyard, a near-zero stretch main halyard is also important. For me the same line applications apply. Keep the mainsail head at full hoist at all costs. I will often match the material I use for main and jib halyards.
It is most important that the main sheet sit in the winch jaws well and tail perfectly. This is a strict combination of sizing and pliability. I’ve found that the New England Ropes Enduro braid and the Samson Warpspeed II work well for club-level boats with and without winches. For a slightly longer lasting product with some chafe resistance, try any manufacturer’s Technora-based covered line.
The most under-appreciated and least thought about rope on a boat always seems to be the outhaul. The last thing you want when the wind comes up is for your mainsail to get fuller. Spend some time here and use very low-stretch rope. Most heat-set Dyneemas will work great for the gross tune side of the purchase.
Pro Tip No. 3: Minimizing the last purchase of an outhaul greatly increases the ease with which it can be pulled on or eased out. For example, you could have a 6-to-1 to one pulling a 2-to-1, pulling a 2-to-1 and then to the sail for a 24-to-1. Or, better yet, you could have a 4-to-1 pulling a 3-to-1, pulling a 2-to-1 for a 24-to-1 as well. The latter example will work better. Trust me. I’m a doctor . . . sort of. We built an outhaul like this on a SC50. I can pull it on upwind in heavy air with little problem. On the flip side, in light air downwind, it eases just as well. In fact, if memory serves me right, we did a 3-to-1 in the end rather than the 4-to-1 for a total of 18-to-1 and it worked well.
Runners and backstays should have extremely low stretch. A pumping mast and sagging forestay in breeze isn’t fast. Runner tails, like the mainsheet, should perfectly fit the winch and tail easily without kinking.
With so many options readily on the market now, it can be very confusing. I always recommend contacting your local rigger if you have any questions at all about what rope is right for you. They’ll get you pulling in the right direction.
- More: cordage , running rigging , sailboat gear

Comfort Rules with Mustang’s Minimalist Buoyancy Aid

Smart Polars Are Here

Reproofing May Be Required

Wingfoiling Gear: A Beginner’s Guide

Mistakes And Misfires On the Final Day of Cup’s Preliminary Regatta

Emirates Team New Zealand Remain the Bullies of Barcelona

Start-Box Sparring in Barcelona on Day 2 of Preliminary Regatta

Real-time Wind Overlay Feature Added to Cup Broadcast

- Digital Edition
- Customer Service
- Privacy Policy
- Terms of Use
- Cruising World
- Sailing World
- Salt Water Sportsman
- Sport Fishing
- Wakeboarding
- Anchoring & Mooring
- Boat Anatomy
- Boat Culture
- Boat Equipment
- Boat Safety
- Sailing Techniques
Sailboat Running Rigging Explained
Running rigging refers to the essential lines, ropes, and hardware responsible for controlling, adjusting, and managing the sails on a sailboat. They directly impact a sailboat’s performance, maneuverability, and overall safety.
As a result, understanding different running rigging components and their functions can help us optimize our boat’s performance and make informed decisions in various sailing situations. This comprehensive guide delves deep into the world of rigging by examining its essential components and various aspects, including materials, maintenance, advancements, troubleshooting, knots, and splices.
Key Takeaways
- Running rigging consists of movable components like halyards, sheets, and control lines that control, adjust, and handle the sails.
- Synthetic materials like Dyneema, Spectra, and Vectran have revolutionized running rigging due to their superior strength-to-weight ratio, low stretch and abrasion resistance, and increased lifespan.
- Troubleshooting common running rigging problems involves untangling or untwisting lines, resolving jammed or stuck hardware, and ensuring lines hold tension correctly.
- Knowing how to tie knots and splice lines is crucial in connecting running rigging components, securing lines, and adjusting sails.
- To achieve the best performance, the boat's rigging should be tailored to specific sailing needs, either racing or cruising.
- Different sailboat types and configurations require specific running rigging setups.
Difference between running and standing rigging
Before diving into the components, it’s essential to understand the difference between standing and running rigging. Standing rigging consists of the fixed lines, cables, and rods responsible for supporting a sailboat’s mast(s) and maintaining stability. Examples of standing rigging include shrouds, stays, and spreaders.
Running rigging, on the other hand, comprises the movable components needed to control, adjust, and handle the sails. These elements allow us to raise, lower, and trim the sails according to wind conditions and the boat’s course. Understanding the distinction between the two types of rigging is vital in operating a sailboat safely and efficiently.
Components of Running Rigging on a Sailboat
Responsible for raising, lowering, and holding sails in their deployed position. The primary types include the main halyard (for the mainsail), jib halyard (for jibs or genoas), and spinnaker halyard (for spinnakers). They typically run from the head of the sail down to mast-mounted winches or lead back to the cockpit for easy adjustment.
Control the angle of a sail relative to the wind. They connect the clew to the deck or another part of the rigging (e.g., tack), allowing adjustments and fine-tuning of sail trim . The two main types of sheets are mainsheets (for mainsails) and jib/genoa sheets (for headsails).
Control Lines
Essential for adjusting the tension and shape of sails. Examples include outhauls (for foot tension), cunninghams (for luff tension), and reef lines (for reducing the area under high wind conditions). Proper use of these lines allows sailors to optimize sail shape, improve efficiency, and manage their boats in various wind conditions.
Maintenance and Care
Regular inspection.
Routine inspection of your rigging is essential to identify wear, damage, or issues before they escalate into severe problems. Conduct a thorough examination at least once a season or more frequently if you sail extensively. When inspecting, check for signs of chafe, abrasion, corrosion, frayed, or damaged rope sections. Address these issues promptly to prevent further complications.
Cleaning and maintaining
Proper cleaning and maintenance of your rigging will improve its lifespan and maintain its performance. Rinse ropes and cordage with fresh water and mild detergent, if necessary. Lubricate and clean hardware components using marine-grade products, following the manufacturer’s guidelines.
When to replace
Advantages and impact of advanced synthetic materials , advantages of synthetic materials.
- Higher strength-to-weight ratio: Advanced materials like Dyneema, Spectra, and Vectran provide impressive strength while remaining lightweight, ensuring a secure connection and control in an easy-to-handle braid
- Low-stretch and abrasion resistance: These materials are incredibly resistant to stretching, providing improved control and accurate responsiveness. They also maintain their integrity and durability in wear, abrasion, and weathering.
- Increased lifespan: Synthetic materials can endure harsh conditions and resist UV damage.
Impact on Sailing Experience
The use of advanced materials like Dyneema, Spectra, and Vectran has had a profound effect on the sailing experience, with benefits including:
- Improved sail control and responsiveness: These low-stretch materials allow precise, user-friendly, and efficient sail handling and adjustments, leading to better overall performance.
- Enhanced durability and reduced maintenance: High-performance materials resist wear and weathering more effectively, increasing the lifespan of rigging and lowering the frequency of maintenance or replacement.
- Greater performance potential: Advanced materials’ increased strength and lightness improve boat performance to higher levels, especially in competitive racing scenarios.
Troubleshooting Common Problems
- Tangled or twisted lines: angled lines can impede adjustments and create hazardous situations, like tangled jib sheets , which can cause control issues with your headsail. Always coil and store lines properly when not in use to solve this issue. Regularly inspect your lines for twists or tangles, and address them before they become problematic.
- Jammed or stuck hardware: Dirt, corrosion, or damage can cause hardware components like blocks or winches to jam or stick, making it difficult to control the lines. Clean and lubricate your hardware according to the manufacturer’s guidelines to fix this issue. Replace any damaged or worn-out components to ensure smooth operation.
- Lines slipping or not holding tension: Runners may sometimes slip from cleats or winches, causing the sail to lose its desired shape or position. To overcome this issue, ensure you use the proper cleating or winching techniques, and double-check the compatibility of your line materials with your hardware.
When to call a professional
Although boat owners can resolve many rigging issues, there are situations where the expertise of a professional rigger may become necessary. Consider consulting a professional when:
- You feel uncertain about your ability to diagnose or fix a problem safely and effectively
- You need to replace or install new running rigging components that require specialized knowledge or skills
- You have encountered complex issues that may require advanced troubleshooting techniques
The Art of Knots and Splices
Importance of knots and splices.
Knots and splices connect rigging components, secure lines, and adjust sails. Proper knowledge and execution of these techniques allow us to:
- Effectively connect lines and hardware
- Quickly and safely secure or adjust lines under various conditions
- Reduce the risk of lines slipping or coming undone while sailing
- Maintain the integrity and strength of our rigging
Commonly used knots and their uses
Numerous knots are available for various purposes within the rigging. Some of the most common and versatile knots include:
- Bowline: This popular and secure knot is used for creating a fixed loop at the end of a line, often employed for attaching sheets to sails or halyards to shackles.
- Cleat hitch: A handy knot that quickly and securely fasten lines to cleats; widely used for halyards, sheets, and dock lines.
- Figure eight: A practical stopper knot prevents lines from slipping through hardware, such as blocks or clutches.
Techniques for splicing lines
Splicing is joining two lines or creating a loop within a single line by weaving rope fibers together. Splicing often results in stronger, more secure connections than tying knots and can improve the overall aesthetic of your rigging. Some techniques include:
- Eye splice: This technique creates a fixed loop at the end of a line, ideal for attaching hardware, such as thimbles, shackles, or blocks.
- Short splice: This method joins two lines by interweaving their ends, resulting in a strong connection suitable for halyards or sheets.
- End-to-end splice: An effective way to join two lines end-to-end, maintaining the line’s integrity and minimizing chafe or bulk.
Safety Practices When Handling Running Rigging
Basic safety rules.
- Be aware of your surroundings: Before making any adjustments to your sails or lines, evaluate the environment, and pay attention to potential hazards, such as nearby boats, obstacles, or changing wind conditions.
- Communicate clearly: When making adjustments or performing maneuvers, communicate your intentions with your crew to prevent confusion and ensure necessary steps are started promptly and coordinated.
- Use appropriate gear: Wear gloves to protect your hands from rope burns, and always have a knife or multi-tool nearby to handle unexpected situations, such as cutting tangled or jammed lines.
Risk and injury prevention
While handling rigging, take precautions to prevent accidents or injuries:
- Maintain proper body positioning: When working with lines or winches, position yourself securely to avoid sudden slips or loss of balance that could result in injuries.
- Keep fingers clear: Be cautious when handling lines around winches or cleats to prevent pinched fingers or rope burns.
- Avoid standing in a “line of fire”: Be mindful of potential line snap-backs or sudden movements when tension is released from sails or hardware.
Emergency procedures related to rigging
Being prepared for emergencies is crucial. Familiarize yourself with procedures such as:
- Man Overboard Recovery: Practice techniques to quickly stop the boat and retrieve someone who has fallen overboard.
- Rapid sail reduction or deployment: In extreme weather or urgent situations, know how to quickly reef, furl, or set sails to maintain control and stability.
Tips and Techniques for Better Performance
Tips for optimizing performance.
- Regular inspection and maintenance: Ensuring your lines, hardware, and sails are in good condition and correctly cared for is crucial for performance optimization on the water.
- Tailor your rigging: Customize your rigging according to your specific requirements, whether racing or cruising, as this can affect your boat’s overall performance.
Techniques for Smoother Sailing
- Match line materials and diameters to their purpose: Select the proper line material and diameter for each rigging component, such as the mainsheet, to ensure better sail control, reduced friction, and smooth operation.
- Stay organized and avoid line clutter: Keep lines and hardware tidy using organizers and storage solutions to prevent tangles and confusion, leading to inefficiency or unsafe situations on the water.
Additional Sailboat Rigging Components and Techniques
- Guys: These lines, in conjunction with spinnaker sheets, offer lateral control of the spinnaker pole and consequently allow better management of the spinnaker shape as they help balance the tension between forestay and backstay , maximizing its efficiency in downwind sailing.
- Vangs (or boom vang or kicking strap): While controlling the boom’s angle to maintain shape, vangs also help prevent accidental gybes, increasing safety on board.
- Outhauls: By managing foot tension and the sail hoist, outhauls aid in achieving optimal sail shape according to the wind conditions and point of sail . Loosening the outhaul creates a deeper shape for light winds, while tightening it flattens the sail for heavier conditions.
Equipment Organization and Storage
- Line bags or organizers: Store coiled lines for different sails, like staysail, and keep aft rolling furling lines neatly organized to minimize tangles and clutter.
- Clutches or labeled cleats: Label the appropriate hardware for each line to prevent confusion when adjusting sails.
- Winch handle holders: Ensure winch handles are secured in a designated holder when not in use, reducing the risk of accidents or loss overboard.
Different Rigging Setups
- Sloop Rig vs. Cutter Rig: A sloop rig typically has one headsail, like a genoa, while a cutter rig features two or more, requiring additional rigging components like adding extra backstays for support, extra halyards, sheets, and control lines for the cutter rig.
- In-Mast vs. In-Boom Furling Systems: These systems allow easy reefing and sail deployment. Running rigging for furling systems will include additional lines and hardware to manage furling and unfurling processes from the cockpit.
- Racing Boats vs. Cruising: Racing boats may require specialized configurations, such as high-performance lines and lightweight hardware, while cruising sailboats may prioritize more versatile, durable, and easy-to-maintain rigging components.
Final Thoughts
Understanding and effectively managing running rigging is critical to sailing, directly affecting the boat’s performance, maneuverability, and safety. This comprehensive guide offers a detailed breakdown of rigging components, their care and maintenance, troubleshooting, and the essential knots and splices. It also explores the revolutionary impact of synthetic materials, provides safety practices, and highlights the importance of customizing your running rigging according to your sailing needs.
Standing rigging refers to the fixed lines, cables, and rods that support the sailboat’s mast and maintain stability. Running rigging refers to the movable components that control, adjust, and handle the sails.
Critical components of running rigging include halyards, sheets, and control lines. Additional components can consist of guys, vangs, and outhauls.
Synthetic materials like Dyneema, Spectra, and Vectran offer superior strength-to-weight ratio, low stretch and abrasion resistance, and an increased lifespan, resulting in better control and durability of running rigging components.
Ideally, if you sail extensively, you should inspect your running rigging at least once a season or more frequently if you sail extensively. Regular cleaning, lubrication, and replacement of worn-out components should be part of your maintenance routine.
Different sailboat types and sail configurations may require specific running rigging setups. For example, a sloop rig and cutter rig have additional requirements for headsails, thus requiring various running rigging components. Similarly, racing boats and cruising sailboats may require different running rigging setups to cater to their needs.
The Importance of the Sailboat Comfort Ratio
What is an impeller on a boat, related posts, whisker pole sailing rig: techniques and tips, reefing a sail: a comprehensive guide, sail trim: speed, stability, and performance.
- Cookie Policy
- Privacy Statement
© 2023 TIGERLILY GROUP LTD, 27 Old Gloucester Street, London, WC1N 3AX, UK. Registered Company in England & Wales. Company No. 14743614
Welcome Back!
Login to your account below
Remember Me
Retrieve your password
Please enter your username or email address to reset your password.
Add New Playlist
- Select Visibility - Public Private
The Running Rigging Technique
Mastering the running rigging technique is crucial for safe and successful heavy weather sailing, allowing sailors to control sail shape and power, reef sails, and maintain stability and balance in challenging conditions.
The Running Rigging Technique: Mastering Heavy Weather Sailing
Sailing in heavy weather can be both exhilarating and challenging. It requires a combination of skill, experience, and the right equipment to ensure the safety of your boat and crew. One of the most important aspects of heavy weather sailing is mastering the running rigging technique. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the ins and outs of running rigging, its importance in heavy weather sailing, and how to effectively use it to your advantage.
Table of Contents
What is running rigging, the importance of running rigging in heavy weather sailing, key components of running rigging, running rigging techniques for heavy weather sailing, maintaining your running rigging.
Running rigging refers to the system of ropes, lines, and hardware used to control and adjust the sails on a sailboat. This is in contrast to standing rigging, which consists of the fixed lines and cables that support the mast and other structural components of the boat. Running rigging allows sailors to manipulate the shape and position of the sails, enabling the boat to harness the wind’s power and move in the desired direction.
In heavy weather conditions, the forces acting on your boat and its rigging are significantly increased. Strong winds and large waves can put immense strain on your sails, mast, and rigging, making it crucial to have a well-maintained and properly set up running rigging system.
Effective running rigging allows you to:
Control sail shape and power : In heavy weather, it’s essential to be able to adjust your sails to reduce their power and prevent them from becoming overpowered. This helps maintain control of the boat and reduces the risk of damage to the sails and rigging.
Reef sails : Reefing is the process of reducing the sail area to make the boat more manageable in strong winds. Running rigging plays a crucial role in reefing, as it allows you to quickly and easily adjust the sails to the appropriate size.
Tack and jibe safely : Tacking and jibing are fundamental sailing maneuvers that involve changing the boat’s direction by turning it through the wind. In heavy weather, these maneuvers can be more challenging and require precise control of the running rigging to ensure the boat’s stability and safety.
Running rigging consists of various lines and hardware that work together to control the sails. Some of the key components include:
Halyards : Halyards are the lines used to hoist and lower the sails. They are typically made of strong, low-stretch materials like polyester or Dyneema and run from the head of the sail to a winch or cleat on the deck.
Sheets : Sheets are the lines used to control the angle of the sails relative to the wind. They are attached to the clew of the sail and run through a series of blocks and fairleads before being secured to a winch or cleat.
Outhauls : The outhaul is a line used to adjust the tension along the foot of the mainsail, which affects the sail’s shape and power. It is typically attached to the clew of the mainsail and runs through a block at the end of the boom before being secured to a winch or cleat.
Cunningham : The Cunningham is a line used to adjust the tension along the luff of the mainsail, which affects the sail’s shape and power. It is typically attached to a grommet near the tack of the mainsail and runs through a block at the base of the mast before being secured to a winch or cleat.
Vang : The vang is a line or system used to control the tension along the leech of the mainsail, which affects the sail’s shape and power. It is typically attached to the boom and runs through a series of blocks before being secured to a winch or cleat.
Reefing lines : Reefing lines are used to reduce the sail area by folding or rolling a portion of the sail and securing it to the boom or the mast. They are typically attached to the sail at specific reef points and run through blocks and fairleads before being secured to a winch or cleat.
When sailing in heavy weather, it’s essential to know how to use your running rigging effectively to maintain control of your boat and ensure the safety of your crew. Here are some key techniques to master:
Reef early and often : As the wind increases, it’s crucial to reduce your sail area to prevent overpowering and maintain control of the boat. Monitor the weather conditions closely and be prepared to reef your sails as needed. Remember that it’s always easier to shake out a reef if the wind decreases than to reef in worsening conditions.
Adjust sail shape for better balance : In heavy weather, it’s essential to have a well-balanced sail plan to reduce the boat’s tendency to round up into the wind or bear away uncontrollably. Use your outhaul, Cunningham, and vang to adjust the shape of your sails and maintain a balanced helm.
Ease the sheets in gusts : When a strong gust hits, it can cause the boat to heel excessively and become difficult to control. By easing the sheets slightly, you can spill some wind from the sails and reduce the heeling force, making the boat more manageable.
Practice tacking and jibing in heavy weather : Tacking and jibing in strong winds and large waves can be challenging and require precise control of the running rigging. Practice these maneuvers in a controlled environment to build your skills and confidence.
Use a preventer to prevent accidental jibes : In heavy weather, the risk of an accidental jibe increases, which can cause damage to the rigging and potentially injure the crew. Rig a preventer (a line attached to the boom and secured to a strong point on the deck) to help prevent the boom from swinging across the boat during an accidental jibe.
Proper maintenance of your running rigging is essential to ensure its reliability and performance in heavy weather sailing. Here are some tips for keeping your running rigging in top condition:
Inspect your running rigging regularly : Check for signs of wear, chafe, or damage, and replace any lines or hardware that show signs of deterioration.
Keep your running rigging clean : Dirt and salt can cause lines to become stiff and difficult to handle. Rinse your running rigging with fresh water regularly and consider washing it with mild soap and water if it becomes excessively dirty.
Lubricate moving parts : Apply a marine-grade lubricant to blocks, sheaves, and other moving parts to ensure smooth operation and reduce wear.
Store your running rigging properly : When not in use, coil your lines neatly and store them in a dry, well-ventilated area to prevent mold and mildew growth.
Mastering the running rigging technique is essential for heavy weather sailing. By understanding the key components of running rigging and learning how to use them effectively, you can maintain control of your boat, ensure the safety of your crew, and enjoy the thrill of sailing in challenging conditions. With practice and proper maintenance, your running rigging will serve you well as you embark on your sailing adventures.
- BOAT OF THE YEAR
- Newsletters
- Sailboat Reviews
- Boating Safety
- Sails and Rigging
- Maintenance
- Sailing Totem
- Sailor & Galley
- Living Aboard
- Destinations
- Gear & Electronics
- Charter Resources
- Ultimate Boat Giveaway
Running Rigging for Cruising Sailors
- By Bruce Bingham
- Updated: October 15, 2020
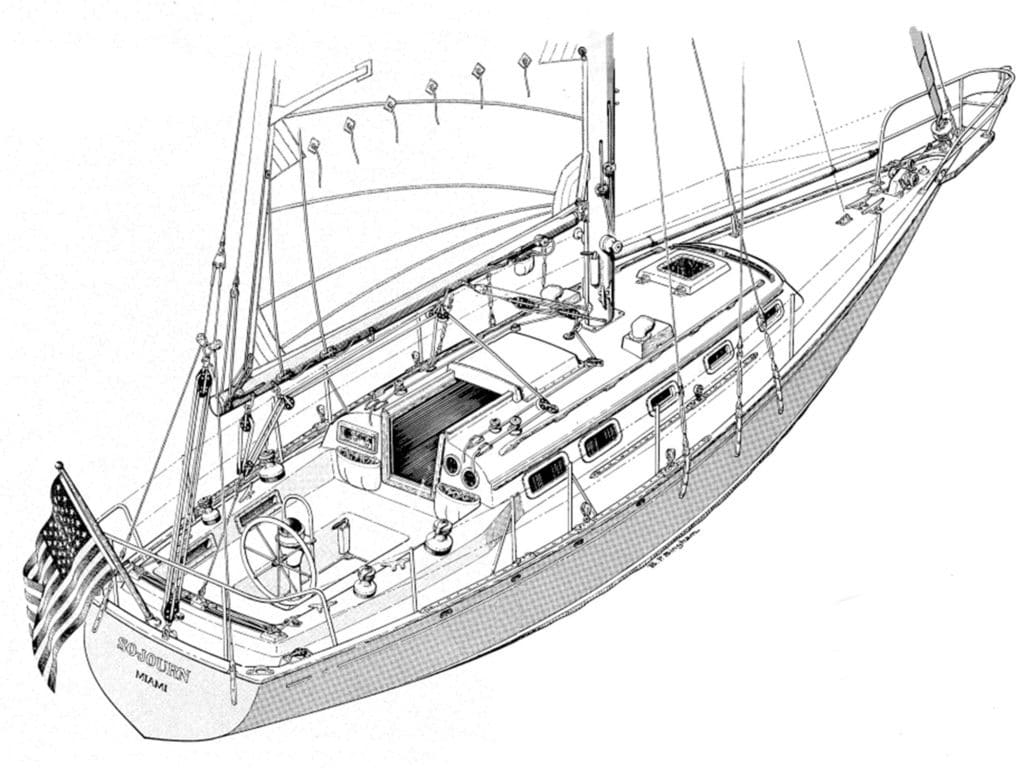
During my 75 years of sailing, I’ve become aware of the chasm between cruisers and racers. But I’ve never understood it because I have always been both. Even when I cruise, I’m racing—against changing weather, the need to get home in time for dinner, whatever. What that really means is that I’m determined to get the most speed out of my boat at all times. And to do so means having excellent running-rigging systems.
There are three issues in play when deciding on whether to install or upgrade your running rigging. First, do you want to increase your ease and convenience when adjusting sail trim? Second, are you willing to add lengths of line (as well as lengths of time) to make sail-trim adjustments? And last, how much investment are you willing to make to reach your sail-handling (i.e., running-rigging) goals?
I can scratch only the surface of this complicated topic and not present a comprehensive guide to all systems and conditions. Hopefully I’ll encourage you to think of how you might be able to improve your systems to make your sailing better and more satisfying.
Let’s begin by looking at sail-trim adjustments, which encompasses many items: sail curve (or draft, also called cord), luff tension, foot tension, sail twist from head to foot, and attack angle (the angle of wind as it approaches the sail’s leading edge, or luff).
On racing boats, all of the power required to make these adjustments is enhanced with more-powerful winches, larger crews, expensive low-friction blocks, and extremely strong and flexible lines. All of the running-rigging systems on racing boats are also appropriate for cruising boats, but cost often plays a deciding factor when making hardware and arrangement choices.
Increasing the power of running-rigging systems will always cost more, but it will also result in ease of handling and efficiency of controlling mainsail and headsail trim. Let’s move on, focusing first on the main.
Main Outhaul
Mainsail draft (depth of the sail’s curve) is controlled primarily by the outhaul but also may be supplemented by halyard tension and mast bend. So, let’s concentrate on the outhaul if for no other reason than its ease of use, as long as it is easily adjustable and also conveniently reachable. Unfortunately, most outhauls that I see on cruising boats are not adjustable and are usually a bundle of knots, difficult to reach when under sail, and almost impossible to untie without a marlinspike or fid. So let’s fix this first.
The mainsail outhaul on my Cape Dory 28 Nikki ’s boom end is a 2-to-1 tackle with its hauling end attached to another 2-to-1 tackle, also called a cascade or Burton. In light air, when sailing to weather, the draft of the main can be flattened by taking in on the 2-to-1 part of the tackle. In strong breezes, flattening the mainsail’s draft is easily done by hauling in on the Burton only, a total power ratio of 4-to-1. Both of the outhaul tackles have their own clam cleats mounted on the side of the boom.

