Catamarans: A Complete Guide to Multihull Boats
Catamarans have been a part of sailing history for centuries and continue to be popular for their stability, spaciousness, and performance. Developed by various cultures around the world, the principles of catamaran design have evolved over time to become optimized for both pleasure cruising and racing. This complete guide will help you understand the essentials of catamarans, their unique characteristics, and how to choose the right one for your needs.
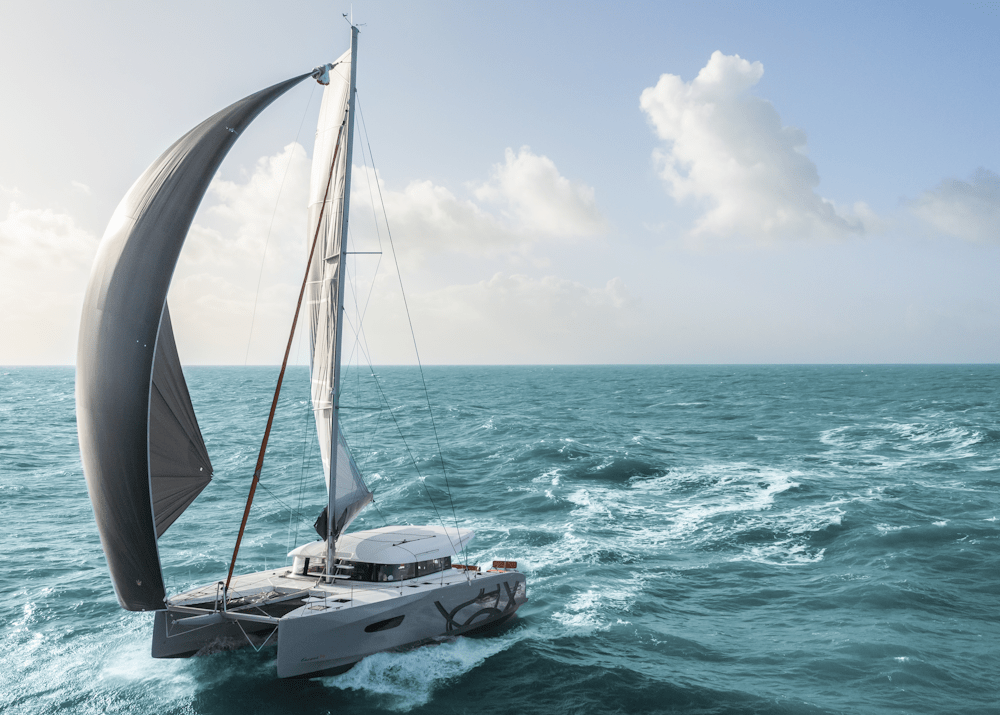

From the basic concepts of multihull design, performance, and handling, we will explore the advantages and benefits of a catamaran in terms of safety and comfort on board.
Along the way, we will discuss maintenance considerations, distinctive catamaran brands and models, and how a catamaran lifestyle can compare to more traditional sailing options .
Finally, we will provide learning resources and frequently asked questions tailored to both seasoned sailors and newcomers to the world of catamarans.

Key Takeaways
- Catamarans are known for their stability, spaciousness, and performance
- This guide covers aspects like design, handling, safety, and choosing the right catamaran
- Resources and frequently asked questions provide additional insights for potential catamaran owners
Understanding Catamarans
Design Characteristics
Catamarans are known for their unique design, which features two parallel hulls connected by a deck. This design provides several advantages over traditional monohull boats, such as stability and speed.
With their wide beam, catamarans have a reduced risk of capsizing and can access shallow waters due to their shallow drafts 1 .
One of the notable aspects of a catamaran is its twin hulls, which offer increased living space and comfort compared to a monohull. Additionally, catamarans are often favored by recreational and competitive sailors for their excellent maneuverability 2 .
The materials used for constructing catamarans range from wood to fiberglass, and even aluminum for high-performance vessels. Aluminum catamarans are known for their strength, lightweight structure, and resistance to corrosion 3 .
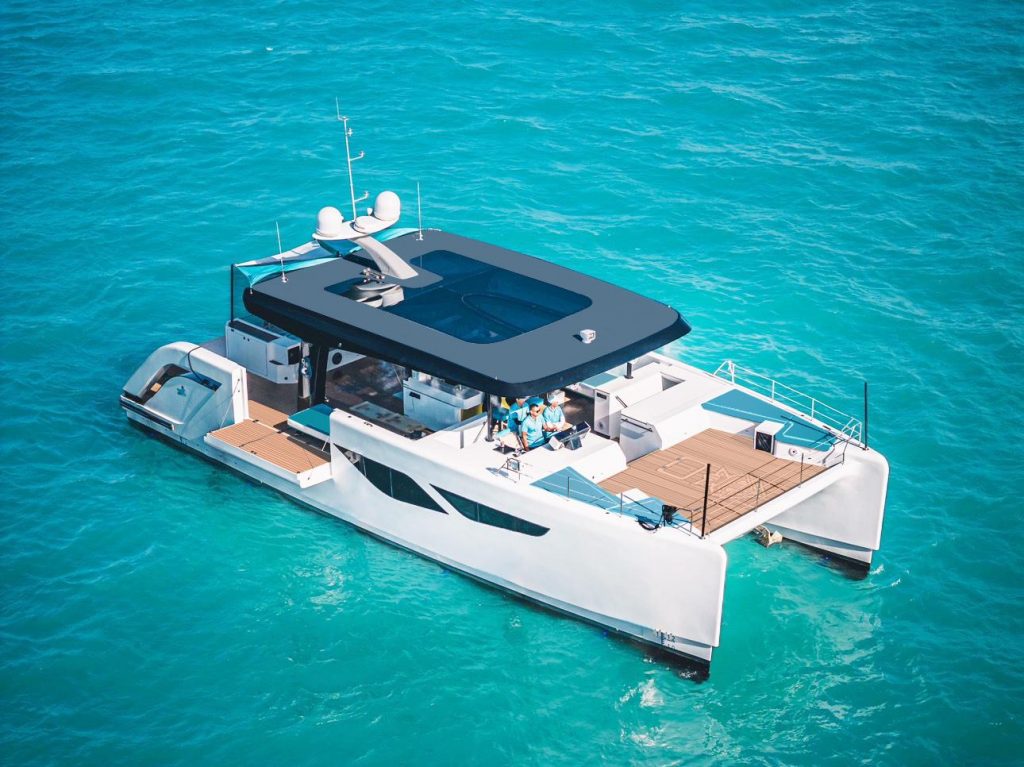

Hulls and Construction
The hulls in a catamaran are crucial to its stability and performance. These hulls help distribute the weight evenly across the water surface, minimizing drag and allowing for smoother sailing.
In general, the hulls can be categorized into two types:
- Symmetrical Hulls : The hull shape is similar on both sides, which enhances balance and stability in various sailing conditions.
- Asymmetrical Hulls : One side of the hull is designed differently than the other, which can be advantageous when sailing upwind.
The construction materials used in building catamaran hulls also play a vital role in the boat's performance and durability. Common materials include:
- Fiberglass : A popular choice due to its lightweight, strength, and ease of maintenance.
- Wood : Traditional material that offers a classic look, but requires more maintenance than fiberglass or aluminum.
- Aluminum : Lightweight and strong, aluminum is an excellent choice for high-performance catamarans 4 .

Multihulls vs Monohulls
There's often a debate between the benefits of multihull boats, such as catamarans or trimarans, and monohull boats. Here are some key differences between the two:
- Stability : Due to their wide beam and reduced heeling, catamarans offer improved stability compared to monohulls. This makes them an attractive option for those who want to avoid seasickness or feel more comfortable on the water 5 .
- Speed : Multihull boats are known for their speed, which results from their ability to minimize drag and maintain a level sail.
- Living Space : Catamarans and other multihulls generally have more living space, as both the hulls and the connecting deck can be utilized for accommodation and storage.
- Maneuverability : While monohulls are known for their agility and ability to point close to the wind, catamarans can still offer exceptional maneuverability when properly sailed 6 .
Performance and Handling
Speed and Efficiency
Power catamarans have gained popularity for offering a unique combination of speed, efficiency, and stability. Their dual-hull design allows for less water resistance, which directly translates to higher speeds and better fuel efficiency compared to traditional monohull boats.
In addition, the wide beam provided by the two hulls ensures a stable ride even at higher speeds. This makes power catamarans ideal for cruising, fishing, and watersports ( Boating Beast ).
Sailing Dynamics
When it comes to sailing catamarans , the performance is affected by factors such as keel, rudders, mast, and sails.
Their wide beam and dual-hull design provide inherent stability and reduced heeling effect, making them less likely to capsize compared to monohulls.
I should also note that catamarans have a shallow draft, which gives them the ability to access shallow waters that may be off-limits to other boats ( Navigating the Waters ).
In my experience, the lighter weight of a catamaran and its aerodynamic design can contribute to remarkable sailing performance under different wind conditions.
The larger sail area relative to hull weight allows them to harness more wind power, further enhancing their speed and agility on the water.
Maneuvering and Docking
Maneuvering and docking a power catamaran involves understanding its unique handling characteristics.
The presence of two engines in separate hulls allows for more precise control in confined spaces such as marinas.
The maneuverability of these boats is typically improved by the use of dual rudders that are located close to each powered hull for efficient steering ( BoatUS ).
When docking under power, I find it helpful to carefully assess the wind and current conditions beforehand.
This is because catamarans can be more sensitive to windage due to their larger surface area above the waterline.
By understanding how these forces may affect the boat, I can make adjustments to my approach and successfully dock the catamaran without any incidents.
Safety and Comfort on Board
Safety Features
Safety is a top priority when sailing any type of vessel, including catamarans. A well-built catamaran offers several features aimed at ensuring the safety of those onboard.
First, catamarans have inherent stability due to their wide beam and twin hull design . This makes them less prone to capsizing than monohull boats. This stability allows me to confidently navigate various water conditions .
In addition to stability, catamarans are designed with positive buoyancy, making them almost unsinkable . Of course, safety equipment such as lifejackets, flares, and first aid kits should always be onboard and well-maintained.
Furthermore, you should also stay updated on weather conditions, avoid sailing in high-risk areas, and learn your boat's safe sail limits.
Living Spaces and Comfort
When it comes to living spaces, I value comfort and practicality as essential features for my time on the water. Catamarans offer a unique advantage in this regard, as their dual hulls create spacious living areas.
Most catamarans are designed with separate cabins in each hull, allowing for privacy and comfort when sleeping. Additionally, these boats typically feature shallow drafts , which means I can access shallow waters and anchor close to shore.
The main living area, or salon, is situated on the bridge deck between the hulls. It usually includes a seating area, a dining table, and a galley (kitchen). Large windows provide ample natural light and panoramic views, making the space feel open and bright. Some catamarans even have the option for an additional living area on the upper deck where you can enjoy the sun and breeze.
One aspect of catamaran living I truly appreciate is the ample storage available. Each cabin typically has built-in storage spaces for clothes, gear, and personal items. There are also designated areas for equipment such as spare sails, tools, and water toys. This makes it easy for me to keep my belongings organized and make the most of my time on the water.
Maintaining a Catamaran
Routine Maintenance
In order to keep my catamaran in the best possible shape, I make sure to perform routine maintenance tasks. These tasks are essential to extend the life of the components and ensure smooth sailing:
- Cleaning : Regularly cleaning the deck, hulls, and sails prevents buildup of dirt, algae, and other debris that could affect performance.
- Inspection : Periodically inspecting my catamaran allows me to detect any potential issues before they become significant problems. I pay close attention to the rigging, sails, and lines on my boat.
- Lubrication : Keeping all moving parts lubricated is vital to prevent friction and wear on components such as winches and pulleys.
- Antifouling : Applying antifouling paint to the hulls of my catamaran helps prevent the growth of marine organisms that can damage the boat and reduce its speed. Make sure to do this at least once a year.
Dealing with Wear and Tear
Despite my best efforts to keep my catamaran well-maintained, wear and tear is inevitable. Here's how I deal with common issues that could arise from regular use:
- Repairs : When I notice signs of wear on sails, lines, or rigging components, I make it a priority to repair or replace them promptly. Neglecting these issues can lead to more significant problems and affect the boat's performance.
- Hull maintenance : If I find dents, scratches, or stiff rudders on my catamaran's hulls, I address them immediately. Repairing any damage not only ensures smooth sailing but also prevents further issues from developing.
- Sail care : Over time, my sails can become stretched, torn, or damaged due to exposure to sun, wind, and saltwater. Regularly inspecting them for signs of wear and making any necessary repairs or replacements helps maintain optimal performance.
- Rust and corrosion prevention : Since my catamaran is made of various metal components, I need to protect them from rust and corrosion. I routinely check for signs of corrosion and apply anti-corrosive treatments when needed.
Catamaran Brands and Models
High-Performance Models
In recent years, there has been a growing interest in high-performance catamarans. I have seen a variety of brands and models that have impressed me with their performance capabilities. One notable brand is Fountaine Pajot , which has a long history of producing a range of sailing catamarans and power catamarans. Some of their popular models include the Tanna 47 and the Bali 4.4 .
Another high-performance catamaran I've come across is the Leopard 40 . Known for their speed and exceptional handling in various conditions, the Leopard brand started with sailing catamarans and has since expanded to include power catamarans. Their models range from 40 to 53 feet long, offering both power and luxury for those looking for a thrilling experience on the water.
Cruising Catamarans
When it comes to cruising catamarans, the Lagoon brand is synonymous with luxury and comfort. With a range of sailing catamarans from 40 to 70 feet long, Lagoon offers spacious catamarans for extended bluewater cruising. Their 60- and 70-foot power catamarans are equally impressive, providing ample living space and smooth sailing experiences.
I've also found the Aquila 42 PC to be a remarkable cruising catamaran. With a focus on design and innovation, Aquila has produced catamarans perfect for exploring the open sea with friends and family. Their spacious, stable designs allow for a more enjoyable and serene journey, ensuring you arrive at your destination comfortably.
The Catamaran Lifestyle
Anchoring and Cruising
I find catamarans to be a fantastic choice for cruising and anchoring , which is a critical part of living the catamaran lifestyle . Catamarans have several advantages when it comes to anchoring and cruising, such as:
- Stability : Due to their wide beam and twin hulls, catamarans remain stable during anchoring, which reduces the risk of seasickness.
- Shallow draft : Thanks to their shallow draft , catamarans can anchor close to shore, enabling better access to protected coves and more beautiful beaches.
- Speed : Despite their large size for cruising vessels , catamarans are generally faster than monohulls. This is a result of their slim hulls and reduced water resistance.
When it comes to anchoring, catamarans can make use of their shallow draft to anchor in locations that other boats cannot. This allows for a greater range of cruising spots, which makes the overall experience much more enjoyable and unique.
Living on a Catamaran Full-time
For many catamaran enthusiasts, the dream of living full-time on a catamaran is entirely possible. While not without challenges, there are several factors that make living aboard a catamaran an enjoyable experience:
- Spacious living areas : Catamarans generally have more living area compared to monohulls, providing ample space for the whole crew.
- Privacy : The separate hulls allow for private cabins, ensuring that everyone on board has their space.
- Stability : As mentioned earlier, catamarans are stable vessels, making living on them more comfortable than monohulls.
Choosing Your Catamaran
Comparing Models and Features
When I start to look for the perfect catamaran, the first thing I focus on is comparing various models and features .
I determine the key factors that are essential for my needs, such as size, passenger comfort, and performance. By doing so, I can identify which catamaran models are most suitable for me.
For example, if I plan to sail with a large group, I would look for a catamaran that offers ample space both inside and out.
To help me with my comparisons, I usually create a table or list of the different models and their features:
| Model | Size | Comfort | Performance |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | 40ft | Spacious | High |
| B | 35ft | Average | Average |
| C | 45ft | Luxury | High |
This visual aid makes it easier for me to sort the options and prioritize my considerations, such as price, yacht type, and brand.
New vs. Second-Hand
Another critical aspect of choosing a catamaran is deciding between a new or second-hand boat.
Both options have their pros and cons, and ultimately it depends on my preferences and budget.
If I can afford a new catamaran, I get the advantage of the latest design , features, and technology. Plus, I typically receive better warranty coverage and support from the manufacturer.
However, new catamarans are more expensive and can have long wait times due to high demand.
On the other hand, purchasing a second-hand catamaran can save me a significant amount of money, and I might find a high-quality boat with low mileage or well-maintained by the previous owner.
However, this option carries more risks, as I need to be knowledgeable about potential maintenance issues and conduct a thorough inspection before purchase.
Learning Resources
Books and Manuals
When it comes to learning about catamarans, there are plenty of books and manuals available.
One of the highly recommended books is Multihull Voyaging by Thomas Firth Jones. This book provides a comprehensive understanding of multihulls, including catamarans, and is an essential guide for any beginner sailor.
Another great book to check out is Catamarans: The Complete Guide for Cruising Sailors by Gregor Tarjan.
With a foreword by Charles K. Chiodi, publisher of Multihulls Magazine, this book covers all aspects of cruising catamarans. It includes detailed information on design, construction, and maintenance, as well as tips and tricks for sailing a catamaran.
Here are a few more books that I find valuable:
- The Catamaran Book by Tim Bartlett, an excellent resource for both beginners and experienced sailors
- Catamaran Sailing: From Start to Finish by Phil Berman and Lenny Rudow, a comprehensive guide to both catamaran racing and cruising
Online Content and Photography
In addition to books, you can find plenty of online content and photography about catamarans.
Websites like Sailaway Blog and Boating Guide offer tips, techniques, and how-to articles for sailing catamarans.
Many of these sites also include stunning photography, showcasing these beautiful vessels in action.
For those who prefer Kindle or e-books, many of these resources are available in digital format.
This makes it easier for you to access them anytime, anywhere, allowing you to keep learning and improving your catamaran sailing skills.
To further enhance your knowledge, you can also join online forums and communities dedicated to catamarans.
These platforms provide invaluable advice and first-hand experiences shared by fellow sailors, as well as recommendations for additional learning resources.
Frequently Asked Questions
What factors should be considered when choosing a catamaran for full-time living?
When choosing a catamaran for full-time living, consider its space and layout , as it will become your home.
Look for a design with a comfortable living area , ample storage, and sufficient berths for the number of people living aboard.
Also, consider fuel efficiency , ease of maintenance, and the catamaran's cruising range .
Lastly, the overall cost of ownership , including insurance and mooring fees, should be considered.
How do catamarans perform in rough sea conditions?
In general, catamarans are known for their stability, which is primarily due to their wide beams. This makes them less prone to capsizing when compared to monohulls.
However, their performance in rough sea conditions will depend on the specific model and design of the catamaran. Some may perform better in certain conditions than others, so researching and selecting the right design is essential.
What are the key differences between sailing a catamaran and a monohull?
One of the main differences between catamarans and monohulls is stability.
Catamarans have a wider beam , which makes them more stable and minimizes the risk of capsizing.
They also have shallower drafts, which allow them to access more shallow waters compared to monohulls.
Additionally, catamarans often have larger living spaces, making them more comfortable and suitable for cruising and full-time living.
What are the advantages of catamarans for long-distance cruising?
Catamarans offer several advantages for long-distance cruising.
Their wide, stable design provides a comfortable ride and reduces the risk of seasickness.
They can also attain higher speeds due to their reduced drag and generally sail faster than monohulls on certain points of sail.
The shallow draft allows them to explore more coastal areas and anchor closer to shore. Lastly, their spacious interiors make them ideal for extended cruises and living aboard.
How does one assess the value of a used catamaran on the market?
Assessing the value of a used catamaran requires thorough research and inspection.
Start by comparing the age, model, and condition of the catamaran to similar listings on the market.
Take note of any upgrades or additions made to the boat, as these can affect the price.
It's essential to inspect the boat in person or hire a professional surveyor to ensure there are no hidden issues that could affect its value.
What essential features should be looked for in a catamaran intended for ocean voyages?
For ocean voyages, look for a catamaran with a strong, well-built hull designed to handle rough conditions.
Safety features such as liferafts, adequate flotation, and sturdy deck hardware are crucial.
A reliable engine and well-maintained rigging and sails are also essential.
In terms of living space, opt for a catamaran with a comfortable, spacious interior and ample storage.
Last but not least, good navigation and communication systems are necessary for long-distance ocean voyages.
Related Articles