I don’t recommend mast bending to most cruisers because its proper application depends largely on the boat owner’s knowledge of the nature and dimensions of the curve built into the sail by the sailmaker. In a nutshell, though, when sailing to weather, mast bend will flatten the luff of the sail. When sailing off the wind or in light air, a straight mast will increase the curve or draft of the sail for better drive.
If your halyards are only general-purpose Dacron line (like those used for dock lines and sheets), as you tighten them, they will stretch and have little to no effect on sail shape with increased wind. Keep in mind that as windspeed increases, the draft of your sails will also increase, causing a greater heeling moment. The increased draft will also cause the sail luff to become fuller and reduce the ability to point upwind.
I really like limited-stretch and no-stretch halyards. They help reduce the sail draft near the luff from increasing when the wind builds. Limited-stretch halyards won’t stretch markedly when tightened in order to flatten the sail luffs. No-stretch or limited-stretch halyards might sound racy and will cost more, but the payoff is better performance, especially in strong winds. Good halyards are an easy fix that pay big dividends.
Cunninghams and Downhauls
Cunninghams and downhauls are essentially the same thing: Their function is to provide tension adjustment to the lower portion of the luff of a sail. A Cunningham, however, is more associated with the mainsail; downhauls are generally used with a headsail or staysail.

The purpose of Cunninghams and downhauls is to provide a rapid and convenient method of changing and distributing the tightness of a sail luff from tack to head, primarily on sails whose luff is in a mast slot, aluminum furling extrusion or attached to a stay with piston hanks; all of which cause friction that resists the luff from equalizing its load along its length. Since the halyard pulls upward from the top and the Cunningham pulls downward from slightly above the tack, the load in both directions equalizes the tension of the sail’s luff.
When you hoist a mainsail, there will often be about twice the tension on the luff above the spreaders than between the spreaders and the gooseneck. The load on the Cunningham is used to increase the lower luff tension. So, instead of cranking the halyard so tight that the winch is nearly torn off the mast or cabin top, raise the sail only until you begin to feel the luff load up, then tighten up the Cunningham until it feels about the same as the halyard. That’s the way your mainsail was designed and made, with about equal tension along the full length of the luff.
The cordage used as a downhaul or tack attachment for staysails and headsails, including those with roller-furling systems, should be set up as tackles that are adjustable under sail. The cord should be long enough to set up a 4-to-1 tackle, and cleated or tied so that rapid luff tension can be adjusted without a hassle, whether slacking off in light air or tightening in a heavier breeze.
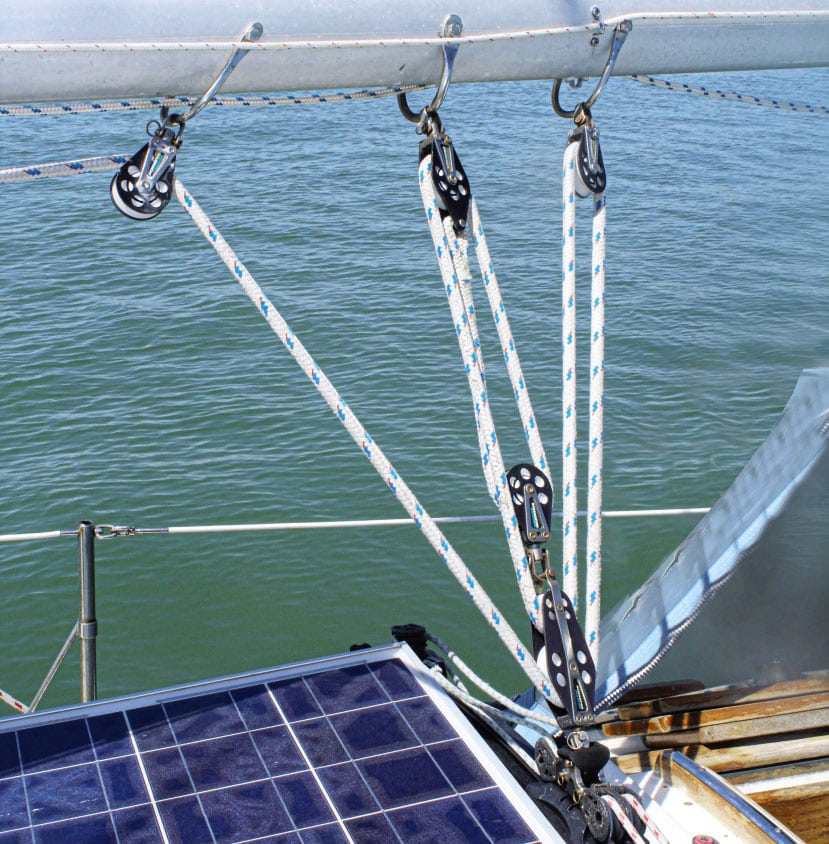
Gaining Mechanical Advantage
When I bought my schooner, At Last , back in the mid-’70s, she had lots of line and blocks but not a single winch. I think that most of her previous sailing had been done by a crew of six or a smaller crew made up of 300-pound gorillas. At that time, I weighed only 135 pounds, and my partner, Katy, was about 15 pounds lighter. Neither of us were what you would call “husky.”
Sailing At Last in light air was not difficult, but when it blew over 8 knots, every evolution became quite physical. We learned the first rule of manpower pretty quickly: The more line we pulled to achieve any sail adjustment (main or foresail sheet trimming, gaff hoisting, etc.), the more power was developed and less personal exertion was required.
Yes, eventually we did install sheet winches for each of the headsail sheets, but not for the main or foresail halyards or sheets, outhauls, vangs or topping lifts. For those, we added blocks and line to each system. It was like multiplying our crew. Every sail-trim maneuver became markedly easier—but slower. So, if we at least doubled the line length by adding sheaves, we also multiplied the power by the same ratio (not deducting for friction) and reduced the hauling load by the same ratio.
The rule of tackles is straightforward: The number of moving parts equals the mechanical advantage (power ratio). Google “block and tackle mechanical advantages,” and you will find excellent graphic diagrams with their power ratios.

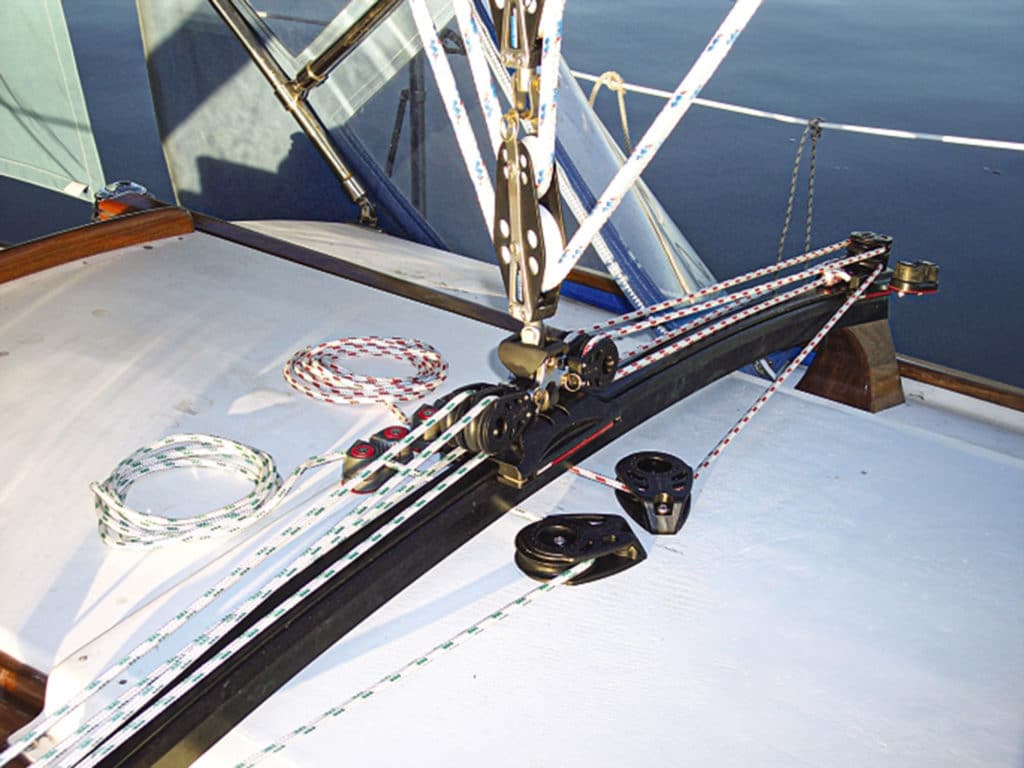
Leading Systems to the Cockpit
More and more boat owners want every sail-control line led to the cockpit. This invariably requires at least three additional blocks or sheaves to be added to most running-rigging systems, thus increasing friction as well as adding lots of line (I call it “spaghetti”) in or near the cockpit. In the case of reefing, leading all lines to the cockpit actually makes most reefing much more difficult and inefficient.
In 2009, my 28-foot Nikki won the Florida West Coast Boat of the Year award in a long series of races over several months’ time. Most wins occurred in extremely high winds because we had practiced reefing in under 45 seconds. That had become possible largely because of deftly efficient tackles, all kept within a single person’s reach. Only the main sheet went to the cockpit and was usually handled by the helmsman.

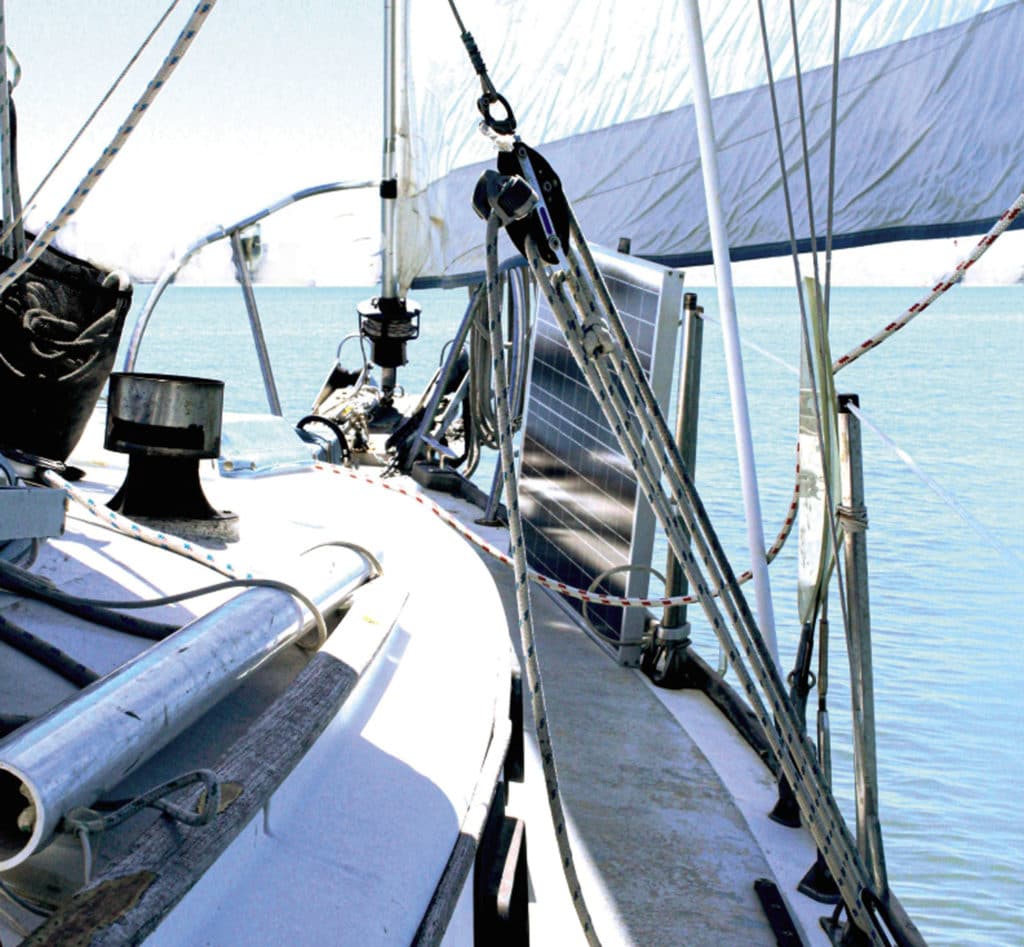
Mainsheets and Travelers
Thirty years ago, virtually all mainsheets were attached to the aft end of the boom and to a multisheave block on a short and mostly inefficient traveler at the stern of the boat. Because of the position of the traveler, its angle of effectiveness was fairly narrow, so when far off the wind (beam and broad reaches and running), the amount of downforce on the boom became little to negligible, rendering the traveler useless.
A double-legged mainsheet never accomplished its intended goal of acting like a traveler. Such a mainsheet always vectors the load to the longitudinal center of the boat on all points of sail regardless how far apart the lower blocks are spread. It was the racers who came up with the idea of moving the mainsheet to the approximate middle of the boom and down to a longer track and adjustable car (the traveler), usually just forward of the main companionway hatch on the cabin top. With this arrangement, the mainsheet becomes the major controller of both boom angle as well as mainsail twist by its increased downforce on the boom and sail.
The traveler car should be controlled by a port and starboard tackle of at least 3-to-1 advantage for boats up to 24 feet, 4-to-1 for boats up to 30 feet, and 5- to 6-to-1 for boats up to 34 feet and beyond. I also recommend the use of cam or clam cleats for all traveler control lines.
Racing sailors also came up with the idea of a boom vang attached to the forward portion of the boom at the upper end, and to a bale at the base of the mast at the lower end. This is what you usually see on most sailboats today. That simple arrangement was a giant leap forward in the area of mainsail-twist control. But almost indiscernible additional improvement seemed to occur. Nowadays, most boom vangs aren’t all that efficient and ought to be brought into this century.
The first improvement should be to pull downward on the boom vang line in order to pull down the boom. However, I rarely see a vang rigged this way, which means it loses about half of its power advantage. Most vangs I see are pulled upward or aft to exert a download on the boom, thus losing more power.
A really practical boom vang should have at least a snap shackle on the lower block so it can be quickly detached from the mast base and moved to a car on the genoa track or a hole in a perforated aluminum toe rail. This will allow the boom vang to exert much more of a vertical download. The more vertical the vang, the more downforce on the boom. Another benefit to the detachable boom vang is that the lower block can be brought forward of the mast and attached to a stout deck-pad eye or perforated toe rail so the boom vang can also act as a preventer when sailing downwind.