Boating License Ontario: Everything You Need to Know
Marine Engineering: Essential Concepts for Aspiring Professionals

SNUBA Diving for Fun: A Thrilling Underwater Adventure

What Should You Do After Your Boat Runs Aground and You Determine There Are No Leaks? Steps for Safe Recovery

Top 10 Boats Made by Lowe: Expert Reviews and Ratings

Bass Boat Brands 2024: Top Picks for Anglers This Year

Dock Box Essentials: Maximize Storage and Organization at the Marina
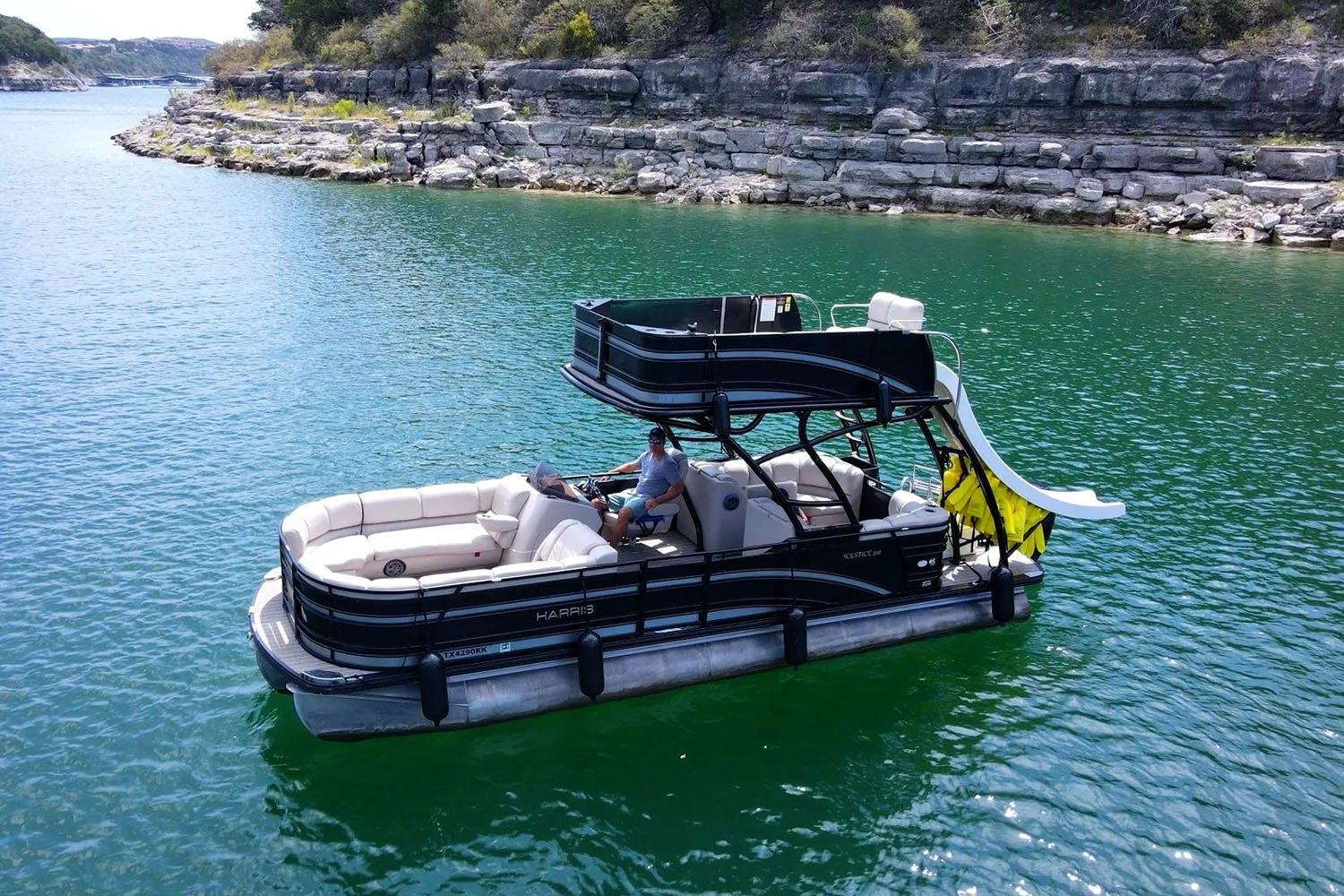

Top 10 Pontoons for Sale Houston Texas: Expert Picks for 2024

What Are Catamarans And Their History?
Catamarans are boats with two connected hulls that are joined by a bridge. Because they are faster, more stable, and capable of carrying larger cargo than their monohull counterparts, catamarans are growing in popularity.
As a result, designers and owners have greater freedom to accommodate space needs in terms of size and usefulness than they would with single-hulled vessels.
The name catamaran came from the Tamil word “kattumaram” which basically meant “logs which were bound together”. These traditional watercraft were basically used on the south coast of India and Srilanka. They were dated back to as early as the 5th century when they were used to transport troops from one island to another.
Let us get into more details to learn more about the different types of catamarans and their functions.

What are the different types of catamarans?
Catamarans are mainly divided into two categories: sailing and power catamarans, however, both categories can be split into smaller groups by their size and use.
Sailing catamarans
These types of catamarans are mainly propelled with help of sails. The sails act as wings with which the vessel moves forward with the help of wind energy. The sailing catamarans have advanced significantly in recent years in terms of both design and performance attributes. Sailing catamarans are further subdivided based on their dimensions and functions and are classified into,
Small, mini, or sports catamarans
Depending on the size, these are also known as leisure catamarans and can carry a load of 6 persons on average. You’ve definitely seen some of them speeding through your local beach waters on hot, sunny weekends; some of them are made to be driven by one person. Those designed for use in sports have a trapeze that enables one to hike out and serve as a counterweight.
Small-day sailing cats are well-liked because they offer a secure and straightforward learning environment, and you can see fleets of them in resorts where guests with little to no sailing experience utilize them. These little cats are often made of roto-molded plastic or fiberglass, and as they frequently lack auxiliary motors, sails are their only means of propulsion
A trampoline that spans the two hulls of the sports catamarans acts as a bridge so that individuals can move from one to the other without falling into the water. They may be launched and landed from a beach as opposed to a dock because of their modest size. They have a rotating mast and a mainsail with full-length battens.
Cruising Catamarans
In the worlds of long-distance cruising and bareboat chartering, larger cruising cats have dominated. These are more stable than their monohull competitors, allowing them to securely transport people across continents. These are more stable than their monohull competitors, allowing them to securely transport people across continents.
For maneuverability, charter cats frequently have two engines—one in each hull—as well as a mast that holds a mainsail and at least one headsail.
Nowadays, cruising catamarans are more widely available than monohulls at bareboat charter firms with tropical bases, and those numbers are rising in places like the Mediterranean.
Power catamarans
Power catamarans, often known as “multi-hull powerboats” or “power cats,” are vessels without masts or sails but with larger and more powerful engines. They can be the most perfect choice for your first boat if you enjoy offshore fishing or other water sports. You get a great balance of performance, stability, and maneuverability with these powerboats. Power cats come in a range of different sizes and shapes. In terms of dimensions and functions, they are also divided into,
Center console fishing catamarans
The fishing industry is flooded with smaller power cat brands, while bareboat charter and cruise platforms are seeing the emergence of larger ones. The multi-hull performance boat frequently has a center console driver layout. They can reach higher top speeds thanks to their higher horsepower, but these cats also need to be strengthened hulls to support the weight and power of these engines.
When used for fishing, normally lesser than 50 ft, there are several options available for live wells, rod holders, gear storage, and built-in coolers for both fish and beverages. Depending on the length and design elements of the boat, certain consoles may locate closer to the bow or aft of the vessel.
Offshore powerboat racing catamarans
Offshore powerboat racing is the aquatic equivalent of off-road auto racing. Since its inception in the late 1960s, offshore racing has changed drastically.
Though V-bottom powerboat classes still exist, twin-engine catamarans with top speeds of 170 MPH in the most powerful classes dominate the sport.
The offshore race course may be the most dynamic setting in all of the motorsports because of the constant fluctuations in a swell, wind, tide, current, and other factors. The track might abruptly change from being friendly to antagonistic.
These boats are designed and built such that they are both lightweight but extremely strong using the most advanced materials like carbon fiber and Kevlar . Manufacturing methods such as infusion are adopted to make sure the properties of the materials are not lost during the production stages.
Motor yachts and ferries
For their roominess and speed, catamaran designs have also become popular among motor yachts and commercial passenger ferries. These cruise-centric yachts offer homelike livability for avid travelers, are fuel efficient, and are fairly intuitive to run.
Motor yacht catamarans have been designed with larger living spaces in mind, as well as more outdoor recreation places. The huge fly bridges provide additional space for relaxing and socializing, and electric boat davits make lifting the dinghy simple. Daily tasks like cooking can be done with ease because catamarans don’t heel.
Why Is There A Shift In Trend From Monohulls To Catamarans?
Recently, more and more often you can find catamarans in the harbors of large cities and small resorts. It can be unequivocally argued that catamarans are gaining popularity among both beginners and experienced sailors and even celebrities. But what makes them gain this popularity?
Catamarans In Terms Of Function And Utility
The enormous interior space expansion can provide the owners considerably more freedom to select furnishings without regard to size limits and more room for additional appliances like washers and dryers, which can make life on board much easier.
Due to their broader decks and roomier interiors, catamarans are frequently employed as party boats. The deck can accommodate more people without giving them the impression of being crammed into a small space.
In terms of storage, catamarans offer more alternatives than monohulls because both hulls can serve a variety of purposes, increasing the vessel’s overall capacity as well.
Catamarans are typically utilized as party boats since they have bigger deck spaces and greater room for movement. The deck can also accommodate more people without giving them the impression of being confined in a small space.
If any equipment breaks down, there is always a backup. For instance, if one of the engines on the port hull fails, we can always use the starboard engine to re-enter landfall. Likewise, if a generator breaks down, there is always a second generator that can be utilized as a backup.
Catamarans In Terms Of Performance And Stability
Due to the narrow hulls of catamarans, which serve to reduce drag forces, they frequently outperform monohulls. On performance power catamarans, the area in between the two hulls known as the “Tunnel” is built in a similar way to an aerofoil so that it behaves like a wing, boosting the aerodynamic lift forces and enhancing the overall effectiveness and top-end speeds of the craft.
Due to their stronger lift forces and lower water friction than monohulls, catamarans typically have a better fuel economy. This is because the strain placed on the engines as a whole is reduced, resulting in less fuel being used.
In terms of roll stability, catamarans are often more stable than monohulls. This offers them an advantage in terms of comfort and the ability to carry out various activities onboard the vessel with ease, as well as lowering the possibility of passengers falling on board. Because they are less likely to make passengers seasick, catamarans are typically used as ferries or passenger ships.
Catamarans provide a more comfortable ride whether they are in shallow water, deep water, or at anchor; they have a decreased chance of keeling over or capsizing in heavy winds.
Also, catamarans have a much lower draft when compared to their mono hull counterpart’s allowing them to easily ply over shallower waters.
What Are The Potential Drawbacks Of Catamarans?
Catamarans have a few minor limitations, much like any other kind of boat:
Finding dock space is frequently challenging and expensive for catamarans because they take up more room.
Power and sailing cats can both smash into the bridge deck when heading to the weather because of the way that they are built.
Additionally, because they have two hulls instead of one, sailing cats can’t necessarily aim as high into the wind as monohulls can.
Overall, a catamaran allows for greater speeds, but at the expense of much-reduced vessel control. Knowing when to accelerate and when to slow down is difficult when sailing a catamaran. A catamaran can be readily overturned in sea conditions that a monohull can maneuver securely in.
Finally, while it may be alluring to add more weight in a catamaran due to the space it provides, doing so will almost certainly degrade the performance of either power or sailing cat—something that is less of an issue on their monohull counterparts.
Catamarans are a growing trend due to their better advantages over their monohull counterparts. Despite having an ancient fundamental design, catamarans are a modern boating alternative that can be used by any boater for both commercial and leisure uses.
- Recent Posts
- Responsibilities of a Fourth Engineer on Cargo Ships – September 10, 2024
- The Role of Cargo Ships in Global Trade – August 22, 2024
- Report: Yang Ming’s YM Mobility Explosion at Ningbo-Zhoushan Port – August 9, 2024
About the author
I worked as an officer in the deck department on various types of vessels, including oil and chemical tankers, LPG carriers, and even reefer and TSHD in the early years. Currently employed as Marine Surveyor carrying cargo, draft, bunker, and warranty survey.
Latest posts

Is Maritime Security Necessary on Modern Ships?
It’s vital for ships to stay vigilant. Isolation from land means having no backup or protection for miles, making them vulnerable to attacks and other threats. Equip modern ships using modern maritime security methods.

Responsibilities of a Fourth Engineer on Cargo Ships
A Fourth Engineer on cargo ships oversees engine room operations, machinery maintenance, and ensures compliance with regulations like MARPOL.

The Quality Control Process in Marine Manufacturing
Companies in the marine manufacturing space must have tight and effective quality control processes. What steps should an effective quality control process include?