Doubling the power of the boom vang can be accomplished simply and easily with a small investment by adding a 2-by-1 cascade (also, again, called a Burton), which is a single 7-by-7-foot or 7-by-37-foot stainless cable run though a wire block on the boom with one end shackled to the vang bale at the mast base. The other end of the wire is fashioned with an eye to which the upper end of the vang tackle is attached. So if your vang tackle is 5-to-1 and the cascade is 2-to-1, your vang will become 10-to-1. Then by moving the lower end of the vang from the mast to the toe-rail eye, a dedicated deck-pad eye or a genoa-track car, you have doubled it again, all for about $40.
The vang that I have described is most efficient when sailing long distances without jibing or tacking, but if you’re simply afternoon daysailing around the bay, the vang would be more conveniently left attached to the bale at the mast base.
I have never seen a rigid boom vang that was routinely adjusted while under sail; they’re really only a boom support system while under power or tied up to a dock.
Main Boom Topping Lift
I put the topping lift in the same underused category with the main outhaul; too often it’s a bundle of knots at the end of the boom that have not been adjusted or adjustable in decades.

A proper topping lift is meant to raise and store the boom off the Bimini when not in use. When under sail, however, its purpose is to adjust the weight of the boom so it changes the sail twist in various wind conditions and points of sail. It works in the opposite direction of a boom vang; it pulls the boom upward while the vang pulls downward. Upward increases sail twist, and downward reduces it.
A topping lift should also be used to take the weight of the boom off the mains’l leech when putting in a reef, then tightened again while shaking out the reef. The topping lift should be adjustable on any point of sail, which translates into “reachable.” Also, lifting your outboard from your dinghy becomes a simple matter by using your boom vang tackle attached to the end of the boom, and “topping” the boom with the topping lift so the outboard can clear the aft pulpit and lifelines.
Backstay Adjusters
These are used to apply tension to the backstay, which is transferred to the headstay for the purpose of flattening the luff of the headsail…or slacking the backstay, thus also easing the headstay to add more draft to the jib or genoa, as would be desirable when off the wind. When closehauled and/or sailing in a stiff breeze, a flattened headsail is preferred to lessen the boat’s heeling moment and to allow the boat to point up a little closer to the wind. With a backstay adjuster, this can be done in a few seconds with an adequate tackle arrangement.
Adjusting a headstay is usually impossible while under sail with the headsail sheeted in tightly. There are special turnbuckles and hydraulic backstay adjusters that can be used while under sail, but they are not as rapid as the appropriate backstay tackle systems. When tightening the backstay, the mast is also slightly bent to help flatten the draft and remove the “cup” from the luff of the mainsail at the same time as the headsail. So double benefits are derived from one simple adjustment.
Making your boat perform better does not have to be, nor should it be, a lot of work. In reality, effective running-rigging systems will make sailing a lot less strenuous, as well as more enjoyable and rewarding. Your boat will look better and perform better, and teach you a lot about getting the most out of the wind while adding joy to your afternoons under the clouds.
Don’t avoid the possibilities. Embrace them.
Boat designer, builder, writer, illustrator and longtime CW contributor Bruce Bingham lives aboard his Cape Dory 28, Nikki , on Florida’s Gulf coast.
- More: deck hardware , How To , lines , print oct 2020 , rigging
- More How To

Grease the Wheels of Your Boat: A Guide to Proper Lubrication

A Bowsprit Reborn: A DIY Renovation Story

Rigging Redo: Our Switch to Synthetic

Top Tools for Sailboat Cruising: Must-Have Gear for 2024

From Paradise to Medical Emergency: A Bahamas Nightmare Turns Lesson Learned

Free Medical Advice: The Unwarranted, Unprofessional Edition

Gatekeepers of the Waterway

- Digital Edition
- Customer Service
- Privacy Policy
- Terms of Use
- Email Newsletters
- Cruising World
- Sailing World
- Salt Water Sportsman
- Sport Fishing
- Wakeboarding
Running Rigging on a Sailboat: Essential Components and Maintenance Tips
by Emma Sullivan | Aug 8, 2023 | Sailboat Maintenance

Short answer running rigging on a sailboat:
Running rigging refers to the ropes and lines used for controlling the sails and other movable parts on a sailboat. It includes halyards, sheets, braces, and control lines. Properly rigged running rigging is essential for efficient sail handling and maneuvering of the boat.
Understanding Running Rigging on a Sailboat: How to Get Started
Title: Deciphering the Intricacies of Running Rigging on a Sailboat: An Enlightened Journey Begins!
Introduction: Ah, the allure of sailing! Picture yourself gracefully gliding across sun-kissed waters, propelled solely by the power of the wind . If you’re new to this mesmerizing world, it’s crucial to understand every aspect – including running rigging. Fear not, fellow adventurer! This comprehensive guide will unravel the mysteries surrounding running rigging and equip you with valuable knowledge to embark upon your own nautical odyssey.
1. The Foundations: What is Running Rigging? Running rigging encompasses all the ropes and lines aboard a sailboat that are used to control sails and their systems. Think of it as a symphony conductor guiding each instrument precisely when they are needed. Understanding its components requires delving into various key elements.
2. The Halyards: Hoisting Your Sails with Elegance Halyards form an integral part of running rigging by facilitating the raising and lowering of sails effortlessly. These vital maneuvering aids connect from the masthead down to specific positions where they secure each sail precisely at one end while granting sailors control at their opposite extremity.
3. Sheets & Controls: Directing Your Power Source Next up in our deconstruction are sheets and controls – essential components for controlling sails’ angles based on wind direction. By cunningly pulling or easing these lines, you can swiftly adjust your sails’ positioning according to weather shifts, resulting in optimal performance .
4. Cleats & Winches: From Taming Lines to Seizing Moments Even Hercules would yield to cleats and winches when taming robust ropes! Cleats serve as steadfast anchors onto which lines can be temporarily secured, providing necessary stability during navigation’s turbulent moments. Winches, on the other hand, offer mechanical assistance by efficiently winding or unwinding lines using a drum mechanism – a sailor’s secret weapon for effortlessly controlling lines under high tension.
5. Blocks & Pulleys: The Silent Workhorses Up Above Blocks and pulleys, hidden amongst the chaos of running rigging, serve as silent heroes deserving recognition. These nifty devices allow lines to redirect their path efficiently, minimizing friction while maximizing mechanical advantage. Imagine them as your trusty allies, ensuring smooth adjustments without burdening you with unnecessary strain.
6. Mainsail Furling Systems: Embracing Elegance in Simplicity To master running rigging effectively, one must grasp the concept of mainsail furling systems. These mechanisms enable swift and straightforward reefing or unfurling of the mainsail using dedicated ropes or electrically-powered systems. By harnessing this technology correctly, you’ll unlock newfound ease in sailing endeavors.
Conclusion: Congratulations! You’ve delved into the intricate world of running rigging on a sailboat and emerged more enlightened than ever before. As you embark upon your maritime journey armed with this invaluable knowledge, remember that practice leads to mastery. Understanding how these distinct elements harmonize will transform you into a maestro, skillfully orchestrating every aspect of your sailing adventure with grace and finesse. Bon voyage!
A Step-by-Step Guide to Setting Up Running Rigging on a Sailboat
Title: Sailing with Confidence: A Masterclass on Setting Up Running Rigging
Introduction:
Embarking on the open sea , feeling the wind against your face as you glide through the water, there’s no greater thrill than sailing. However, to truly harness the power of the wind and have a seamless experience, it is essential to understand how to set up your running rigging. In this comprehensive guide, we will take you through each step of this crucial process, equipping you with the knowledge and confidence necessary for smooth sailing adventures.
1. Assessing Your Needs: The Foundation for Success
Before diving into the nitty-gritty details of setting up your running rigging, it’s important to assess your specific needs according to your sailboat’s design and intended use. Factors such as boat size, mast height, and sail types play a significant role in determining which rigging configurations will work best for you.
2. Selecting Materials: Optimal Performance, Durability & Safety
Choosing suitable materials for running rigging is paramount to ensure reliable performance while maintaining the safety of both crew and vessel. From strong yet lightweight synthetic fibers like Dyneema or Spectra to traditional options such as polyester or nylon, understanding their properties and appropriate applications is essential in making informed decisions.
3. Understanding Key Terminology: Speaking Sailors’ Language
Like any specialized field, sailing has its own set of terminology that can feel overwhelming at first. Fear not! We’ll guide you through key terms such as halyards (hoisting lines), sheets (lines controlling sails), reefing lines (to reduce sail area), allowing you to converse confidently with fellow sailors.
4. Anchoring Your Mast: Secure Your Foundation
The process begins by firmly anchoring your mast at its base using a fitting called a mast step or deck collar. This immovable foundation provides stability throughout various sailing conditions while reducing unnecessary strain on all related rigging components .
5. Hoisting the Sails: Halyards & Their Art
To set sail, a crucial step involves hoisting your sails with precision. Correctly attaching halyards to the designated points on the mast and sail, while ensuring proper tension and alignment, will enable you to control raising, lowering, and reefing the sails with ease—an art form in itself.
6. Harnessing the Wind’s Power: Sheets & Trimming
Once your sails are aloft, skillful manipulation of sheets becomes paramount. Understanding how to trim them properly allows you to harness the wind’s power effectively while achieving maximum speed and maneuverability—a true dance between sailor and nature.
7. Streamlining Movement: Fairleads & Blocks
Efficiency is key when it comes to running rigging. By employing fairleads (pulleys) strategically placed around your vessel and appropriately using blocks (pulley combinations), you can minimize friction within your system, allowing for fluid movement with less effort during sail adjustments.
8. Reducing Sail Area: Reefing Lines at the Ready
As conditions change or storms approach, being able to reduce sail area swiftly is essential for safety purposes. Learning how to utilize reefing lines effectively enables you to adapt your sails according to environmental demands without sacrificing control or stability.
9. Fine-Tuning Your Set-Up: Tension & Balance
The final touch lies in adjusting tension throughout your running rigging system to achieve optimal balance and performance. Maintaining proper tension prevents undesirable effects like excessive wrinkles on sails or slack lines that compromise efficiency—fine-tuning that separates amateurs from seasoned sailors.
10. Everyday Maintenance: Caring For Your Rigging
Just as a well-maintained engine ensures peak performance, regularly caring for your running rigging also guarantees smooth operation over time. Simple tasks such as rinsing off saltwater residue or inspecting for wear and tear go a long way in prolonging the life of your rigging and ensuring a safe voyage.
Conclusion:
With this step-by-step guide, you are now equipped with the knowledge needed to set up running rigging on your sailboat like a seasoned sailor. By understanding the essential components, choosing suitable materials, and mastering the techniques necessary for trimming and maintenance, you’ll confidently navigate the open seas while experiencing the true joy of sailing . Bon voyage!
Frequently Asked Questions about Running Rigging on a Sailboat Demystified
Welcome to the world of sailing! If you’re a beginner or even if you’ve been sailing for a while, running rigging can often seem like a complex and confusing topic. But fear not! In this blog post, we are here to demystify all your frequently asked questions about running rigging on a sailboat.
Q: What is running rigging? A: Running rigging refers to all the lines and ropes that control and adjust the sails on a sailboat. It includes halyards, sheets, reefing lines, downhauls, and any other line used to set or trim sails .
Q: Why is running rigging important? A: Running rigging plays a crucial role in controlling the shape and position of the sails, allowing the boat to harness wind power efficiently . Properly adjusted running rigging enables better sail control, improved performance, and increased safety on board.
Q: How many types of running rigging are there? A: There are several types of running rigging found on most sailboats. Some common ones are halyards (used to lift or lower the sails), sheets (used to control the tension and angle of the sails), outhauls (used to adjust the foot of the mainsail), furling lines (used for rolling up or unfurling headsails), and vang systems (used for controlling boom height).
Q: What materials are used in running rigging? A: Traditionally, natural fibers like hemp or manila were used for ropes. However, modern sailboats mostly use synthetic fibers such as polyester or Dyneema due to their durability, low stretching properties, and resistance to UV degradation.
Q: How do I choose the right running rigging for my boat? A: The choice of running rigging depends on various factors such as boat size/type, sailing conditions, intended use, personal preference, and budget. It’s always advisable to consult with a reputable rigging professional who can assess your specific requirements and recommend the appropriate type and diameter of ropes for your boat .
Q: How often should I replace my running rigging? A: The lifespan of running rigging depends on various factors including usage, exposure to sunlight, and regular maintenance. As a general rule of thumb, inspect your running rigging regularly for signs of wear and tear. If you notice any fraying, excessive stretching, or damage, it’s essential to replace the affected lines promptly.
Q: Can I maintain my own running rigging? A: Yes! Regular maintenance is key to prolonging the life of your running rigging. Simple tasks like washing with fresh water after use, removing dirt or salt residue, and storing the lines properly can significantly extend their lifespan. However, if you’re unsure about any specific maintenance tasks or need assistance with more complex issues, it’s best to seek advice from a professional rigger.
Q: Are there any advanced techniques related to running rigging? A: Absolutely! Advanced sailing techniques often involve various adjustments using different lines simultaneously. For example, using barberhaulers to control genoa sheeting angles or implementing cunningham systems for mainsail shape adjustments. These techniques require practice and knowledge but can greatly enhance sail efficiency and boat performance.
Now that we’ve demystified some frequently asked questions about running rigging on a sailboat, we hope you feel more confident in understanding this vital aspect of sailing. Remember that every boat is unique, so investing time in learning about and maintaining your specific running rigging system will undoubtedly pay off in smoother sailing experiences ahead!
Choosing the Right Materials for Your Sailboat’s Running Rigging
When it comes to your sailboat’s running rigging, choosing the right materials can make all the difference in ensuring optimal performance and longevity. But with a plethora of options available, it can be a daunting task. Fear not, for we are here to guide you through this decision-making process, providing you with a detailed professional, witty and clever explanation.
First and foremost, let’s clarify what we mean by “running rigging.” In sailing terms, this refers to all the lines (ropes) used to control the sails and their adjustments while underway. These lines include halyards (used for raising and lowering the sails), sheets (controls the angle and trim of the sails), and various other control lines like reefing lines or vang lines. Each requires specific characteristics based on its purpose.
When considering materials for running rigging, durability is paramount. You want something that can withstand constant exposure to UV rays, saltwater, friction wear, and general wear and tear. One material that stands out in terms of resilience is Dyneema®. This high-performance synthetic fiber boasts an incredible strength-to-weight ratio similar to steel but without the weight or corrosion concerns. Paired with excellent resistance to UV degradation and abrasion resistance properties, Dyneema® offers a long-lasting solution for your running rigging needs.
But hold on! While Dyneema® may seem like an obvious choice, there are other factors to consider as well. For instance, ease of handling plays a significant role in determining which material is right for you. Some sailors prefer traditional materials like polyester or nylon due to their familiar feel and ease of tying knots. However, these materials tend to stretch more under load compared to Dyneema®, which can affect sail shape and overall performance .
To address this issue without compromising on durability or ease of handling completely, manufacturers have developed hybrid rope constructions where different fibers are combined strategically within a single line. For example, a Dyneema® core can be paired with a polyester or Technora cover, harnessing the best of both worlds. This combination provides the strength and low stretch characteristics of Dyneema® while maintaining that traditional feel when handling.
Now, let’s sprinkle in some wit and cleverness as we delve into the importance of reliability. When out on the open seas, you don’t want to be caught off guard by a line failure because you chose an unreliable material. Imagine your excitement as the wind picks up, preparing for an exhilarating sail, only to have your sailing dreams dashed due to a snapped halyard! Trust me; it’s not an experience you’ll find amusing, nor will your crew appreciate your comedic skills at such moments. So, don’t skimp on quality.
To ensure reliability and avoid any unplanned comedy acts on board, investing in well-respected brands known for their commitment to excellence is key. Reputable manufacturers like New England Ropes or Marlow Ropes are popular choices among sailors worldwide. Their rigorous testing processes and innovative designs guarantee performance reliability no matter what Mother Nature throws your way.
We hope this detailed professional, witty and clever explanation has shed some light on choosing the right materials for your sailboat’s running rigging. Remember to consider durability, ease of handling, and reliability when making your decision. And if you’re still unsure or need further assistance—don’t hesitate to reach out to fellow sailors or consult with professionals who can offer personalized advice tailored to your unique sailing style. Happy rigging!
Essential Tips for Properly Maintaining and Inspecting Running Rigging on a Sailboat
As any experienced sailor knows, properly maintaining and inspecting the running rigging on a sailboat is crucial for optimal performance and safety on the water. The running rigging refers to all the lines or ropes that control the sails, such as halyards, sheets, and control lines. Neglecting this essential aspect of sailboat ownership can lead to inefficiencies in sailing, potential equipment failures, or even dangerous situations while out at sea. So, whether you’re a seasoned sailor or just starting out, here are some essential tips to keep your running rigging in top shape.
1. Regular Inspection: The first step in proper maintenance is conducting regular inspections of your running rigging. Look for signs of wear and tear such as fraying, chafing, or any weakening spots in the ropes. Pay close attention to areas where lines are frequently under tension or make contact with other hardware, as these are typically high-stress areas prone to damage.
2. Cleaning: It’s vital to keep your running rigging clean and free from contaminants like dirt, saltwater residue, or mildew buildup that can affect their performance over time. Use a mild soap and water solution along with a soft brush to scrub away any grime.
3. Protect from UV Damage: Exposure to sunlight can accelerate the wear and degradation of your ropes due to UV radiation. Consider covering them with protective sleeves or using UV-resistant coatings specifically designed for sailing applications.
4. Lubrication: Keeping your running rigging well-lubricated ensures smooth operation and prolongs their lifespan. Apply a suitable marine-grade lubricant to reduce friction between moving parts like pulleys and cleats but be cautious not to apply excessive amounts that could attract dirt or create messy situations.
5. Check Fittings & Hardware: A comprehensive inspection should include examining all fittings and hardware associated with your running rigging – blocks, shackles, cam cleats – to ensure they are in proper working order. Tighten any loose fittings and replace any worn or damaged hardware promptly.
6. Replace Worn-out Lines: As with anything made of rope, running rigging will eventually reach the end of its serviceable life. Don’t wait for lines to fail before replacing them. Look out for signs like significant diameter reduction, loss of flexibility, or extensive wear and tear. Replacing worn-out lines early can save you from potential accidents or interruptions during your sailing adventures .
7. Proper Storage: When not in use, it’s essential to store your running rigging properly to avoid unnecessary damage or deterioration. Coil the lines neatly and hang them in a cool, dry place where they are protected from direct sunlight and extreme temperatures.
By following these essential tips for maintaining and inspecting your sailboat’s running rigging, you’ll be able to enjoy smooth sailing while ensuring your safety out on the water. Regular inspections, cleaning, UV protection, lubrication, checking fittings and hardware, timely replacements when necessary, and proper storage – all these factors contribute to keeping your running rigging in top shape for optimal performance on every voyage.
Remember that sailboat ownership is an ongoing learning process – stay curious and educate yourself further through reputable sources such as books or online forums dedicated to sailing techniques and equipment maintenance. Happy sailing!
Upgrading Your Sailboat’s Running Rigging: What You Need to Know
When it comes to sailing, few things are as important as the running rigging of your sailboat. From controlling your sails to maneuvering through tricky waters, the quality and functionality of your running rigging can make all the difference in your sailing experience. In this blog post, we will explore everything you need to know about upgrading your sailboat’s running rigging.
Why Upgrade?
Before diving into the details of upgrading your running rigging, let’s discuss why it is necessary in the first place. Over time, the wear and tear on a sailboat’s running rigging can lead to compromised performance and safety concerns. As such, periodic upgrades become essential to ensure optimal functionality and reliability on the water .
Choosing Material
One of the most critical decisions when upgrading your running rigging is choosing the right material. Traditionally, sailboats have used materials like polyester or Dacron for their ropes. While these options are cost-effective and suitable for casual sailors, advanced materials like Dyneema or Spectra offer superior strength-to-weight ratio and lower stretch capabilities.
Furthermore, these modern fibers provide exceptional durability against UV degradation and abrasion resistance – perfect for longer ocean passages or demanding racing environments. Investing in high-quality lines may be more expensive upfront but pays off by enhancing both safety and performance while extending the overall lifespan of your rigging system.
Understanding Line Construction
Now that we’ve covered material options let’s move onto line construction. When choosing new lines for your running rigging upgrade, understanding their construction plays a vital role in achieving desired results.
Double braid construction is one popular option known for its balance between stretch resistance and knotability. It consists of a core surrounded by a braided outer cover – providing both strength and flexibility when handling heavier loads.
Alternatively, single braid construction offers improved flexibility by using only one continuous rope with a braided or twisted cover. This design is perfect for smaller sailboats, giving you lighter and more manageable lines while sacrificing some load-bearing capacity.
Finding the Perfect Fit
Upgrading your running rigging goes beyond simply replacing old lines with new ones; finding the perfect fit for your specific needs is crucial. Before making any purchases, take time to assess how you use your sailboat and what characteristics matter most to you.
Consider factors like line diameter, breaking strength, elongation under load, and grip comfort when evaluating potential options. While durability is essential, striking the right balance between strength and weight can significantly enhance your sailing experience .
Installation 101
Now that you’ve selected the ideal running rigging components let’s talk about installation. Proper installation ensures optimal functionality and reduces potential snags or accidents on the water.
Start by studying your sailboat’s existing rigging setup and create a detailed plan to avoid confusion during installation. If possible, consult with experts or refer to manufacturer guidelines for best practices.
Lastly, pay careful attention to tensioning techniques when installing your new lines – correct tension prevents slack that may hinder overall performance during navigation.
Maintaining Your Upgrade
Once completed, maintaining your newly upgraded running rigging becomes an essential part of owning a sailboat. Regular inspection of ropes for wear and tear is necessary since even high-quality materials require upkeep.
Additionally, proper storage away from UV rays and harsh weather conditions can further extend the life of your upgraded running rigging. By following maintenance guidelines provided by manufacturers and incorporating routine checks in pre-sail preparations, you can ensure continued reliability throughout every journey.
Upgrading your sailboat’s running rigging is a worthwhile investment that guarantees enhanced safety and performance while providing endless possibilities on the water. Choosing suitable materials based on usage patterns, understanding line construction principles, finding the perfect fit for specific needs, meticulous installation processes, and regular maintenance are key elements in achieving desired results.
So, take the plunge and upgrade your running rigging today – it’s time to elevate your sailing experience to new heights!
Recent Posts