A catamaran (from Tamil kattumaram ) [1] is a type of multihulled boat or ship consisting of two hulls, or Vakas , joined by a frame, formed of Akas. Catamarans can be sail- or engine-powered. The catamaran was first discovered being used by the paravas, a fishing community in the southern coast of Tamil Nadu, India . Catamarans were used by the ancient Tamil Chola dynasty as early as the fifth century C.E. to move their fleets to invade such Southeast Asian regions as Burma , Indonesia , and Malaysia .
Catamarans are a relatively recent introduction to the design of boats for both leisure and sport sailing, although they have been used for millennia in Oceania , where Polynesian catamarans and outrigger canoes allowed seafaring Polynesians to settle the world's most far-flung islands .
- 1 Multihull component terms
- 3.1 Pontoon Boat or Hydroairy Ship
- 4.1 Sailing Beach Catamarans
- 4.2 Catamarans for passenger transport
- 4.3 Powered catamarans
- 4.4 Cruising Sail Cats
- 4.5 Mega catamarans
- 7 References
- 8 External links
In recreational sailing, catamarans and multihulls, in general, have been met by a degree of skepticism from Western sailors accustomed to more "traditional" monohull designs. [2] The main source of that skepticism was that multihulls were based on concepts that were completely alien and strange to them, with balance based on geometry rather than weight distribution. The second source of that skepticism is that catamarans work better than traditional designs, and with less weight, therefore ridiculing the traditional concepts. In the realm of fast ferries, where their powering characteristics and spacious arrangements are of value, the catamaran has become arguably the hull form of first choice.
Multihull component terms
There are three terms that describe the components of modern multihulls (catamarans and trimarans): vaka , aka , and ama . [3] The term vaka , like the related terms aka and ama , come from the Malay and Micronesian language group terms for parts of the outrigger canoe, and vaka can be roughly translated as canoe or main hull. [4]
- Aka [4] - The aka of a multihull sailboat is a member of the framework that connects the hull to the ama(s) (outrigger). The term aka originated with the proa, but is also applied to modern trimarans.
- Ama [4] - The term ama comes from the proa. The vaka is the main hull, the ama is the outrigger, and the aka [4] or iako (Hawaiian) is the support connecting the two (not three) hulls. The term ama and aka have been widely applied to modern trimarans.
- Vaka [4] - A proa consists of a vaka, the main canoe-like hull; an ama, the outrigger; and akas, the poles connecting the ama to the vaka.
Semantically, the catamaran is a pair of Vaka held together by Aka , whereas the trimaran is a central Vaka , with Ama on each side, attached by Aka .

The English adventurer and buccaneer William Dampier , traveling around the world in the 1690s in search of business opportunities, once found himself on the southeastern coast of India, in Tamil Nadu. He was the first to write in English about a kind of vessel he observed there. It was little more than a raft made of logs.
”On the coast of Coromandel," he wrote in 1697, "they call them Catamarans. These are but one Log, or two, sometimes of a sort of light Wood ... so small, that they carry but one Man, whose legs and breech are always in the Water.”
While the name came from Tamil, the modern catamaran came from the South Pacific . English visitors applied the Tamil name catamaran to the swift, stable sail and paddle boats made out of two widely separated logs and used by Polynesian natives to get from one island to another.
The design remained relatively unknown in the West for almost another 200 years, until an American, Nathanael Herreshoff, began to build catamaran boats of his own design in 1877 (US Pat. No. 189,459), namely 'Amaryllis', which immediately showed her superior performance capabilities, at her maiden regatta (The Centennial Regatta held on June 22, 1876, off the New York Yacht Club's Staten Island station [2] ). It was this same event, after being protested by the losers, where Catamarans, as a design, were barred from all the regular classes [2] and they remained barred until the 1970s.
This ban relegated the catamaran to being a mere novelty boat design until 1947. [5] In 1947, surfing legend, Woodbridge "Woody" Brown and Alfred Kumalae designed and built the first modern ocean-going catamaran, Manu Kai, in Hawaii . Their young assistant was Rudy Choy, who later founded the design firm Choy/Seaman/Kumalae (C/S/K, 1957) and became a fountainhead for the catamaran movement. The Prout Brothers, Roland and Francis, experimented with catamarans in 1949 and converted their 1935 boat factory in Canvey Island, Essex (England) to catamaran production in 1954. Their Shearwater catamarans won races easily against the single hulled yachts.
The speed and stability of these catamarans soon made them a popular pleasure craft, with their popularity really taking off in Europe, and was followed soon thereafter in America. Currently, most individually owned catamarans are built in France , South Africa , and Australia .
In the mid-twentieth century, the catamaran inspired an even more popular sailboat, the Beach Cat . In California, a maker of surfboards, Hobie Alter produced (in 1967) the 250-pound Hobie Cat 14, and two years later the larger and even more successful Hobie 16. That boat remains in production, with more than 100,000 made in the past three decades.
The Tornado catamaran is an Olympic class sailing catamaran, with a crew of two. It has been in the Olympic Games since 1976. It was designed in 1967 by Rodney March of Brightlingsea, England, with help from Terry Pierce, and Reg White, specifically for the purpose of becoming the Olympic catamaran. At the IYRU Olympic Catamaran Trials, it easily defeated the other challengers.
The normal catamaran multihull, powered or not, consists of two Amas separated by two Akas, which may suspend a platform or trampoline between them. They can be of various sizes and recently, they have become very large.
Pontoon Boat or Hydroairy Ship

The hydroairy ship appears to be nothing more than an upgraded and enlarged pontoon boat with a formed and shaped underplatform. The general architecture is identical, consisting of two flotation chambers, for the Amas, joined by a load carrying platform, which carries the superstructure.
In 1952, Minnesota farmer Ambrose Weeres had an idea that if you put a wooden deck on top of two columns of steel barrels welded together end to end, you would have a sturdy deck that would be more stable on a lake than a conventional boat. [6] Weeres was walking the same idea paths as the early Polynesians, while proving that the ideas behind the multihull are not all that counterintuitive.
These sorts of boats are cheap and easy to make, require no ballast, and thus have good performance. Although, this design is almost exclusively restricted to power boats. It is still, essentially, a catamaran. No displacement is lost towards ballast, therefore yielding huge operational efficiencies.

The Small Waterplane Area Twin Hull (SWATH) is a hull form used for vessels that require a ship of a certain size to handle in rough seas as well as a much larger vessel. An added benefit is a high proportion of deck area for their displacement—in other words, large without being heavy. The SWATH form was invented by Canadian Frederick G. Creed, who presented his idea in 1938 and was later awarded a British patent for it in 1946. It was first used in the 1960s and 1970s as an evolution of catamaran design for use as oceanographic research vessels or submarine rescue ships.

Catamarans provide large, broad decks, but have much higher water resistance than monohulls of comparable size. To reduce some of that resistance (the part that generates waves), as much displacement volume as possible is moved to the lower hull and the waterline cross-section is narrowed sharply, creating the distinctive pair of bulbous hulls below the waterline and the narrow struts supporting the upper hull. This design means that the ship's flotation runs mostly under the waves, like a submarine (the smooth ride of a sub was the inspiration for the design). The result is that a fairly small ship can run very steady in rough seas. A 50-meter ship can operate at near full power in nearly any direction in waves as high as 12 meters
The S.W.A.T.H. theory was further developed by Dr Thomas G. Lang, inventor of improvements to the semi-submerged ship (S3) in about 1968. Basically, a SWATH vessel consists of two parallel torpedo like hulls attached to which are two or more streamlined struts which pierce the water surface and support an above water platform. The US Navy commissioned the construction of a SWATH ship called the 'Kaimalino' to prove the theory as part of their ship research program. The Kaimalino has been operating successfully in the rough seas off the Hawaiian islands since 1975.
Usage and Application
Sailing beach catamarans.