- Sailboat Gear and Equipment
- Sailboat Lifestyle
- Sailboat Maintenance
- Sailboat Racing
- Sailboat Tips and Tricks
- Sailboat Types
- Sailing Adventures
- Sailing Destinations
- Sailing Safety
- Sailing Techniques
- New Sailboats
- Sailboats 21-30ft
- Sailboats 31-35ft
- Sailboats 36-40ft
- Sailboats Over 40ft
- Sailboats Under 21feet
- used_sailboats
- Apps and Computer Programs
- Communications
- Fishfinders
- Handheld Electronics
- Plotters MFDS Rradar
- Wind, Speed & Depth Instruments
- Anchoring Mooring
- Running Rigging
- Sails Canvas
- Standing Rigging
- Diesel Engines
- Off Grid Energy
- Cleaning Waxing
- DIY Projects
- Repair, Tools & Materials
- Spare Parts
- Tools & Gadgets
- Cabin Comfort
- Ventilation
- Footwear Apparel
- Foul Weather Gear
- Mailport & PS Advisor
- Inside Practical Sailor Blog
- Activate My Web Access
- Reset Password
- Customer Service

- Free Newsletter

Ericson 41 Used Boat Review

Mason 33 Used Boat Review

Beneteau 311, Catalina 310 and Hunter 326 Used Boat Comparison

Maine Cat 41 Used Boat Review
Tips From A First “Sail” on the ICW

Tillerpilot Tips and Safety Cautions

Best Crimpers and Strippers for Fixing Marine Electrical Connectors

Thinking Through a Solar Power Installation

Getting the Most Out of Older Sails

How (Not) to Tie Your Boat to a Dock

Stopping Mainsheet Twist

Working with High-Tech Ropes

Fuel Lift Pump: Easy DIY Diesel Fuel System Diagnostic and Repair

Ensuring Safe Shorepower

Sinking? Check Your Stuffing Box

The Rain Catcher’s Guide

Boat Repairs for the Technically Illiterate

Boat Maintenance for the Technically Illiterate: Part 1


Whats the Best Way to Restore Clear Plastic Windows?

Mastering Precision Drilling: How to Use Drill Guides

Giving Bugs the Big Goodbye

Galley Gadgets for the Cruising Sailor

Those Extras you Don’t Need But Love to Have

UV Clothing: Is It Worth the Hype?

Preparing Yourself for Solo Sailing

How to Select Crew for a Passage or Delivery

Preparing A Boat to Sail Solo

On Watch: This 60-Year-Old Hinckley Pilot 35 is Also a Working…

On Watch: America’s Cup

On Watch: All Eyes on Europe Sail Racing

Dear Readers

Chafe Protection for Dock Lines
- Sails, Rigging & Deck Gear
Testers Examine Running Rigging Options
Braided lines face torture tests to determine the top picks for halyards and sheets..

The first sign of cordage use dates back about 28,000 years. Archeological findings in Europe have carbon dating confirmation of twine imprints found in clay shards. The Egyptians (circa 4,500 BC) appear to be the first to utilize rope-making tools, and for millennia, natural fibers such as hemp, manila, sisal, jute, cotton, and others were the material of choice when it came to making laid or twisted rope.

Photos by Ralph Naranjo
The playing field changed in 1935 when DuPonts young research director Wallace Carothers and his team came up with a synthetic polymer dubbed nylon, a fiber that soon found its way into stockings, toothbrushes, and the capable hands of rope manufacturers around the world. Polyethylene terephthylate, another long-chain polymer, was synthesized in Britain in the 1940s, and eventually found its way into the DuPont lineup as Terylene in 1951. Terylene was rechristened Dacron, and the new polyester fiber soon joined nylon on the rope walks of cordage manufacturers around the world.
Dacron proved to be much less stretchy than nylon, 90 percent as strong, and more resistant to ultraviolet (UV) rays. Nylon and Dacron grew to be nautical buzzwords indicative of the rope of the future, at least up until chemical engineers with post doctoral degrees and ample grant dollars got serious about conjuring up new fibers. Today, Spectra, Vectran, Technora, and a whole host other tongue-twisters are the new, new thing in fiber technology. Truly stronger than steel, and 10 times lighter, they offer much less stretch and double or triple the tensile strength of the synthetic prototypes nylon and Dacron. Unfortunately, some also have inherent downsides such as reaction to UV, creep (permanent deformation under stress or heat), and the reluctance to be wrapped around a tight radius.
Fiber to Rope
For centuries, cordage was made in a time-honored tradition that began with fibers being spun into yarns, twisted together into strands, and finally twisted again in the opposite direction combining the strands into a rope. The opposing twists locked the bundle in place, and when tension was added to such three-strand laid ropes, the yarns torqued and rubbed against one another in response to elongation.
When it comes to making running rigging aboard sailboats, laid rope takes a back seat to braided line. The 26 samples of rope we evaluated for this test, all fall into what can be called braided rope. We looked at 24 ropes with braided covers that comprised eight, 12, even 24 tows combined in patterns ranging from loose to tight weaves. Most incorporated a braided core, although a few ropes had parallel-strand cores. Two samples of Amsteel, a single-braid rope, were included in the test for comparative purposes. By doing away with most of the twist involved in laid rope, braided lines tend to have less stretch, and the fiber bundles can be better aligned with load paths.
In early Dacron braided line, the tensile strength was usually evenly distributed (50-50 split) between the cover and core. Todays crop of high-tech lines often favors an uneven load distribution between the cover and the core. One example of this approach is found in a type of braided rope known as kernmantle, which comprises a braided cover and a high-tensile, parallel-strand core. In this design, the tensile strength is often split 70-30, with the core carrying most of the load. Such load sharing means that even when abrasion has jeopardized the outer cover, the cordage still retains most of its original tensile strength. Mountaineering rope-just like anchor and mooring line-can be engineered to retain such a cache of tensile strength in the center.
The flip side of this approach, however, is that once the cover of a sheet, guy, or halyard frays, it is time to replace the line regardless of how much tensile strength is still left deeper in the core. So cordage manufacturers have been engineering braided rope comprising a tough, abrasion resistant cover and a core that meets the required tensile strength. In addition to careful selection of cover fiber, engineers have turned to anti-abrasion urethane coatings that reduce the damaging effects of abrasion, UV, and acid rain. In this round of testing, testers directly measured the abrasion resistance of each line, tested its resistance to stretch and observed how it coiled, handled, and behaved on a winch drum. (See “How We Tested.”)

A Note on Breaking Strength
Breaking strength figures listed in the above table are astounding and represent the end of the line both figuratively and literally. At that point, the line has elongated as far as its elastic and plastic limits allow, and when it exceeds its yield, the result is an explosive bang. According to the Cordage Institute, the rope industrys amalgam of technical gurus, safe working loads (SWL) are five to 12 times less than the breaking strength for non “lifeline” uses. When used as a safety line, the SWL is calculated by dividing the breaking strength by 12 or more. The reason for this seemingly hyper-conservative safety margin is because shock loading can cause the static tensile load to skyrocket, and there needs to be plenty of safety margin to compensate for these momentary spikes.
What We Found
With so many lines to consider, we grouped the products by material and construction, more or less keeping the apples, oranges, and bananas in separate boxes. We began the process by sorting the rope into three fairly distinct performance groups (low, mid, and high tech) based upon their fiber content. Once sorted, the ropes were evaluated for their elongations, abrasion resistance, and handling. Results are tabulated on the pages above.
There were similarities among the types of ropes manufactured and marketed by different companies. For example, each offered a polyester double braid that afforded excellent UV stability and handling characteristics at a bargain price. However, these lines were also the most prone to elongation under even modest working load, and were poor candidates as halyard material.
Testers confirmed that high-modulus fibers and new coating treatments do enhance performance traits in rope. Theres no question that fibers such as Technora, Dyneema, and Vectran boost the breaking strength of rope and lessen stretch, but theres also a flip side that needs to be taken into consideration. Many of these fibers have an inherent stiffness and tendency to hockle that makes them hard to coil and handle. Notice that many of the higher performing ropes scored low for handling.
Whether you should make low-stretch or easy-handling a priority will depend upon the ropes application. A conventional all-Dacron 7/16-inch halyard may easily have 60 feet of its length in tension, and with normal sailing conditions, halyard stretch could be as much as 16.4 inches. Swap out the all-polyester halyard and replace it with a high modulus, 3/8-inch diameter rope such as Yales Maxibraid Plus and the stretch is reduced to 4.1 inches.
This four-time reduction in elongation makes a big difference in mainsail draft control. The last thing a crew wants is more draft in the mainsail just as a gust fills in. The bottom line when it comes to halyards is that its worth putting up with a line that coils like a tree branch, if once it is winched into place, it resists elongation as well as wire.
Sheets on a cruising boat are quite a different story. Most short-handed, long range passagemakers arent obsessed with continuous trimming and turn the drudgery over to an autopilot. Sail trim consists of an occasional look at sail shape and telltale behavior. Eliminating the last bit of stretch in a sheet is of little advantage, but having a line that can put up with the abrasion, UV harassment, and the fatigue that adds up during days, or weeks at sea is a vital asset. Handling ability is another key factor, especially with so many lines leading to the cockpit. A halyards can’tankerous demeanor is tolerable, since the rope is effectively a set-it-and-forget-it one-act play. But sheets are handled more often, and easily coiled tails are always appreciated by every crew.

Ultimately, when all the stretching, abrading, and coiling was done, testers were able to find some clear choices based on price range and offer some general guidance for those who are shopping for new cordage.
Budget ropes: At the low-tech and lower cost end of the spectrum, Samsons SLX 456 nudged ahead of competitors. Yales Yacht Braid, New England Ropes Sta-Set and Novabraid XLE were all high- quality polyester double braids. Each made the grade as an easy-to-handle general purpose cordage, but none was optimized for use as a halyard material. The reason Samson SLX topped our list was its superior showing in the abrasion test, a feature of its cover construction and proprietary coating process.
Sta-Set X by New England Ropes took polyester cover-and-core technology to a higher performance level, keeping the price down but sacrificing some handling ease and abrasion resistance in the process. The cover has an odd feel, and coiling is not as easy as with the other all-polyester products, but stretch has been reduced significantly and tensile strength was upped by 10 percent or so. This has been accomplished through the use of parallel yarns in the core. The bottom line is that this is an all-polyester line that can be used as a halyard, and it retains the price-point advantage found in all polyester ropes.
Mid-range value: Five of the products we tested are grouped as mid-price, mid-level performers, and the stats speak for themselves. Our favorite in this grouping was New England Ropes VPC. This line isn’t as nice to handle as the all-polyester braids, but it has 50 percent less stretch, superior abrasion resistance, and a price that is half that of the top contenders. Yales Vizzion rated a solid “Good” across the board but had a lower breaking strength. New England Ropes T-900, a low-stretch and high-tensile strength alternative, was especially stiff to handle, and its smaller-diameter 5/16-inch version was more prone to cover abrasion. Samson entered a larger 7/16-inch diameter sample of XLS Extra-T, and even with the extra diameter advantage, its stretch was greater than VPC. However, this tuned-up XLS has many excellent attributes. It slips onto and grips a winch drum nicely and handles very well, making it an excellent choice for sheets-if you can handle the extra expense.
Big bucks for the best: The skys the limit at the upper end of the cordage range. In fact, rope made with esoteric PBO (Zylon) is so costly that we left it out of our evaluation altogether, calling the game at line that pushed to $4 foot in the discount houses. In this grouping, we find rope with the highest breaking strength, the most cover abrasion resistance, and the least stretch. Evidently, you do get what you pay for when it comes to cordage. The reason New England Ropes Endura Braid and Yales Maxi Braid Plus topped our list was that they delivered the three features mentioned above, but also garnered high marks for handling.

Samsons Amsteel was hard not to like. The 15-foot section of 5/16-inch single braid Dyneema took abrasion testing in stride, was soft and supple, weighed in at just 5.5 ounces, and had little more bulk than a handful of shoelaces. Yet it was strong enough to support a pickup truck with a couple of J/24 keels in the bed. The downside was how the all Dyneema line behaves on a winch drum. Its lubricity or slipperiness combines with a coating that glazes under pressure, creating a line thats difficult to set and ease on a winch drum. Despite this complaint, it makes a superb halyard-just use a winch with a well-textured drum face. Its also worthwhile to keep a good supply of this line in the damage control kit, for emergency lashings and jury-rigging.
The least surprising verification from our testing was the inverse relationship between stretch and cost. Esoteric, low-stretch fibers come with a higher price tag, and the old saga of paying more for performance played out in spades. However, the real surprise came when PS started looking to fill in the “street” prices for specific products. Searching West Marine, Defender, Mauri Pro, PYacht, Jamestown Distributors, Boat Locker, and a few other sources, testers discovered a wide range in discounted prices per foot. In some cases, there were 60-percent variations for the identical product. The figures in our table serve as a good guide, but smart rope buying is most certainly a shop-around enterprise.
Dont buy more tech than youre going to put to use. From our perspective, it makes sense to invest a little extra in a good mainsail halyard. Unless youre a hard-core competitor, the genoa that rides in a roller-furler luff grove doesn’t need as much no-stretch chemistry. When it is blowing hard, and the jib is partially furled, the load dynamics spread out to the entire foil headstay and halyard, and some luff sag is expected. Those who still fly a conventional spinnaker will love the reduced stretch of high-tech cordage in an after guy. Lighter weight, no water absorption, and smaller diameter light air sheets can also improve ghosting performance. A lightweight mainsheet with good handling characteristics and a low desire to twist can also be worth the investment.
In short, the polyester double-braided lines are like hubcaps over steel rims-just plain practical. Ratchet up to lines with less stretchy fiber blends in the core, and youve arrived at an all-around good compromise. For those who don’t choke on the $3-per-foot pricetag for hundreds of feet of line, there are spools of great technology just itchin to make sailing faster, easier, and more costly.
- How We Tested
- Practical Sailor Value Guide: Braided Cover Running Rigging Performance
- Download PDF Format
RELATED ARTICLES MORE FROM AUTHOR
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Log in to leave a comment
Latest Videos

What’s the Best Sailboats for Beginners?