Although the principles of sailing are the same for both catamarans and monohulls, there are some "peculiarities” to sailing catamarans. For example:
- Catamarans can be harder to tack if they don't have dagger boards or centre boards. All sailboats must resist lateral movement in order to sail in directions other than downwind and they do this by either the hull itself or else dagger boards or centre boards. Also, because catamarans are lighter in proportion to their sail size, they have less momentum to carry them through the turn when they are head to wind. Correct use of the jib sail (back-filling the jib to pull the bow around) is often essential in successfully completing a tack without ending up stuck in irons (pointing dead into the wind and sailing backwards, see: No-Go Zone).
- They have a higher speed than other sailboats of the same size. This is because they can have a much larger sail area due to the larger righting moment. They can reach over 1.5 times the speed of the wind.
- Catamarans are less likely to capsize in the classic 'beam-wise' manner but often have a tendency to pitchpole instead—where the leeward (downwind) bow sinks into the water and the boat 'trips' over forward, leading to a capsize.
Teaching for new sailors is usually carried out in monohulls as they are thought easier to learn to sail, a mixture of all the differences mentioned probably contributes to this.
Catamarans, and multihulls in general, are normally faster than single-hull boats for three reasons:
- catamarans are lighter due to the fact there is no keel counterweight;
- catamarans have a wider beam (the distance from one side of the boat to the other), which makes them more stable and therefore able to carry more sail area per unit of length than an equivalent monohull; and
- the greater stability means that the sail is more likely to stay upright in a gust, drawing more power than a monohull's sail which is more likely to heel (lean) over.
A catamaran is most likely to achieve its maximum speed when its forward motion is not unduly disturbed by wave action. This is achieved in waters where the wavelength of the waves is somewhat greater than the waterline length of the hulls, or it is achieved by the design piercing the waves. In either case pitching (rocking horse-like motion) is reduced. This has led to it being said that catamarans are especially favorable in coastal waters, where the often sheltered waters permit the boat to reach and maintain its maximum speed.
Catamarans make good cruising and long distance boats: The Race (around the world, in 2001) was won by the giant catamaran Club Med skippered by Grant Dalton. It went round the earth in 62 days at an average speed of eighteen knots.
Catamarans for passenger transport

An increasing trend is the deployment of a catamaran as a high speed ferry. The use of catamaran for high speed passenger transport was pioneered by Westermoen Hydrofoil in Mandal, Norway , who launched the Westamaran design in 1973. The Westamarans, and later design, some of them consisting of a catamaran hull resting on an air cushion between the hulls, became dominant for all high speed connections along the Norwegian coast. They could achieve speeds comparable to the hydrofoils that it replaced, and was much more tolerant to foul water and wave conditions.
Powered catamarans
A recent development in catamaran design has been the introduction of the power catamaran. The 'power' version incorporates the best features of a motor yacht and combines it with the characteristics of a multihull.
Usually, the power catamaran is devoid of any sailing apparatus as demonstrated by one of the top-selling models in the United States, the Lagoon Power 43. This vessel has now been introduced to a number of charter fleets in the Caribbean and the Mediterranean and is becoming an increasingly common sight.
Smaller powered catamarans are becoming quite common in the United States with several manufacturers producing quality boats. A small "cat" will almost certainly have two engines while a similar sized mono-hull would only one engine. All mid-size and larger cats will have two engines.

Cruising Sail Cats
Below a minimum size, about eight meters (24 ft.), the catamaran's hulls do not have enough volume to allow them to be used as living space. At the same time, the bridgedeck area isn't sufficiently sized to make effective live-aboard space either. This limits their use to beachcats and day sailors. However, once one gets above that, both the bridgedeck area and the hulls gain sufficient size for use as compartments and navigation decks. These are the cruising catamarans that are being seen more often at yacht clubs that host circumnavigators.
While more popular in the EU, they are gaining popularity in the US as well due to their superior comfort, stability, safety, and speed, over monohulls. These boats can maintain a comfortable 300 nmpd (nautical miles per day) passage, with the racing versions recording well over 400 nmpd, and they do this while being unsinkable. This is extremely desirable, for circumnavigating the world. In addition, they don't heel more than 10-12 degrees, even at full speed on a reach.
Even without the actual need to circumnavigate, these catamaran megayachts allow a level of comfort and life-style not possible on a monohull sailboat and only previously possible on large power cruisers. This is their attraction.
Due to the perceived need to retain single-handed sail handling, 45 m is expected to remain the upper limit for this class of yacht.
Mega catamarans

One of the biggest developments over the last decade in the yachting arena has been the rise of the super catamaran: a multihull over 100 feet in length, in semi-custom and custom designs.
Various international manufacturers are leading the way in this area including Blubay, Yapluka, Sunreef, Lagoon and Privilege. A catamaran 150 feet in length is under construction at Derektor shipyards in Bridgeport, Connecticut .

The emergence of the super or mega catamaran is a relatively new event which is akin to the rise of the mega or super yacht which was used to describe the huge growth in luxury, large motor yachts in the French Riviera and Floridian Coast.
One of the reasons for increased mega catamaran construction was The Race , a circumnavigation challenge that departed from Barcelona, Spain , on New Year's Eve, 2000. Due to the prize money and prestige associated with this event, four new catamarans (and two highly modified ones) over 100 feet in length were built to compete. The largest, "PlayStation", owned by Steve Fossett, was 125 feet long and had a mast which was 147 feet above the water. Virtually all of the new mega cats were built of pre-preg carbon fiber for strength and the lowest possible weight. Top speeds of these boats can approach 50 knots.
References ISBN links support NWE through referral fees
External linksAll links retrieved November 30, 2023.
New World Encyclopedia writers and editors rewrote and completed the Wikipedia article in accordance with New World Encyclopedia standards . This article abides by terms of the Creative Commons CC-by-sa 3.0 License (CC-by-sa), which may be used and disseminated with proper attribution. Credit is due under the terms of this license that can reference both the New World Encyclopedia contributors and the selfless volunteer contributors of the Wikimedia Foundation. To cite this article click here for a list of acceptable citing formats.The history of earlier contributions by wikipedians is accessible to researchers here:
The history of this article since it was imported to New World Encyclopedia :
Note: Some restrictions may apply to use of individual images which are separately licensed.
 The Fascinating Catamaran History: From Ancient Roots to Modern Sailingby OmSailingCharters | Aug 31, 2024 | Charleston Sailboat Charter  Have you ever marveled at the sight of a catamaran gliding across the water, its twin hulls slicing through the waves with grace and stability? These remarkable vessels, with their distinctive design, have become a popular choice for modern sailing adventures, offering a unique blend of convenience, speed, and spaciousness. The Ancient Origins of CatamaransThe evolution of catamaran design, the role of catamarans in luxury and adventure sailing, catamarans and om sailing charters: a perfect match. Many charter companies recognize the allure of these historic vessels and incorporate them into unforgettable sailing experiences, allowing you to explore the beauty of the open water in style and comfort. OM Sailing Charters, for example, provides Charleston catamaran charters , a unique and luxurious way to enjoy the scenic beauty of Charleston’s harbor and its surrounding waterways. But what’s the story behind the double-hulled wonder? Let’s explore the fascinating catamaran history, from its humble beginnings to its prominent place in the world of sailing today. The history of the catamaran started in the distant past, long before the advent of modern sailing. Evidence suggests that the concept of a double-hulled vessel dates back to ancient civilizations, particularly in Polynesia and South India. Early catamarans, often crafted from logs or reeds, were essential for fishing, trade, and even long-distance voyages. The Polynesian people, in particular, were masters of catamaran construction. Their outrigger canoes, with a main hull and a smaller float connected by spars, were remarkably stable and swift. These vessels allowed them to navigate the vast Pacific, exploring new islands and establishing trade routes that spanned thousands of miles. In South India, catamarans served a similar purpose. Fishermen relied on these sturdy boats to venture into the ocean, while traders used them to transport goods along the coast. The Tamil people, who inhabited the southeastern coast of India, are credited with giving catamarans their name. The word “catamaran” is derived from the Tamil term “kattumaram,” which means “tied logs.”  As maritime exploration expanded and new technologies emerged, catamaran design began to evolve. The introduction of sails, for instance, revolutionized the way these vessels were propelled, allowing them to travel greater distances and with increased speed. The use of wood, fiberglass, and even carbon fiber has enabled the creation of lighter, stronger, and more aerodynamic catamarans. These innovations have not only improved performance but also enhanced the safety and comfort of these vessels. The adoption of catamarans in Western maritime practices fueled their evolution. In 1877, American designer Nathanael Herreshoff built a catamaran named “Amaryllis,” showcasing its superior performance capabilities. However, despite its success, the design was considered too advanced and was banned from regular races for nearly a century. The breakthrough came in 1947 when Woody Brown , alongside Alfred Kumalae, designed and built Manu Kai, the first modern ocean-going catamaran, in Hawaii. Their ingenious design, featuring improved stability and seaworthiness, opened up new possibilities for leisure sailing and even racing. Today, catamarans are at the forefront of sailing innovation, offering a perfect blend of comfort and performance. Their versatile design makes them ideal for a wide range of activities, from leisurely sunset cruises to thrilling water adventures . Imagine yourself on a catamaran, basking in the sun on the expansive deck, feeling the gentle breeze as you glide effortlessly across the waves. The stability of the vessel ensures a comfortable ride, even in choppier conditions, allowing you to fully relax and enjoy the stunning scenery. The shallow draft of catamarans enables them to navigate pristine coral reefs, anchor in secluded coves, and discover hidden beaches that are inaccessible to larger vessels. The freedom to roam off the beaten path is a major draw for adventure seekers and nature enthusiasts. OM Sailing Charters takes full advantage of the unique features that make catamarans the perfect vessel for creating memorable sailing experiences. Our sailing catamaran, OM , is designed to provide you with the ultimate blend of luxury and adventure on the water. OM boasts a bright and airy saloon that’s perfect for relaxing or entertaining. The plush V-shaped settee invites you to unwind after a day of exploring, while the four luxurious double staterooms, each featuring en suite heads and showers, offer the privacy and comfort you deserve. With years of sailing expertise and intimate knowledge of the local waters, our seasoned captains can guarantee your safety and provide a personalized experience tailored to your interests, whether you’re seeking a peaceful escape, an adventurous exploration, or a combination of both. Ready to set sail? Book your Charleston catamaran charter with us today here or contact us at 843-973-0761, and let us help you create the perfect sailing experience. Discover why catamarans and OM Sailing Charters are a match made in heaven.
 A Complete Catamaran Guide
 Disclaimer: You might notice that we recommend products in some articles. We may earn a commission for referring you if you click the link and buy a product. We only recommend products we’ve tried/tested/own (that’s why you won’t find thousands of affiliate links on my site). If you have experience with one of the products we’ve mentioned, please share your experiences in the comments at the end. There you are, out on the water when a strange craft approaches. Is it a sailboat? It sure looks like one until it turns to face you. That’s when you notice this boat doesn’t have just one hull. It has two hulls and it’s called a catamaran. Catamarans are unique, and highly stable watercraft. We’ll explore all the ins and outs of sailing the waters in one of these weird, and awesome multi-hulled craft. Join me as we explore the wild world of sailing catamarans. A History Of The CatamaranIt is believed that the first people to use a catamaran design were those living in Australasia. The succession of boat design in this region was actually very interesting. The beginning of boats in the area was simple, albeit conventional rafts. These were fashioned from logs strewn together with plant fiber lashings such as those formed using bamboo fiber. Catamaran EvolutionThe conventional raft gave way to a minimal raft. This design was basically a conventional raft with two cross beams added in the form of logs. These would be eventually hollowed out to improve buoyancy. The next step in the evolution of boats in the Australasian region was the double canoe. This proved to be the first real catamarans. After some time, the form evolved further into the asymmetrical double canoe design. In this design, one canoe was large and the other attached canoe was smaller. The asymmetrical design quickly evolved into the single-outrigger boat like the one shown in the photo below. The final stage of the evolution of the catamaran in the region was to gain a second outrigger. This in effect created the trimaran with the single central hull and dual outriggers. Eye Witness Accounts Of CatamaransIn 1697, William Dampier wrote of witnessing a type of seafaring vessel off the coast of Coromandel. He noted how the locals called the type of boat a catamaran. He also noted that it had multiple hulls (logs) and that they were small vessels that the person operating would have to hang partway into the water, straddling the hull (log). The name catamaran came from the Tamil. And yet, it was easily applied by the European visitors to the two hulled sailing vessels that sped across the water in the region. Although Dampier may have described the catamaran in the 1690s, the type of boat was actually used as early as the 5th century by the Tamil Chola dynasty. They used boats to move their troops from one island to another. Using this design of boat allowed them to travel heavy, travel quickly and was partially responsible for the conquering of neighboring Burma, Malaysia, and Indonesia. Building A Boat – Basics Of Catamaran ConstructionA boat is usually thought of as being a single-hulled vessel that travels along the surface of the water. It can have multiple types, shapes, and designs of the hull. However, it is often only thought of as having a single hull. But, what if it had two hulls? Would that be like taking two separate boats, and making a raft over both of them? In essence, that is exactly what a catamaran is: two boats made into one. Advantages Of Multiple Hulls
Disadvantages Of Multiple Hulls
Conclusion? Well, it looks to me like everything about catamarans points towards superiority over monohulls in nearly every way. But, you get what you pay for. I think the same thing likely applies to cars too. For instance, I have a performance car that cost me about 10k more than the equivalent non-sports car within the same class. Yet to drive the vehicle, it performs so much better than the normal version of the car, it really speaks volumes to the difference between a common vehicle, and a performance one. Speaking of performance vehicles, let’s take a look now at the different kinds and uses of a catamaran. Catamaran TypesCommercial catamarans – ferries. One of the most common uses for a catamaran is the commercial use of the vehicle design when it comes to ferries. This is likely due to the wide, flat deck possibilities of a catamaran versus a monohulled boat. Not only that, but the catamaran is also a much more stable bodied vessel. This again makes it a superior design for transporting larger land vessels like trucks and so forth. They can easily drive on the ferry without fear of the ferry tipping over. Some ferries are designed for taking vehicles, like the one you might find in the city of Toronto. Where it transports cars from the mainland to Toronto Island. Others are designed specifically with the sole purpose of transporting people. I took a look at one such ferry that operates in Germany. Take a look at the following case study. Commercial Use Case Study – The FerryThe FRS Helgoline is a ferry catamaran operating out of Flensburg, Germany, close to the Danish border. According to the ferry company’s website, the ferry runs using four main engines which are run to a capacity of 12,182 hp combined. This blasts this ferry at a speed of 35 knots or 65 km/hour. This is equivalent to 40 miles per hour. That’s pretty good considering the size and weight of the ship body this catamaran can carry. Speaking of capacity, the ship can carry 680 passengers. At 56.4 meters long (185 feet) by 14 meters wide (45.9 feet), that’s a decent passenger capacity. Catamaran Passenger Capacity Versus Monohull Boat Passenger CapacityThe general rule for calculating passenger capacity for a boat is as follows. Length x Width / 15 = Passenger Capacity Therefore, the FRS Helgoline should have a calculated capacity calculated as follows. 185 x 45.9 / 15 = 566 But it actually has a capacity of 680 which is a 20% increase in capacity over a standard monohull. For comparison, let’s look at a superyacht. A 48.5m (159 feet) long by 10.7m (35 feet) beam (width of the boat) Palmer Johnson Supersport 48 (valued at about $28.5 million dollars) should have a capacity calculated as follows. 