Why Does A Sailboat Keel Fall Off?

The Perfect Family Sailboat! Hunter 27-2 – Boat Review

Pettit EZ-Poxy – How to Paint a Boat
Latest sailboat review.

- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell My Personal Information
- Online Account Activation
- Privacy Manager
Yachting World
- Digital Edition

How to fix running rigging at sea: Top tips from pro sailor Pip Hare
- October 24, 2019
Pip Hare shares her top tips on how to fix running rigging while at sea and reveals what's in her jury rig fix-it kit

When racing across oceans I am constantly torn between loading my spares and repairs kit with everything including the kitchen sink, and the need to keep weight to a minimum.
Over the years I’ve been learning to make do with less and the reality is with modern materials most rigging problems can be addressed using the same simple, lightweight kit which will do well for any sailing.
My jury rig fix-it kit contains:
- Plenty of lashing of different sizes
- Soft shackles
- Spare blocks and low friction rings
- Pre-made Dyneema loops
- Webbing strops
- Hanks of strong elastic
Using this kit the following are some of my solutions to address common failures on ocean-going yachts.
Jib cars and travellers
Breakages to sliding cars will leave you with an uncontrollable sail and a problem that cannot be fixed in a matter of minutes. The issue with jury rigging anything that has been on a track is finding suitable fixing points and then spreading the load adequately across them.
Making a jury rig for anything on a track will take time, so first tame your sails. If fixing a traveller drop the main and sail under jib alone; for the jib, try sailing on the other tack – particularly if beating as this will keep your repair side out of the water, using a staysail if you have one or simply dropping the jib.
The simplest way to jury rig a traveller is to create a single fixed point for the mainsheet in the middle of the boat, then use the vang to maintain leech tension when the mainsheet is eased.
If there happens to be a central padeye to the correct rating directly under the after end of the boom then that is your solution. However, as travellers are more normally over a coachroof or the aft deck, the main problems to address are spreading the load, avoiding chafe, and keeping the fixing point for the mainsheet low in the boat.
If the track is raised off the deck you could loop Dyneema or webbing strops under several sections of the traveller, then join them in one central point for the main sheet. Ensure your looped strops are as short as possible so there can be maximum travel on the mainsheet purchase system.
If the track is flush to the deck you’ll need to create a bridle across the boat to attach the mainsheet to. Find four suitable fixing points (two on each side); these could be mooring cleats, padeyes for spinnaker blocks, or the toerail itself.
Take four lengths of Dyneema lashing and make a loop from each fixing point that ends in the centre of the boat (try to make all of the loops the same length). The mainsheet bottom block can be attached through all of the loops in the centre of the boat. Check regularly for chafe on the loops, especially if using the toerail as a fixing point.
Jib car systems can be simpler to fix with a single block attached either to the toerail or a padeye on the deck. Try to place the block in an average setting for jib leech tension – if you still want the ability to close off the leech while sailing, try setting up a barber hauler further forward along the jib sheet, using a small diameter line and a block.
Dead-end the line and the block to the same fixing point on the deck, forward of your jib sheeting point. Run the line up and over the jib sheet then back down through the block and along the deck to the cockpit.
Pulling down on the line will move the sheeting angle for the jib forward and close the leech. There will be friction in this system and care needs to be taken when releasing it, but it is surprisingly efficient. Likewise, if the new sheeting position is too far outboard upwind an inhauler can be rigged in the same way.
Article continues below…

Atlantic sailing spares and repairs: Experienced skippers explain what you’ll need
You’ve got the plan, you’ve got the ideal offshore cruising yacht, you’ve got the time window – you’re set to…

Sail repairs on the fly – how to make essential fixes while at sea
During last year’s ARC I was to be found at one point on the pulpit restitching the foot tape of…
Vang problems
The usual problem with jury rigging a vang is connecting it to the boom – and this can be done using a couple of webbing strops. In this case I would use webbing rather than Dyneema as the flatter surface area will spread load across the boom.
Attach one broad strop around the boom, join it at the bottom and attach a top block to it. Take a line around the top of the strop and then aft along the boom to hold the strop in position under load – the vang itself will be pulling forward.
It is likely your original vang system used double blocks – you may be able to reuse them, or you may need to set up a cascade system using blocks or low friction rings to create enough purchase to hold the boom down.
Broken winches
If one of your winches breaks on passage and you are not carrying the spares or do not have a weather window to fix it, you will need to get inventive routing ropes around the cockpit. If winching straight across the boat to the same winch on the other side, use the broken winch as a turning post to gain the right height.
If the winches are outboard of a raised coaming then instead set up a turning block or low friction ring on the toerail or a padeye to gain height before going across the cockpit.
I prefer to use soft shackles for my snatch blocks and jury rigs, but if fixing blocks to aluminium toerails, check for rough edges and use a stainless steel shackle on the toerail if concerned about chafe.
Hold the block up to a guardrail with elastic so it doesn’t hit the deck when the sheet is not under load. For temporarily holding a line while looking to route to an alternative winch, use a good old fashioned riding turn to create a hobble to keeping the rope in place.
When making splint repairs or lashing two solid items together use wide diameter elastic to make the first lashing, then finish with Dyneema once they are in place. When pulled tight, a strong elastic is best able to hold items in position and under tension, making it much easier to make the more permanent Dyneema lashing tight.
First published in the October 2019 edition of Yachting World.

Please verify you are a human
Access to this page has been denied because we believe you are using automation tools to browse the website.
This may happen as a result of the following:
- Javascript is disabled or blocked by an extension (ad blockers for example)
- Your browser does not support cookies
Please make sure that Javascript and cookies are enabled on your browser and that you are not blocking them from loading.
Reference ID: ed4f6865-655c-11ef-8a73-696d59be547d
Powered by PerimeterX , Inc.
10% Off Hobie Parts / 15% Off Rigging / 10-15% Off Select Kayaks - SHOP NOW

- Call Us +1-503-285-5536
- Sign in & Register
- Recently Viewed
- Guides & Advice
Rigging Guides

Not sure how to rig your boat or looking to brush up on a certain part of your rigging? Check out these Rigging Guides with photos and tips for rigging a variety of small sailboats. Available as PDF downloads for ease of use.
Hobie Cat Rigging Guides
Hobie Bravo Rigging Guide
Hobie Wave Rigging Guide
Hobie Getaway Rigging Guide
Hobie 16 / Hobie 14 Rigging Guide
Hobie 17 Rigging Guide
Hobie 17 Sport Rigging Guide
Hobie 18 / 18SX Rigging Guide
Hobie Tandem Island Rigging Guide
Hobie Adventure Island Rigging Guide
RS Sailing Rigging Guides
RS Aero Rigging Guide ( Current 'Overdeck' Style )
RS Aero Rigging Guide ( Previous 'Underdeck' Style )
RS Feva Rigging Guide
RS Tera Rigging Guide
RS Zest Rigging Guide
RS Quest Rigging Guide
RS Toura Rigging Guide
RS Quba Rigging Guide
RS Neo Rigging Guide
RS Vision Rigging Guide
RS Venture Rigging Guide
RS Venture Connect Rigging Guide
RS 21 Rigging Guide
RS Cat 14 Rigging Guide
RS Cat 16 Rigging Guide
RS 200 Rigging Guide
RS 400 Rigging Guide
RS 500 Rigging Guide
RS 800 Rigging Guide
Optimist Rigging Guides
Mclaughlin Owner's Manual
Opti Sailors Hull Booklet
Guide to Optimist Spars
Instructions for School Spars
Laser Performance Rigging Guides
C420 Rigging Guide
Bahia Rigging Guide
Laser Rigging Guide
Pico Rigging Guide
Stratos Rigging Guide
Sunfish Rigging Guide
Vago Rigging Guide
Zuma Rigging Guide
Bug Rigging Guide
Miscellaneous Rigging Guides
Tasar Rigging Guide
29er Rigging Guide
Weta Rigging Guide
Subscribe To Our Newsletter
Sign up for our newsletter to receive exclusive discounts, new product announcements, and upcoming sales.
Sailboat Parts Explained: Illustrated Guide (with Diagrams)
When you first get into sailing, there are a lot of sailboat parts to learn. Scouting for a good guide to all the parts, I couldn't find any, so I wrote one myself.
Below, I'll go over each different sailboat part. And I mean each and every one of them. I'll walk you through them one by one, and explain each part's function. I've also made sure to add good illustrations and clear diagrams.
This article is a great reference for beginners and experienced sailors alike. It's a great starting point, but also a great reference manual. Let's kick off with a quick general overview of the different sailboat parts.
General Overview
The different segments
You can divide up a sailboat in four general segments. These segments are arbitrary (I made them up) but it will help us to understand the parts more quickly. Some are super straightforward and some have a bit more ninja names.
Something like that. You can see the different segments highlighted in this diagram below:
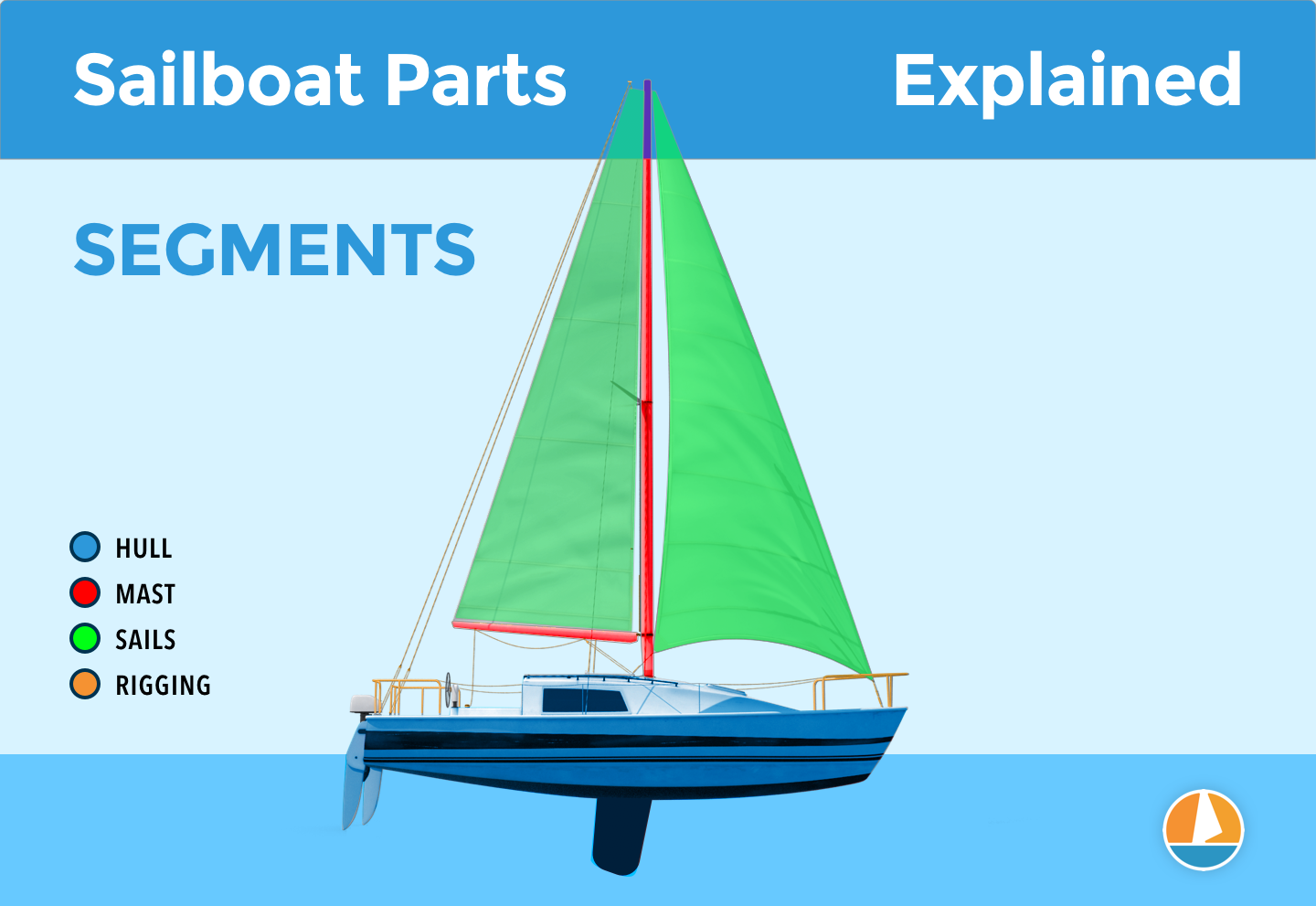
The hull is what most people would consider 'the boat'. It's the part that provides buoyancy and carries everything else: sails, masts, rigging, and so on. Without the hull, there would be no boat. The hull can be divided into different parts: deck, keel, cabin, waterline, bilge, bow, stern, rudder, and many more.
I'll show you those specific parts later on. First, let's move on to the mast.

Sailboats Explained
The mast is the long, standing pole holding the sails. It is typically placed just off-center of a sailboat (a little bit to the front) and gives the sailboat its characteristic shape. The mast is crucial for any sailboat: without a mast, any sailboat would become just a regular boat.
I think this segment speaks mostly for itself. Most modern sailboats you see will have two sails up, but they can carry a variety of other specialty sails. And there are all kinds of sail plans out there, which determine the amount and shape of sails that are used.
The Rigging
This is probably the most complex category of all of them.
Rigging is the means with which the sails are attached to the mast. The rigging consists of all kinds of lines, cables, spars, and hardware. It's the segment with the most different parts.
The most important parts
If you learn anything from this article, here are the most important parts of any sailboat. You will find all of these parts in some shape or form on almost any sailboat.

Okay, we now have a good starting point and a good basic understanding of the different sailboat parts. It's time for the good stuff. We're going to dive into each segment in detail.
Below, I'll go over them one by one, pointing out its different parts on a diagram, listing them with a brief explanation, and showing you examples as well.
After reading this article, you'll recognize every single sailboat part and know them by name. And if you forget one, you're free to look it up in this guide.
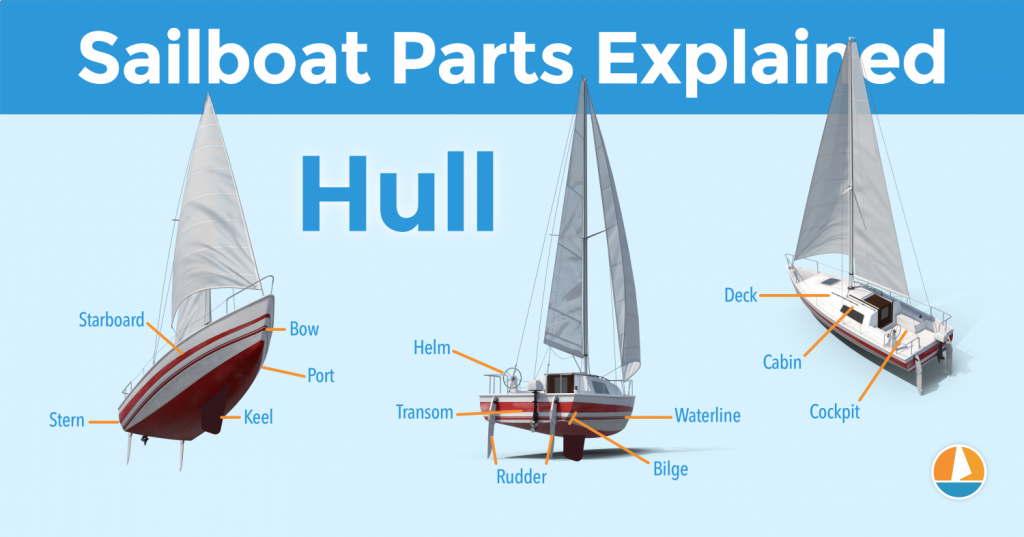
On this page:
The hull is the heart of the boat. It's what carries everything: the mast, the sails, the rigging, the passengers. The hull is what provides the sailboat with its buoyancy, allowing it to stay afloat.
Sailboats mostly use displacement hulls, which is a shape that displaces water when moving through it. They are generally very round and use buoyancy to support its own weight. These two characteristics make sure it is a smooth ride.
There are different hull shapes that work and handle differently. If you want to learn more about them, here's the Illustrated Guide to Boat Hull Types (with 11 Examples ). But for now, all we need to know is that the hull is the rounded, floating part of any sailboat.
Instead of simply calling the different sides of a hull front, back, left and right , we use different names in sailing. Let's take a look at them.
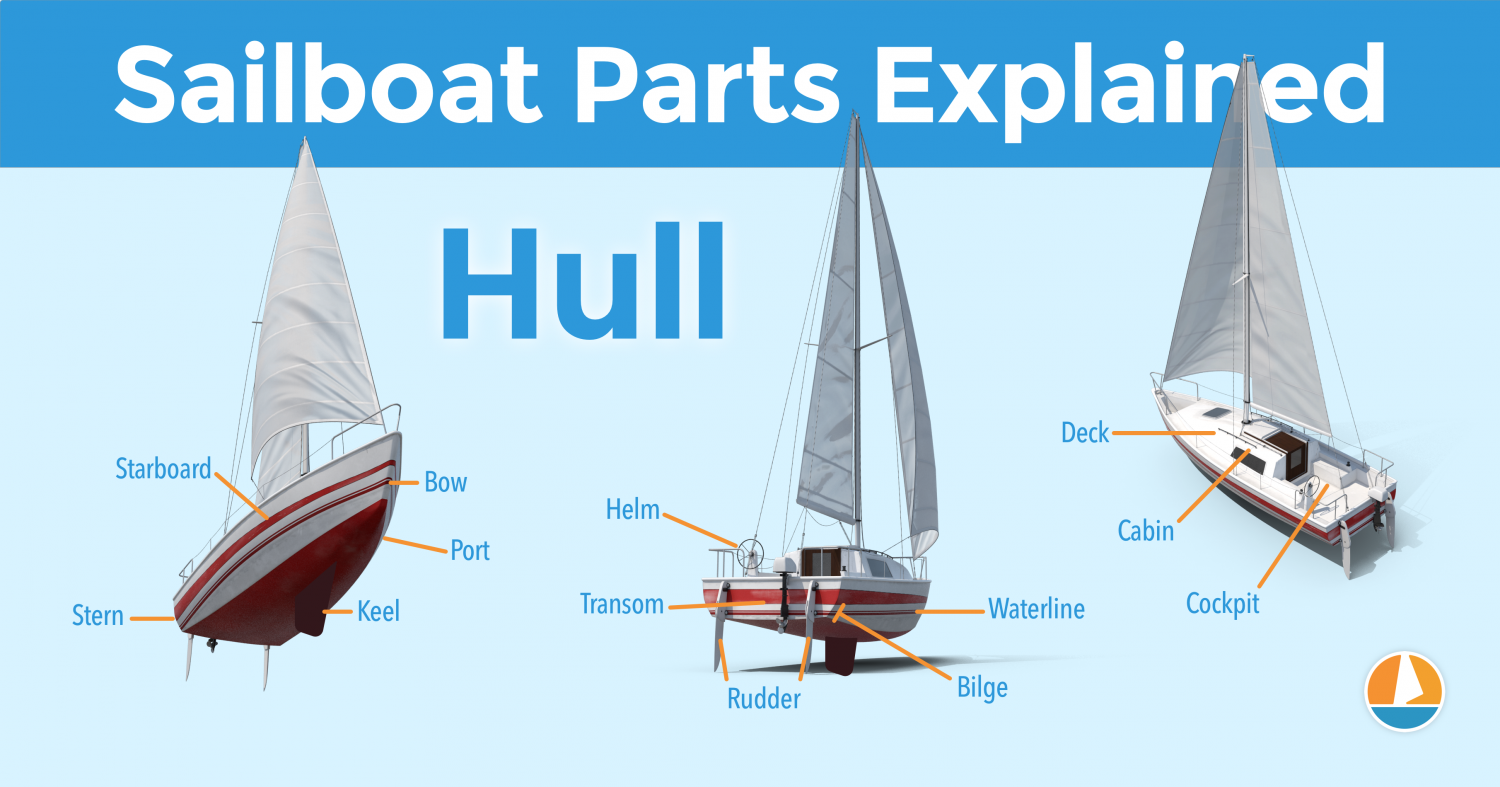
The bow is the front part of the hull. It's simply the nautical word for 'front'. It's the pointy bit that cuts through the water. The shape of the bow determines partially how the boat handles.
The stern is the back part of the hull. It's simply the nautical word for 'back'. The shape of the stern partially determines the stability and speed of the boat. With motorboats, the stern lies deep inside the water, and the hull is flatter aft. Aft also means back. This allows it to plane, increasing the hull speed. For sailboats, stability is much more important, so the hull is rounded throughout, increasing its buoyancy and hydrodynamic properties.
The transom is the backplate of the boat's hull. It's the most aft (rear) part of the boat.
Port is the left side of a sailboat.
Starboard is the right side of a sailboat
The bilges are the part where the bottom and the sides of the hull meet. On sailboats, these are typically very round, which helps with hydrodynamics. On powerboats, they tend to have an angle.
The waterline is the point where the boat's hull meets the water. Generally, boat owners paint the waterline and use antifouling paint below it, to protect it from marine growth.
The deck is the top part of the boat's hull. In a way, it's the cap of the boat, and it holds the deck hardware and rigging.
Displacement hulls are very round and smooth, which makes them very efficient and comfortable. But it also makes them very easy to capsize: think of a canoe, for example.
The keel is a large fin that offsets the tendency to capsize by providing counterbalance. Typically, the keel carries ballast in the tip, creating a counterweight to the wind's force on the sails.
The rudder is the horizontal plate at the back of the boat that is used to steer by setting a course and maintaining it. It is connected to the helm or tiller.
Tiller or Helm
- The helm is simply the nautical term for the wheel.
- The tiller is simply the nautical term for the steering stick.
The tiller or helm is attached to the rudder and is used to steer the boat. Most smaller sailboats (below 30') have a tiller, most larger sailboats use a helm. Large ocean-going vessels tend to have two helms.
The cockpit is the recessed part in the deck where the helmsman sits or stands. It tends to have some benches. It houses the outside navigation and systems interfaces, like the compass, chartplotter, and so on. It also houses the mainsheet traveler and winches for the jib. Most boats are set up so that the entire vessel can be operated from the cockpit (hence the name). More on those different parts later.
Most larger boats have some sort of roofed part, which is called the cabin. The cabin is used as a shelter, and on cruising sailboats you'll find the galley for cooking, a bed, bath room, and so on.
The mast is the pole on a sailboat that holds the sails. Sailboats can have one or multiple masts, depending on the mast configuration. Most sailboats have only one or two masts. Three masts or more is less common.
The boom is the horizontal pole on the mast, that holds the mainsail in place.
The sails seem simple, but actually consist of many moving parts. The parts I list below work for most modern sailboats - I mean 90% of them. However, there are all sorts of specialty sails that are not included here, to keep things concise.

The mainsail is the largest sail on the largest mast. Most sailboats use a sloop rigging (just one mast with one bermuda mainsail). In that case, the main is easy to recognize. With other rig types, it gets more difficult, since there can be multiple tall masts and large sails.
If you want to take a look at the different sail plans and rig types that are out there, I suggest reading my previous guide on how to recognize any sailboat here (opens in new tab).
Sail sides:
- Leech - Leech is the name for the back side of the sail, running from the top to the bottom.
- Luff - Luff is the name for the front side of the sail, running from the top to the bottom.
- Foot - Foot is the name for the lower side of the sail, where it meets the boom.
Sail corners:
- Clew - The clew is the lower aft (back) corner of the mainsail, where the leech is connected to the foot. The clew is attached to the boom.
- Tack - The tack is the lower front corner of the mainsail
- Head - The head is the top corner of the mainsail
Battens are horizontal sail reinforcers that flatten and stiffen the sail.
Telltales are small strings that show you whether your sail trim is correct. You'll find telltales on both your jib and mainsail.
The jib is the standard sized headsail on a Bermuda Sloop rig (which is the sail plan most modern sailboats use).
As I mentioned: there are all kinds, types, and shapes of sails. For an overview of the most common sail types, check out my Guide on Sail Types here (with photos).
The rigging is what is used to attach your sails and mast to your boat. Rigging, in other words, mostly consists of all kinds of lines. Lines are just another word for ropes. Come to think of it, sailors really find all kinds of ways to complicate the word rope ...
Two types of rigging
There are two types of rigging: running and standing rigging. The difference between the two is very simple.
- The running rigging is the rigging on a sailboat that's used to operate the sails. For example, the halyard, which is used to lower and heave the mainsail.
- The standing rigging is the rigging that is used to support the mast and sail plan.
Standing Rigging
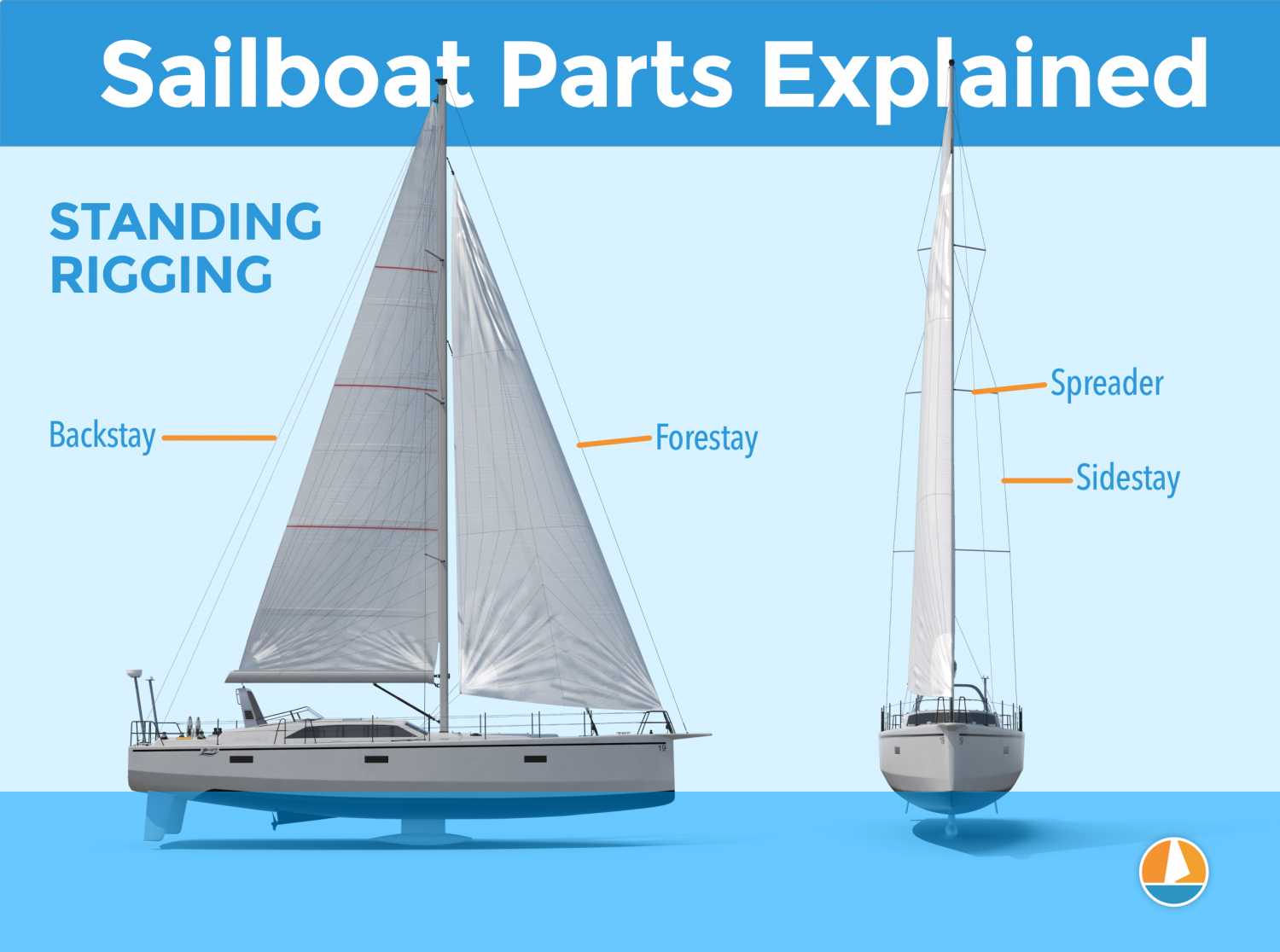
Here are the different parts that belong to the standing rigging:
- Forestay or Headstay - Line or cable that supports the mast and is attached to the bow of the boat. This is often a steel cable.
- Backstay - Line or cable that supports the mast and is attached to the stern of the boat. This is often a steel cable.
- Sidestay or Shroud - Line or cable that supports the mast from the sides of the boat. Most sailboats use at least two sidestays (one on each side).
- Spreader - The sidestays are spaced to steer clear from the mast using spreaders.
Running Rigging: different words for rope
Ropes play a big part in sailing, and especially in control over the sails. In sailboat jargon, we call ropes 'lines'. But there are some lines with a specific function that have a different name. I think this makes it easier to communicate with your crew: you don't have to define which line you mean. Instead, you simply shout 'mainsheet!'. Yeah, that works.
Running rigging consists of the lines, sheets, and hardware that are used to control, raise, lower, shape and manipulate the sails on a sailboat. Rigging varies for different rig types, but since most sailboats are use a sloop rig, nearly all sailboats use the following running rigging:
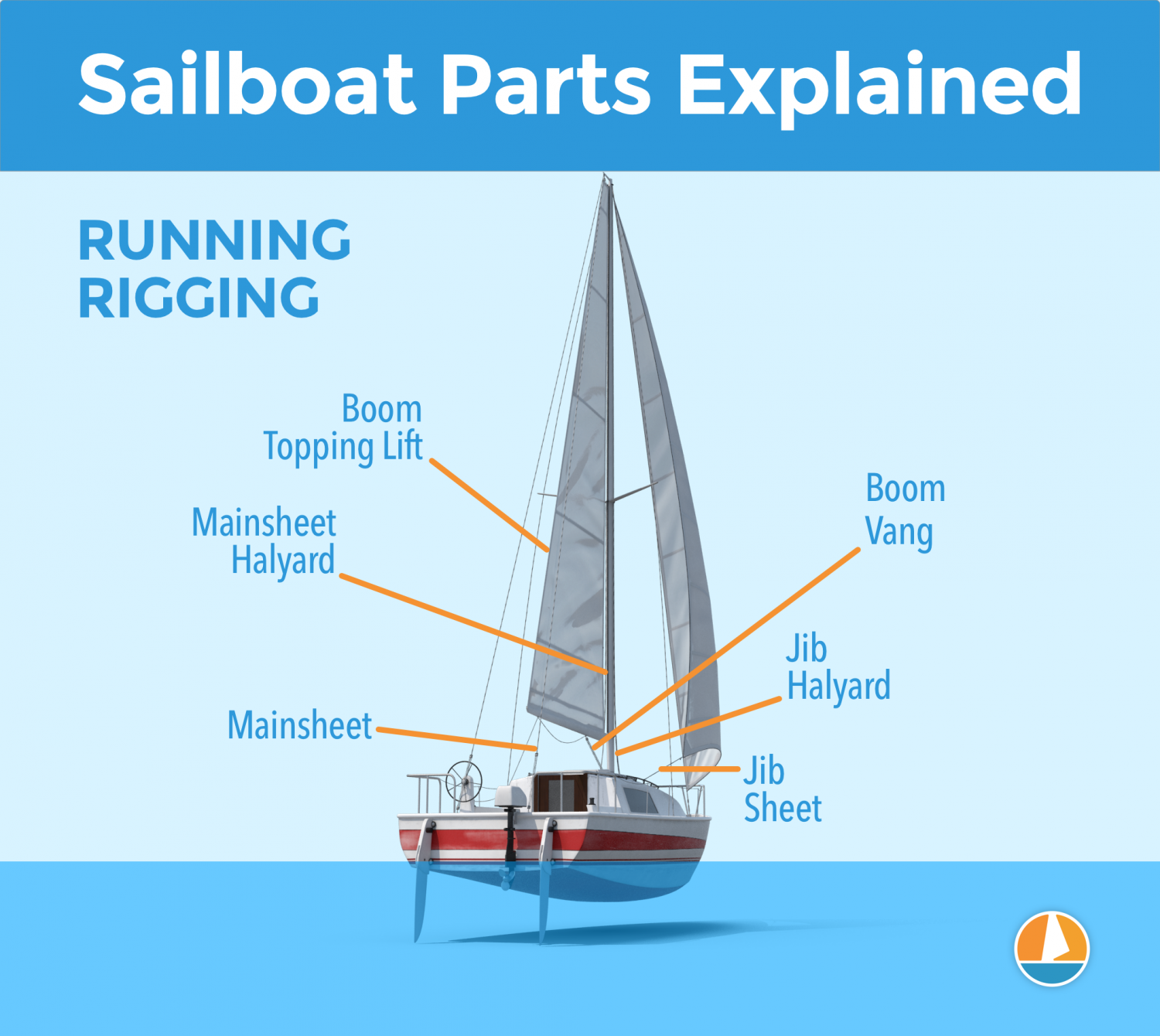
- Halyards -'Halyard' is simply the nautical name for lines or ropes that are used to raise and lower the mainsail. The halyard is attached to the top of the mainsail sheet, or the gaffer, which is a top spar that attaches to the mainsail. You'll find halyards on both the mainsail and jib.
- Sheets - 'Sheet' is simply the nautical term for lines or ropes that are used to set the angle of the sail.
- Mainsheet - The line, or sheet, that is used to set the angle of the mainsail. The mainsheet is attached to the Mainsheet traveler. More on that under hardware.
- Jib Sheet - The jib mostly comes with two sheets: one on each side of the mast. This prevents you from having to loosen your sheet, throwing it around the other side of the mast, and tightening it. The jib sheets are often controlled using winches (more on that under hardware).
- Cleats are small on-deck hooks that can be used to tie down sheets and lines after trimming them.
- Reefing lines - Lines that run through the mainsail, used to put a reef in the main.
- The Boom Topping Lift is a line that is attached to the aft (back) end of the boom and runs to the top of the mast. It supports the boom whenever you take down the mainsail.
- The Boom Vang is a line that places downward tension on the boom.
There are some more tensioning lines, but I'll leave them for now. I could probably do an entire guide on the different sheets on a sailboat. Who knows, perhaps I'll write it.
This is a new segment, that I didn't mention before. It's a bit of an odd duck, so I threw all sorts of stuff into this category. But they are just as important as all the other parts. Your hardware consists of cleats, winches, traveler and so on. If you don't know what all of this means, no worries: neither did I. Below, you'll find a complete overview of the different parts.
Deck Hardware
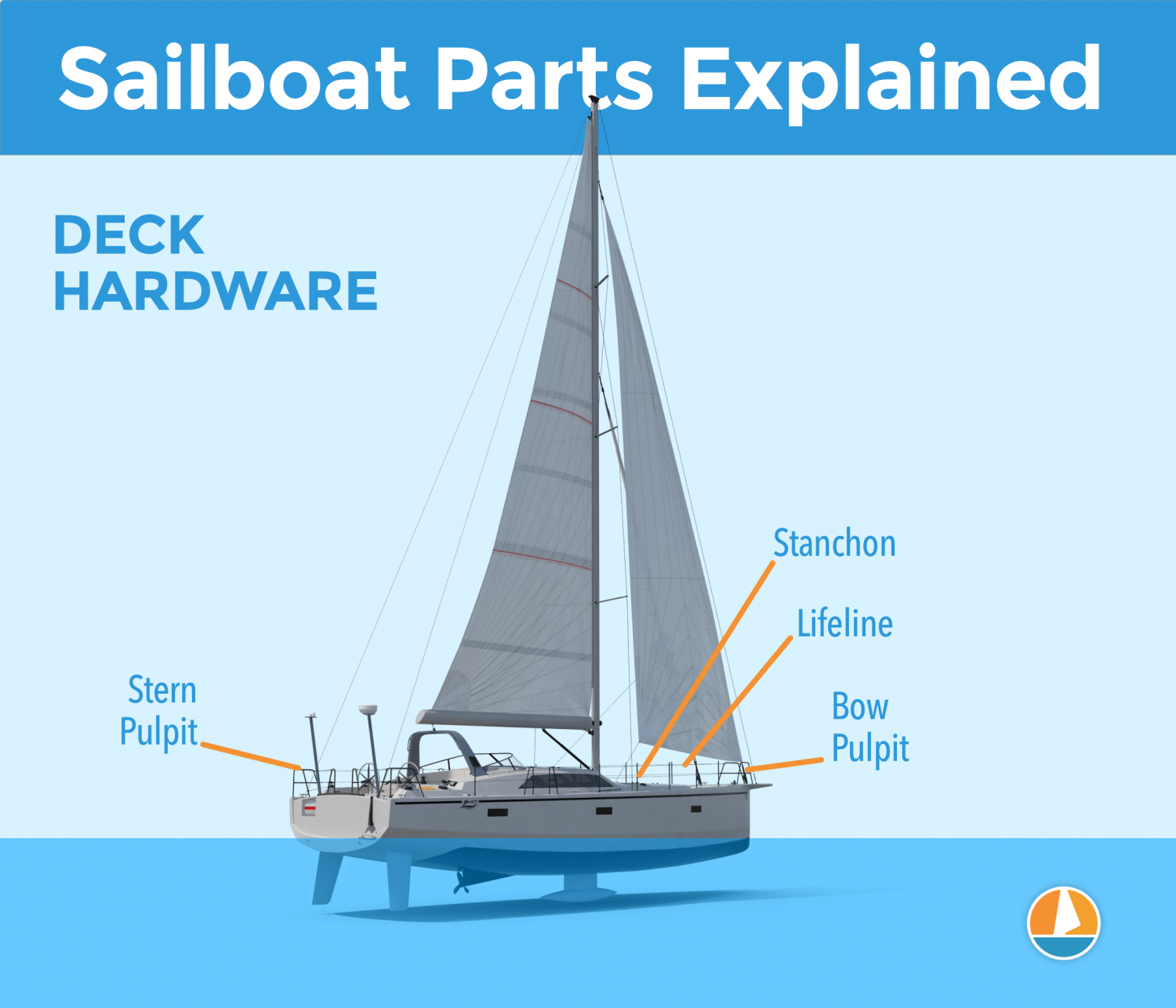
Just a brief mention of the different deck hardware parts:
- Pulpits are fenced platforms on the sailboat's stern and bow, which is why they are called the bow pulpit and stern pulpit here. They typically have a solid steel framing for safety.
- Stanchons are the standing poles supporting the lifeline , which combined for a sort of fencing around the sailboat's deck. On most sailboats, steel and steel cables are used for the stanchons and lifelines.
Mainsheet Traveler
The mainsheet traveler is a rail in the cockpit that is used to control the mainsheet. It helps to lock the mainsheet in place, fixing the mainsails angle to the wind.

If you're interested in learning more about how to use the mainsheet traveler, Matej has written a great list of tips for using your mainsheet traveler the right way . It's a good starting point for beginners.
Winches are mechanical or electronic spools that are used to easily trim lines and sheets. Most sailboats use winches to control the jib sheets. Modern large sailing yachts use electronic winches for nearly all lines. This makes it incredibly easy to trim your lines.
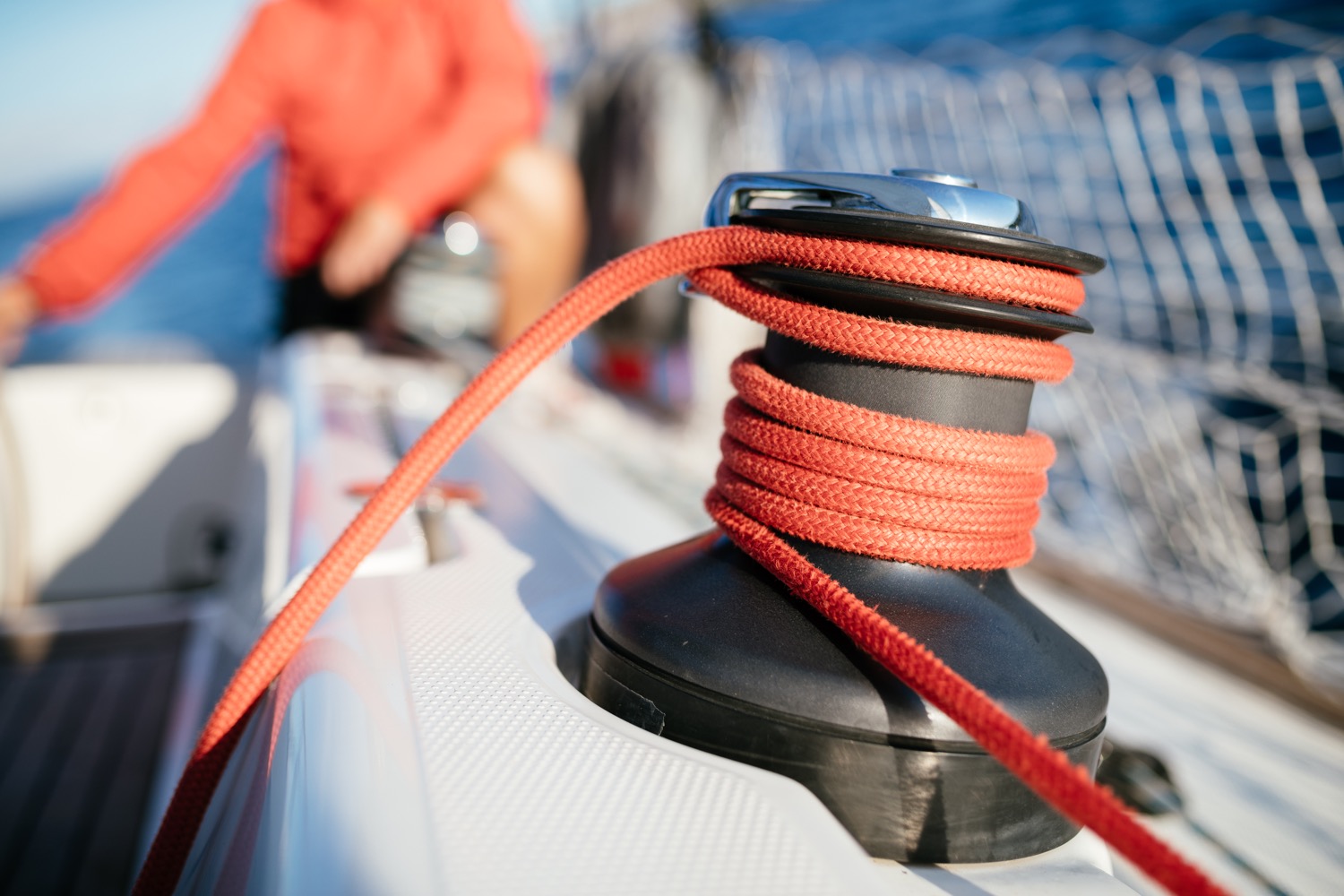

You'll find the compass typically in the cockpit. It's the most old-skool navigation tool out there, but I'm convinced it's also one of the most reliable. In any way, it definitely is the most solid backup navigator you can get for the money.
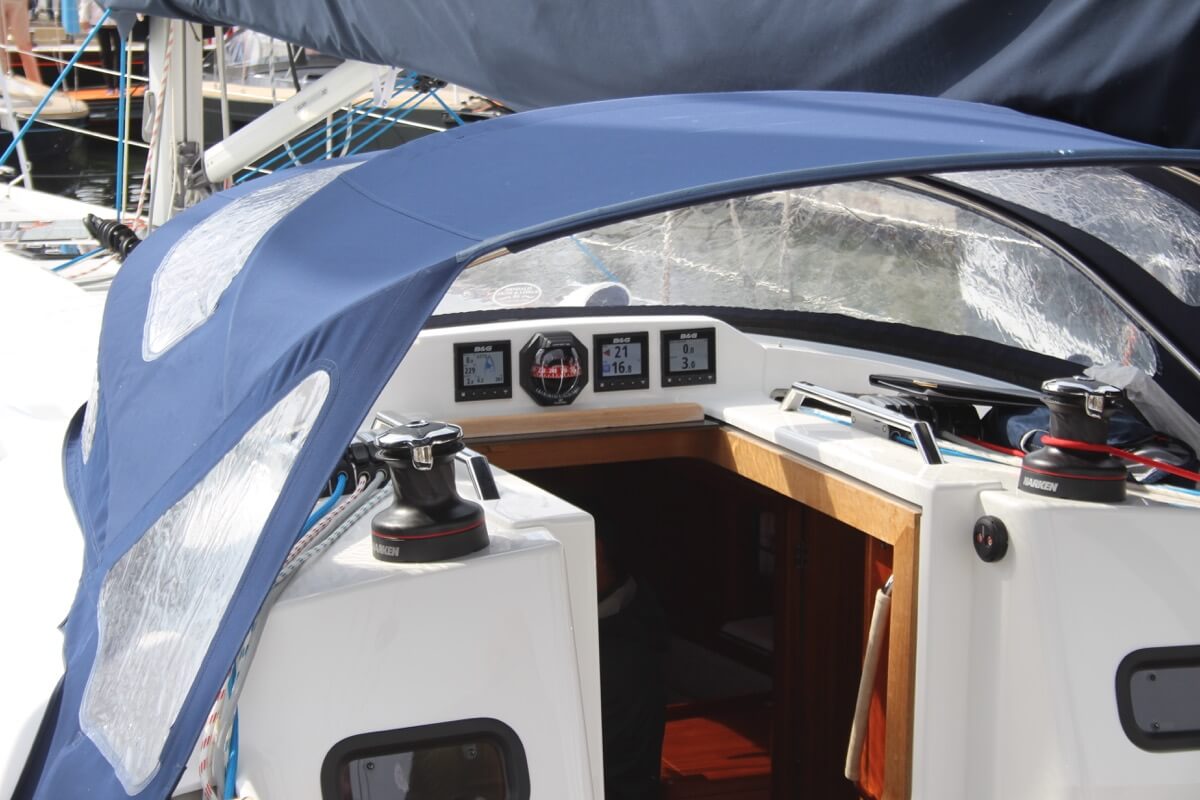

Want to learn how to use a compass quickly and reliably? It's easy. Just read my step-by-step beginner guide on How To Use a Compass (opens in new tab .
Chartplotter
Most sailboats nowadays use, besides a compass and a map, a chartplotter. Chartplotters are GPS devices that show a map and a course. It's very similar to your normal car navigation.
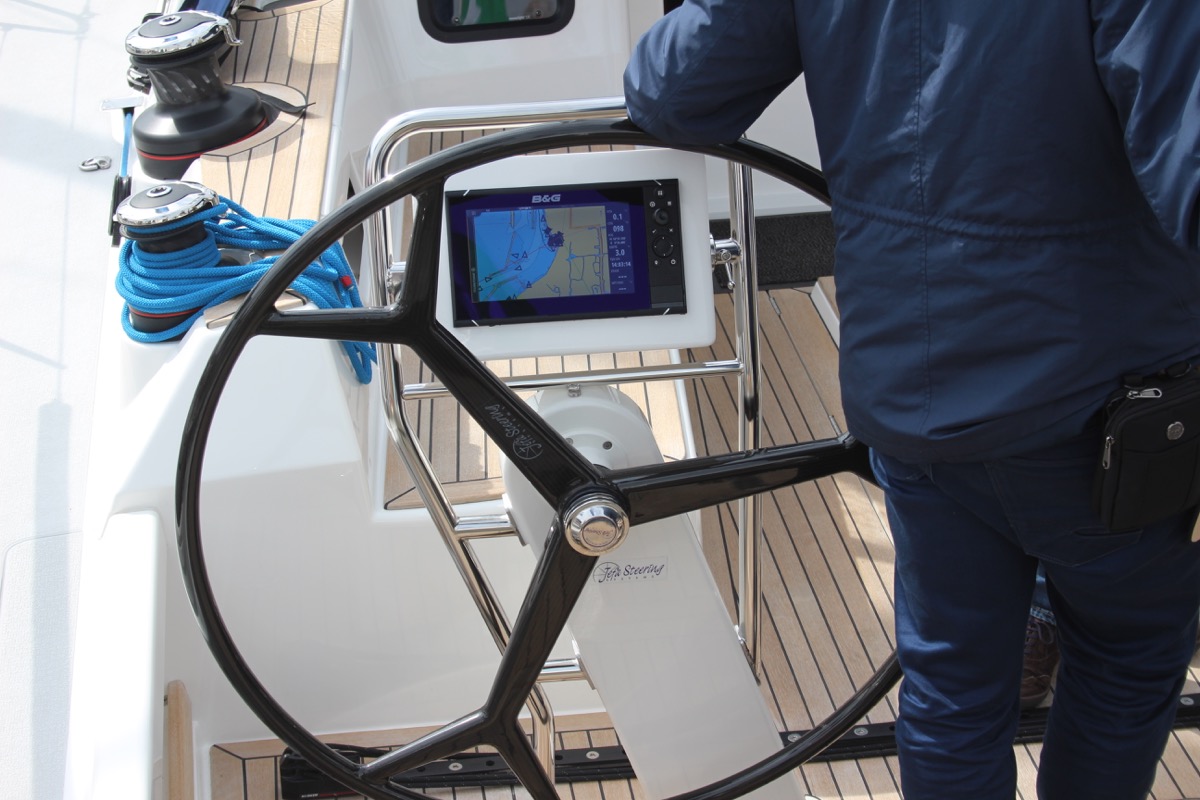

Outboard motor
Most sailboats have some sort of motor to help out when there's just the slightest breeze. These engines aren't very big or powerful, and most sailboats up to 32' use an outboard motor. You'll find these at the back of the boat.

Most sailboats carry 1 - 3 anchors: one bow anchor (the main one) and two stern anchors. The last two are optional and are mostly used by bluewater cruisers.

I hope this was helpful, and that you've gained a good understanding of the different parts involved in sailing. I wanted to write a good walk-through instead of overwhelming you with lists and lists of nautical terms. I hope I've succeeded. If so, I appreciate any comments and tips below.
I've tried to be as comprehensive as possible, without getting into the real nitty gritty. That would make for a gigantic article. However, if you feel I've left something out that really should be in here, please let me know in the comments below, so I can update the article.
I own a small 20 foot yacht called a Red witch made locally back in the 70s here in Western Australia i found your article great and enjoyed reading it i know it will be a great help for me in my future leaning to sail regards John.
David Gardner
İ think this is a good explanation of the difference between a ”rope” and a ”line”:
Rope is unemployed cordage. In other words, when it is in a coil and has not been assigned a job, it is just a rope.
On the other hand, when you prepare a rope for a specific task, it becomes employed and is a line. The line is labeled by the job it performs; for example, anchor line, dock line, fender line, etc.
Hey Mr. Buckles
I am taking on new crew to race with me on my Flying Scot (19ft dingy). I find your Sailboat Parts Explained to be clear and concise. I believe it will help my new crew learn the language that we use on the boat quickly without being overwhelmed.
PS: my grandparents were from Friesland and emigrated to America.
Thank you Shawn for the well written, clear and easy to digest introductory article. Just after reading this first article I feel excited and ready to set sails and go!! LOL!! Cheers! Daniel.
steve Balog
well done, chap
Great intro. However, the overview diagram misidentifies the cockpit location. The cockpit is located aft of the helm. Your diagram points to a location to the fore of the helm.
William Thompson-Ambrose
An excellent introduction to the basic anatomy and function of the sailboat. Anyone who wants to start sailing should consider the above article before stepping aboard! Thank-you
James Huskisson
Thanks for you efforts mate. We’ve all got to start somewhere. Thanks for sharing. Hoping to my first yacht. 25ft Holland. Would love to cross the Bass Strait one day to Tasmania. 👌 Cheers mate
Alan Alexander Percy
thankyou ijust aquired my first sailboat at 66yrs of age its down at pelican point a beautifull place in virginia usa my sailboat is a redwing 30 if you are ever in the area i wouldnt mind your guidance and superior knowledge of how to sail but iam sure your fantastic article will help my sailboat is wings 30 ft
Thanks for quick refresher course. Having sailed in California for 20+ years I now live in Spain where I have to take a spanish exam for a sailboat license. Problem is, it’s only in spanish. So a lot to learn for an old guy like me.
Very comprehensive, thank you
Your article really brought all the pieces together for me today. I have been adventuring my first sailing voyage for 2 months from the Carolinas and am now in Eleuthera waiting on weather to make the Exumas!!! Great job and thanks
Helen Ballard
I’ve at last found something of an adventure to have in sailing, so I’m starting at the basics, I have done a little sailing but need more despite being over 60 life in the old dog etc, thanks for your information 😊
Barbara Scott
I don’t have a sailboat, neither do l plan to literally take to the waters. But for mental exercise, l have decided to take to sailing in my Bermuda sloop, learning what it takes to become a good sailor and run a tight ship, even if it’s just imaginary. Thank you for helping me on my journey to countless adventures and misadventures, just to keep it out of the doldrums! (I’m a 69 year old African American female who have rediscovered why l enjoyed reading The Adventures of Robert Louis Stevenson as well as his captivating description of sea, wind, sailboat,and sailor).
Great article and very good information source for a beginner like me. But I didn’t find out what I had hoped to, which is, what are all those noisy bits of kit on top of the mast? I know the one with the arrow is a weather vane, but the rest? Many thanks, Jay.
Louis Cohen
The main halyard is attached to the head of the mainsail, not the to the mainsheet. In the USA, we say gaff, not gaffer. The gaff often has its own halyard separate from the main halyard.
Other than that it’s a nice article with good diagrams.
A Girl Who Has an Open Sail Dream
Wow! That was a lot of great detail! Thank you, this is going to help me a lot on my project!
Hi, good info, do u know a book that explains all the systems on a candc 27,
Leave a comment
You may also like, guide to understanding sail rig types (with pictures).
There are a lot of different sail rig types and it can be difficult to remember what's what. So I've come up with a system. Let me explain it in this article.

The Ultimate Guide to Sail Types and Rigs (with Pictures)

The Illustrated Guide To Boat Hull Types (11 Examples)

How To Live On a Boat For Free: How I'd Do It

How To Live on a Sailboat: Consider These 5 Things
Running Rigging Calculator
Get an instant estimate for your boat, select your boat brand.

Leaves warehouse: 12 business days
- Copyright 1998-2024 SB Owners, LLC. All rights reserved.

- Policies | Contact Us
No products in the cart.
Sailing Ellidah is supported by our readers. Buying through our links may earn us an affiliate commission at no extra cost to you.
The Standing Rigging On A Sailboat Explained
The standing rigging on a sailboat is a system of stainless steel wires that holds the mast upright and supports the spars.
In this guide, I’ll explain the basics of a sailboat’s hardware and rigging, how it works, and why it is a fundamental and vital part of the vessel. We’ll look at the different parts of the rig, where they are located, and their function.
We will also peek at a couple of different types of rigs and their variations to determine their differences. In the end, I will explain some additional terms and answer some practical questions I often get asked.
But first off, it is essential to understand what standing rigging is and its purpose on a sailboat.
The purpose of the standing rigging
Like I said in the beginning, the standing rigging on a sailboat is a system of stainless steel wires that holds the mast upright and supports the spars. When sailing, the rig helps transfer wind forces from the sails to the boat’s structure. This is critical for maintaining the stability and performance of the vessel.
The rig can also consist of other materials, such as synthetic lines or steel rods, yet its purpose is the same. But more on that later.
Since the rig supports the mast, you’ll need to ensure that it is always in appropriate condition before taking your boat out to sea. Let me give you an example from a recent experience.
Dismasting horrors
I had a company inspect the entire rig on my sailboat while preparing for an Atlantic crossing. The rigger didn’t find any issues, but I decided to replace the rig anyway because of its unknown age. I wanted to do the job myself so I could learn how it is done correctly.
Not long after, we left Gibraltar and sailed through rough weather for eight days before arriving in Las Palmas. We were safe and sound and didn’t experience any issues. Unfortunately, several other boats arriving before us had suffered rig failures. They lost their masts and sails—a sorrowful sight but also a reminder of how vital the rigging is on a sailboat.
The most common types of rigging on a sailboat
The most commonly used rig type on modern sailing boats is the fore-and-aft Bermuda Sloop rig with one mast and just one headsail. Closely follows the Cutter rig and the Ketch rig. They all have a relatively simple rigging layout. Still, there are several variations and differences in how they are set up.
A sloop has a single mast, and the Ketch has one main mast and an additional shorter mizzen mast further aft. A Cutter rig is similar to the Bermuda Sloop with an additional cutter forestay, allowing it to fly two overlapping headsails.
You can learn more about the differences and the different types of sails they use in this guide. For now, we’ll focus on the Bermuda rig.
The difference between standing rigging and running rigging
Sometimes things can get confusing as some of our nautical terms are used for multiple items depending on the context. Let me clarify just briefly:
The rig or rigging on a sailboat is a common term for two parts:
- The standing rigging consists of wires supporting the mast on a sailboat and reinforcing the spars from the force of the sails when sailing.
- The running rigging consists of the halyards, sheets, and lines we use to hoist, lower, operate, and control the sails on a sailboat.
Check out my guide on running rigging here !
The difference between a fractional and a masthead rig
A Bermuda rig is split into two groups. The Masthead rig and the Fractional rig.
The Masthead rig has a forestay running from the bow to the top of the mast, and the spreaders point 90 degrees to the sides. A boat with a masthead rig typically carries a bigger overlapping headsail ( Genoa) and a smaller mainsail. Very typical on the Sloop, Ketch, and Cutter rigs.
A Fractional rig has forestays running from the bow to 1/4 – 1/8 from the top of the mast, and the spreaders are swept backward. A boat with a fractional rig also has the mast farther forward than a masthead rig, a bigger mainsail, and a smaller headsail, usually a Jib. Very typical on more performance-oriented sailboats.
There are exceptions in regards to the type of headsail, though. Many performance cruisers use a Genoa instead of a Jib , making the difference smaller.
Some people also fit an inner forestay, or a babystay, to allow flying a smaller staysail.
Explaining the parts and hardware of the standing rigging
The rigging on a sailing vessel relies on stays and shrouds in addition to many hardware parts to secure the mast properly. And we also have nautical terms for each of them. Since a system relies on every aspect of it to be in equally good condition, we want to familiarize ourselves with each part and understand its function.
Forestay and Backstay
The forestay is a wire that runs from the bow to the top of the mast. Some boats, like the Cutter rig, can have several additional inner forestays in different configurations.
The backstay is the wire that runs from the back of the boat to the top of the mast. Backstays have a tensioner, often hydraulic, to increase the tension when sailing upwind. Some rigs, like the Cutter, have running backstays and sometimes checkstays or runners, to support the rig.
The primary purpose of the forestay and backstay is to prevent the mast from moving fore and aft. The tensioner on the backstay also allows us to trim and tune the rig to get a better shape of the sails.
The shrouds are the wires or lines used on modern sailboats and yachts to support the mast from sideways motion.
There are usually four shrouds on each side of the vessel. They are connected to the side of the mast and run down to turnbuckles attached through toggles to the chainplates bolted on the deck.
- Cap shrouds run from the top of the mast to the deck, passing through the tips of the upper spreaders.
- Intermediate shrouds run from the lower part of the mast to the deck, passing through the lower set of spreaders.
- Lower shrouds are connected to the mast under the first spreader and run down to the deck – one fore and one aft on each side of the boat.
This configuration is called continuous rigging. We won’t go into the discontinuous rigging used on bigger boats in this guide, but if you are interested, you can read more about it here .
Shroud materials
Shrouds are usually made of 1 x 19 stainless steel wire. These wires are strong and relatively easy to install but are prone to stretch and corrosion to a certain degree. Another option is using stainless steel rods.
Rod rigging
Rod rigging has a stretch coefficient lower than wire but is more expensive and can be intricate to install. Alternatively, synthetic rigging is becoming more popular as it weighs less than wire and rods.
Synthetic rigging
Fibers like Dyneema and other aramids are lightweight and provide ultra-high tensile strength. However, they are expensive and much more vulnerable to chafing and UV damage than other options. In my opinion, they are best suited for racing and regatta-oriented sailboats.
Wire rigging
I recommend sticking to the classic 316-graded stainless steel wire rigging for cruising sailboats. It is also the most reasonable of the options. If you find yourself in trouble far from home, you are more likely to find replacement wire than another complex rigging type.
Relevant terms on sailboat rigging and hardware
The spreaders are the fins or wings that space the shrouds away from the mast. Most sailboats have at least one set, but some also have two or three. Once a vessel has more than three pairs of spreaders, we are probably talking about a big sailing yacht.
A turnbuckle is the fitting that connects the shrouds to the toggle and chainplate on the deck. These are adjustable, allowing you to tension the rig.
A chainplate is a metal plate bolted to a strong point on the deck or side of the hull. It is usually reinforced with a backing plate underneath to withstand the tension from the shrouds.
The term mast head should be distinct from the term masthead rigging. Out of context, the mast head is the top of the mast.
A toggle is a hardware fitting to connect the turnbuckles on the shrouds and the chainplate.
How tight should the standing rigging be?
It is essential to periodically check the tension of the standing rigging and make adjustments to ensure it is appropriately set. If the rig is too loose, it allows the mast to sway excessively, making the boat perform poorly.
You also risk applying a snatch load during a tack or a gybe which can damage the rig. On the other hand, if the standing rigging is too tight, it can strain the rig and the hull and lead to structural failure.
The standing rigging should be tightened enough to prevent the mast from bending sideways under any point of sail. If you can move the mast by pulling the cap shrouds by hand, the rigging is too loose and should be tensioned. Once the cap shrouds are tightened, follow up with the intermediates and finish with the lower shrouds. It is critical to tension the rig evenly on both sides.
The next you want to do is to take the boat out for a trip. Ensure that the mast isn’t bending over to the leeward side when you are sailing. A little movement in the leeward shrouds is normal, but they shouldn’t swing around. If the mast bends to the leeward side under load, the windward shrouds need to be tightened. Check the shrouds while sailing on both starboard and port tack.
Once the mast is in a column at any point of sail, your rigging should be tight and ready for action.
If you feel uncomfortable adjusting your rig, get a professional rigger to inspect and reset it.
How often should the standing rigging be replaced on a sailboat?
I asked the rigger who produced my new rig for Ellidah about how long I could expect my new rig to last, and he replied with the following:
The standing rigging should be replaced after 10 – 15 years, depending on how hard and often the boat has sailed. If it is well maintained and the vessel has sailed conservatively, it will probably last more than 20 years. However, corrosion or cracked strands indicate that the rig or parts are due for replacement regardless of age.
If you plan on doing extended offshore sailing and don’t know the age of your rig, I recommend replacing it even if it looks fine. This can be done without removing the mast from the boat while it is still in the water.
How much does it cost to replace the standing rigging?
The cost of replacing the standing rigging will vary greatly depending on the size of your boat and the location you get the job done. For my 41 feet sloop, I did most of the installation myself and paid approximately $4700 for the entire rig replacement.
Can Dyneema be used for standing rigging?
Dyneema is a durable synthetic fiber that can be used for standing rigging. Its low weight, and high tensile strength makes it especially popular amongst racers. Many cruisers also carry Dyneema onboard as spare parts for failing rigging.
How long does dyneema standing rigging last?
Dyneema rigging can outlast wire rigging if it doesn’t chafe on anything sharp. There are reports of Dyneema rigging lasting as long as 15 years, but manufacturers like Colligo claim their PVC shrink-wrapped lines should last 8 to 10 years. You can read more here .
Final words
Congratulations! By now, you should have a much better understanding of standing rigging on a sailboat. We’ve covered its purpose and its importance for performance and safety. While many types of rigs and variations exist, the hardware and concepts are often similar. Now it’s time to put your newfound knowledge into practice and set sail!
Or, if you’re not ready just yet, I recommend heading over to my following guide to learn more about running rigging on a sailboat.
Sharing is caring!
Skipper, Electrician and ROV Pilot
Robin is the founder and owner of Sailing Ellidah and has been living on his sailboat since 2019. He is currently on a journey to sail around the world and is passionate about writing his story and helpful content to inspire others who share his interest in sailing.
Very well written. Common sense layout with just enough photos and sketches. I enjoyed reading this article.
Thank you for the kind words.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

Sailboat Running Rigging

You don't want to have faulty sailboat running rigging. Strong, durable lines are essential for controlling the sails on your boat without risking your own safety, or that of the sails. Our sailboat ropes and lines were designed to withstand any weather condition without fraying, tearing, or catching. When you are ready to trim and hoist your sails, you can rest assured that the sailboat rigging equipment that you purchase from us will provide the smoothest and fastest transitions. From tack to jibe, our sailboat halyards and mainsheets make it easy, durable and always the right choice.
Order our sailboat running rigging lines today for fast, free shipping on qualifying orders, and rig up your boat with the most trusted sailboat riggings around!
Lines by type of sailing
- Club/Racing
- Dinghy/One Design
- Kite & Surf
Lines by Application*
- Jib/Genoa Sheets
- Spinnaker Sheets
- * Sailboat lines selector by application.
Lines by Material
- Polyester Double Braid
- Dyneema Single Braid
- Dyneema Double Braid
- Vectran Core Double Braid
- Dyneema Core Double Braid
Lines by Brand
- Alpha Ropes
- FSE Robline
- G&B Ropes
- New England
- Yale Cordage
Our sailboat rigging include mainsail halyards, spinnaker halyards, and Genoa halyards that are made from a double braid polyester line, double braid Dyneema line or Vectran. Our mainsheets are also made from durable double braid polyester and hybrid fibers with blend of Dyneema and Technora. This material has the best reputation in the industry.
* Visit our quick sailboat lines selector by application.
- Yachting Monthly
- Digital edition

How to tension your yacht’s rig with wire or rod rigging
- August 28, 2024
Ivar Dedekam author of Illustrated Sail & Rig Tuning gives his guide on tensioning a yacht's wire or rod rigging

If you want to trim your rig correctly you should have some idea of the tension in the shrouds and stays, either by rules of thumb or a more exact method, such as this. Here, you measure the stretch of the wire as a percentage and then establish the tension as a percentage of the wire or rod’s breaking load.
You can either measure the stretch of all the wire or a part of it, e.g. 2m. Accuracy will improve with the sample length. Begin with a minimum tension in the wire.
Mark off a 2m length of the shroud on one side of the boat using the shroud terminal for reference. Measure the elastic extension (f) of the measured length as the rigging screws are alternately tightened, little by little. Stop when f = 3mm. (4mm on fractional rigs with aft swept spreaders).
Note that stretch of f = 1mm over a sample of 2m of the wire corresponds to 5% of breaking load independent of the wire diameter. For rod, an f = 1mm stretch over 2m corresponds to 7.5% of breaking load. Use a similar method to establish backstay tension. Remember that a different sample length will have a different stretch for the same load. Also remember that the stretch is always measured from hand tight wire/rod (minimum tension).

Mark up the shroud Mark up 2m of shroud using the terminal for reference…
Rod rigging is made of a straight, single strand. Wire rigging is made of many twisted strands. Normally rod rigging is 20% stronger than wire of the same diameter.
Wire has the advantage of an early warning of fatigue when a strand breaks. Fatigue in rod happens without any warning at all. It can be sudden and sometimes catastrophic.
Tensioning cap shrouds
When you have straightened the mast sideways and adjusted the rake, it is time to look at the cap shrouds. Tighten the cap shrouds to approximately 15% of breaking load. This corresponds to a stretch (f) of 3mm over a length of 200cm. On a fractional rig with aft swept spreaders the cap shrouds should be tensioned to 20% of the breaking load. This corresponds to a stretch of f = 4mm.

Measure the stretch…then measure the elastic extension when the rigging has been tightened.
To avoid excessive forestay sag upwind, the cap shrouds should be relatively highly tensioned. If 20% cap shroud tension is not sufficient to keep sag at an acceptable level, increase the tension to 25% of breaking load. Do not exceed this tension.
Slack rigging will produce shock loads that can cause rig failure and may even bring the mast down. Note that you will not be able to overtighten a wire of 40-50cm length with hand tools. The lower shrouds and intermediate shrouds should be quite loose at this stage.
If the mast has distinct bends you should try to straighten them by sight and hand tensioning.
Many yachtsmen intuitively tension their standing rigging and adjust it later when sailing has begun. This may lead to acceptable results but the methods described above, while taking some time, are more certain and reliable.
Enjoyed reading this?
A subscription to Yachting Monthly magazine costs around 40% less than the cover price, so you can save money compared to buying single issues .
Print and digital editions are available through Magazines Direct – where you can also find the latest deals .
YM is packed with information to help you get the most from your time on the water.
- Take your seamanship to the next level with tips, advice and skills from our experts
- Impartial in-depth reviews of the latest yachts and equipment
- Cruising guides to help you reach those dream destinations
Follow us on Facebook , Twitter and Instagram.

IMAGES
COMMENTS
The running rigging on a sailboat consists of all the lines used to hoist, lower, and control the sails and sailing equipment. These lines usually have different colors and patterns to easily identify their function and location on the vessel. Looking at the spaghetti of lines with different colors and patterns might get your head spinning.
Standing rigging keeps the mast in place, but it's the running rigging that handles all the action aboard a boat under sail. The many components in a modern running rigging system—sheets, outhauls, vang control, halyards—work in conjunction with wide range of blocks to keep friction to a minimum. Ralph Naranjo.
A beginners guide to sailboat rigging, including standing rigging and running rigging. This animated tutorial is the first in a series and covers sails, line...
Short answer running rigging for sailboats: Running rigging refers to the set of lines or ropes used to control the sails on a sailboat. It includes halyards, sheets, and control lines that regulate sail positioning, trim, and hoisting. These essential components are crucial for maneuverability and sail adjustment during sailing. Introduction to Running Rigging for
PLEASE NOTE: THIS VIDEO HAS BEEN UPDATED WITH ENHANCED GRAPHICS AND IMPROVED SOUND. CHECK IT OUT HERE https://youtu.be/tRgWtPaCQQcA beginners guide to sailbo...
Sailboat Rigging: Part 2 - Running Rigging. Sailboat rigging can be described as being either running rigging which is adjustable and controls the sails - or standing rigging, which fixed and is there to support the mast. And there's a huge amount of it on the average cruising boat... You'll need a whole lot more of it if you fly a spinnaker!
Running rigging is the rigging of a sailing vessel that is used for raising, lowering, shaping and controlling the sails on a sailing vessel—as opposed to the standing rigging, which supports the mast and bowsprit. Running rigging varies between vessels that are rigged fore and aft and those that are square-rigged.
Pro sailor Erik Shampain provides a guide and tips to match the right cordage for a specific running rigging applicaiton. ... pulling a 2-to-1 and then to the sail for a 24-to-1. Or, better yet ...
Running rigging, on the other hand, comprises the movable components needed to control, adjust, and handle the sails. These elements allow us to raise, lower, and trim the sails according to wind conditions and the boat's course. Understanding the distinction between the two types of rigging is vital in operating a sailboat safely and ...
Running rigging refers to the system of ropes, lines, and hardware used to control and adjust the sails on a sailboat. This is in contrast to standing rigging, which consists of the fixed lines and cables that support the mast and other structural components of the boat. Running rigging allows sailors to manipulate the shape and position of the ...
In part 3 of our series on sailboat parts, we dive into two types of rigging: standing rigging and running rigging. I use a 3D model and some diagrams to giv...
When it comes to running rigging, cruising sailors can learn a lot from racers, and in the process maximize their fun while getting the most out of their sails, hardware and lines. This rendering of a roughly 40-foot cruising boat shows a deck layout optimized for performance sailing, with plenty of lines that are well-led for trimming and ...
Short answer running rigging on a sailboat: Running rigging refers to the ropes and lines used for controlling the sails and other movable parts on a sailboat. It includes halyards, sheets, braces, and control lines. Properly rigged running rigging is essential for efficient sail handling and maneuvering of the boat. Understanding Running Rigging on a
A conventional all-Dacron 7/16-inch halyard may easily have 60 feet of its length in tension, and with normal sailing conditions, halyard stretch could be as much as 16.4 inches. Swap out the all-polyester halyard and replace it with a high modulus, 3/8-inch diameter rope such as Yales Maxibraid Plus and the stretch is reduced to 4.1 inches.
Take four lengths of Dyneema lashing and make a loop from each fixing point that ends in the centre of the boat (try to make all of the loops the same length). The mainsheet bottom block can be ...
Polyester double braid works great for frequently adjusted lines, like main and jib sheets, or moderately loaded control lines. It is very flexible and easy to handle, and is still the line of choice for most applications on cruisers and club racers. Specific Gravity is 1.38, so it does not float.
Rigging guides and helpful info for rigging and turning your sailboat from the experts at West Coast Sailing. Free Shipping Over $99 - 366 Day Returns - Expert Advice. Menu. Search. Close Search. Call Us +1-503-285-5536; Sign in & Register Compare ; Recently Viewed. Cart. More Back Apparel. Life Jackets; Tops; Bottoms ...
Redoing the running rigging on a cruising sailboat involves measuring, measuring and measuring. Then we head over to Bacon Sails and Marine Supplies for a tu...
The running rigging is the rigging on a sailboat that's used to operate the sails. For example, the halyard, which is used to lower and heave the mainsail. ... Running rigging consists of the lines, sheets, and hardware that are used to control, raise, lower, shape and manipulate the sails on a sailboat. Rigging varies for different rig types ...
Our running rigging calculator can instantly spec lines for more than 5,000 sailboats. Just select your boat below and you're a couple clicks away from new, top quality rigging. We've reduced the choices to a minimum to make ordering as simple as possible. (If you prefer more choices, please see our Running Rigging Builder.)
The difference between standing rigging and running rigging. Sometimes things can get confusing as some of our nautical terms are used for multiple items depending on the context. Let me clarify just briefly: The rig or rigging on a sailboat is a common term for two parts:. The standing rigging consists of wires supporting the mast on a sailboat and reinforcing the spars from the force of the ...
With the help of the rigging experts at West Marine, Cruising World shows us how to re-rig a sailboat with new running rigging to bring a pal's boat back int...
Our sailboat rigging include mainsail halyards, spinnaker halyards, and Genoa halyards that are made from a double braid polyester line, double braid Dyneema line or Vectran. Our mainsheets are also made from durable double braid polyester and hybrid fibers with blend of Dyneema and Technora. This material has the best reputation in the industry.
Rod rigging is made of a straight, single strand. Wire rigging is made of many twisted strands. Normally rod rigging is 20% stronger than wire of the same diameter. Wire has the advantage of an early warning of fatigue when a strand breaks. Fatigue in rod happens without any warning at all. It can be sudden and sometimes catastrophic.