159 x 35 / 15 = 371 In short, 26 feet of difference in length equates to 309 fewer passengers. It is almost half of the capacity of the catamaran at 26 feet longer length. Photo courtesy of https://sysyachtsales.com/ Commercial Catamarans – Service VehiclesAlthough Catamarans are typically used as ferries due to their stability and ability to carry wide loads on their flat decks, there are many different service catamarans out there as well. From a support vessel to a crew transfer or search and rescue, catamarans are a solid and stable platform to build a ship on. This is the Ardea which is a 20 meter (65.6 feet) catamaran to be used for crew transport and as a support ship. This ship was built by the Echo Marine Group and delivered to Western Australia in early 2019. This particular vessel is in the service of the Cape Preston Sino Iron Project. Catamarans are used all around the world, for a variety of tasks, not just ferries or support craft. Commercial Catamarans – Cruise LinesNow these are the catamarans we all want to be aboard, aren’t they? Due to the wide stance, these ships can feature massive halls and wide-open interior areas. These ships are stable, and some would say even more stable and safer than monohull design ships. There are many cruise ship catamarans in use today around the world. Some of the more ‘famous’ catamaran cruises are those which investigate the Galapagos Islands. There are several high-end, small fleet, cruise lines operating to the Galapagos which utilize catamaran design vessels as their primary ship type. These ships can be extremely comfortable and stable and often offer some reprieve to those who may otherwise feel seasick. It won’t stop the feeling, but the more stable the hull, the less the boat rocks around.  Military CatamaransCatamarans make excellent military transport vessels. They are stable and the potential to have a large, flat and wide deck for transporting land craft, troops or acting as a landing pad for vertical take-off aerial craft. The stability of the two hulls makes the vessel an excellent candidate for military use, and thus it is used for said purpose. As you can clearly see in the image of the USNS Spearhead, the rear of the vessel has a moveable ramp that can be used for loading and unloading land vehicles. The interior bay of the craft is visible in the image as well, a large area for storage of vehicles, supplies and more. The crane arm on the back of the ship also shows how it is a versatile craft, set up to act as an excellent support craft with a helicopter landing pad and ample storage and freight capacity. Recreational CatamaransCatamaran Personal WatercraftThe wind is in your hair, the warm spray from the hull cutting over the edge of each wave as you skip over the water. That is life, let me tell you. Personal watercraft have come a long way over the years and the small one, two, three and four-person catamarans have come a long way as well. Depending on the options, you can get a small one or two-person catamaran for as little as $1500 new. That might be an inflatable though. There are some very nice, rigid hull designed catamarans for 1-4 people that range from $3500 to $15000. And these are basically open, personal watercraft like that shown in the image below. Using a small catamaran can be quite challenging to learn at first. Sailing is not for the faint of heart. It requires skill, technique, knowledge of the wind and sea, and a bit of hard work. But it can be fun, rewarding and a great way to catch some sun and fresh air out on the water. It’s a relatively GREEN sport as well. Given the use of sails over gas-powered motors that is. ‘Sailing Cats’ – Sailing Catamarans – Yacht & Luxury ClassHere’s where we get into the dreamy boats of the rich and famous. I priced out a small 43’ luxury Leopard 40 sailing catamaran. Even before I added any extras at all, the base price was $399,000 USD. I imagine if I added a few of the multiple extras available, and some tax, freight and that sort of thing, I’m easily in half a million dollars. And that’s the smallest base model. There are all kinds of luxury catamaran shipbuilders across the world. From Asia to Europe and The Americas, it seems any major boating country has at least one company building luxury catamarans. It’s weird that you don’t see more of them on the water though, don’t you think? Being sailing vessels, these luxury cats require some training in sailing before you get behind the wheel. And considering the price point, I would definitely want to be at least a semi-decent sailor with some good few years experience under my belt before I would comfortable at the helm of a half-million-dollar sailing cat. It’s all relative I suppose. I imagine a billionaire might bat an eye at the prospect of wrecking a half-million-dollar boat. But to me, and most of you reading this, that’s likely a lot of money. ‘Power Cats’ – Powered CatamaransThe powered catamaran is one of my favorite boats. They have sort of a muscle car appearance with the wide and often tall front end of the boats. I find it to be reminiscent of a large air intake on the front hood of a rally race car like the Subaru WRX, for instance. These boats are fast, they are stable and handle very well. Catamarans are often considered the boat of choice for long sea voyages due to their stability. A powered catamaran will definitely cost more than a powered monohull boat of the same length. Why? Well, the powered catamaran has one crucial downside. That is, it needs two engines. One for each of the two hulls. Otherwise, it’s off balance for propulsion. These two engines or motors have to be in sync with each other or again, the propulsion will be off-balance. Because they have two motors, they have double the maintenance when it comes to maintaining the propulsion system. More components also means a greater chance of things breaking down. In essence, it doubles the chances of the ship having a motor break down. The saving grace is that should one motor break, they have a backup, even if it does mean very unbalanced propulsion. In contrast, a monohull vessel of the same length may only have half the chance of motor failure due to only having one motor, but if that one motor breaks, then what? Call for help, that’s what. A cat would have a struggling chance to get itself back to port. A monohull would be dead in the water unless it was carrying spare parts or another motor onboard somewhere. Catamaran Frequently Asked QuestionsWhat is a catamaran cruise. A catamaran cruise is simply a cruise on a dual hull design boat. Often used for river cruises, the catamaran which is used as cruise ships are often considerably smaller than their giant monohulled counterparts. What is the purpose of a catamaran?A catamaran is a design for a boat that utilizes two hulls. Due to the flat, platform-like-potential for the deck of the boat, the catamaran is often purposed with transporting materials, vehicles, and people. For instance, catamarans are quite often used as ferries. Is catamaran safe?Catamaran are very safe water craft. The design of riding on two hulls separated by a gap in between, in essence is like giving a car a double-wide wheel base. The wider the stance, the more stable the craft, from side to side anyway. And if the length of the boat is proportional to the width, then it becomes an extremely stable craft. That is why catamarans are often considered the best to be used for long voyages. Yes, catamaran are safe. What is the difference between a catamaran and a sailboat?A traditional sailboat is a deep, monohull vessel that has at least one mast extending high into the air above the deck to hold sails. A catamaran refers to the design of a dual-hull boat and really has nothing to do with sails. Although, catamaran do make excellent sailing boats as well, they are quite capable of acting as power boats and do not require sails if they have the correct amount of powered motors to propel them. Sailboats, although also able to be powered if a motor is provided, are traditionally monohull and wind-powered exclusively. Do catamarans have small interiors?The size of an interior cabin on a boat is typically proportional to the size of the boat itself. If a catamaran has above-deck cabins, they will likely be able to be of a larger design than those you would find on deck of a monohull boat. This is because a catamaran has a much wider footprint than a monohull boat of the same length. This extra width would allow for larger on deck cabins. How much does a catamaran cost?A personal watercraft (1-2 person) inflatable catamaran will run you anywhere from $1500-$12000 USD, depending on the quality and features. The rigid hull catamarans of the same size start at about $4500 USD. A small cabin cruiser type of catamaran will typically start at about $60000 for a small base model and the price just goes up and up depending on size and features. For Instance, a 40’, 3 cabin with 1 washroom cat will cost you about $500,000 USD for the base model. They are considerably more expensive that a monohull of the same length. However, the trade-off is greater stability and a smoother, more comfortable ride. Is a catamaran more work to maintain?Technically yes. Due to having two hulls and if powered, two motors and likely also water jets, this means you have double the oil changes of a boat that would have a single motor. Once you get past the basic engine and hull maintenance, a catamaran is not that much more work than a monohull ship of the same length. The trouble with catamarans in terms of maintenance, is that once they reach a certain length, the width becomes more than a standard lane on the road. That being said, if you ever need to transport the boat via land, it can be quite the challenge. Especially if you need to pay to have a police escort for an extra-wide trailer. And special licensing might be involved as well. What is the difference between a catamaran and a trimaran?A catamaran is a dual hull boat. In other words, it has two hulls. A trimaran has three hulls. Is a catamaran considered a yacht?According to Oxford dictionary, a yacht is a medium-sized sailboat equipped for cruising or racing. A catamaran, on the other hand, is a boat with two hulls. Therefore, a catamaran can most certainly also be a yacht. And likewise, if a yacht has two hulls, then it is a catamaran as well. Can you get seasick on a catamaran?Seasickness occurs when a person feels nauseous from the swaying motion of a rocking ship. These feelings may be lessened on a catamaran, due to their extra stability. However, a catamaran may be slightly more stable than a monohull of the same length, but it is still a boat. And it will still make someone who experiences seasickness continue to feel the ill effects. Are catamarans more stable in rough seas?Catamarans are known to be more stable than monohull ships of the same length. This is why catamarans are often the ship type of choice for long sea voyages due to their stability. Why do catamarans capsize?Catamarans are not known for capsizing. The larger vessels that is anyway. But, it does happen from time to time. Catamarans are known for their stability, so typically if a capsize event should occur, it is typical for them to be extreme circumstances. Personal watercraft catamarans are a different story though. These are in fact known for tipping over. Not because they are less stable than their monohull counterparts of the same length. But instead, because they are able to go considerably faster than monohull personal watercraft of the same length (not including powered craft though). This is due to the sailing cats being able to have a larger sail than a small monohull sailboat of the same length. Due to the extra sail, they are able to travel faster than monohull sailboats of the same length. This allows them to whip around on the water and at higher speeds, whipping your cat about quick can easily send it over sideways. Extra speed means fast turns carry momentum in the direction of travel and that extra speed equates to tipping over if turned too fast. To sum up, they capsize due to user error or extreme events. Which is safer, a catamaran or a monohull?Due to the extra stability of having a wider footprint than a monohull, a catamaran of the same length is the safer vessel. Are catamarans safer than sailboats?The same rule applies to stability versus the length of the hull. A cat will always be the more stable length for length. However, due to their ability to go much faster than a monohull sailboat, this kind of cancels out some of the added safety due to stability. With that in mind, they may just be about the same but there is one generalization we can make when comparing the safety of catamarans vs sailboats: At the same speed, and of equal length, sailing or power catamaran will be safer than a monohull sailboat. How fast can catamarans go?The speed a catamaran can go is entirely dependent upon the hull design, weight of the vessel, the strength of propulsion (be it wind or powered) and so on. The general rule is that in terms of sailing cats vs monohull sailboats, a cat of equal length can typically go faster than a sailboat. In terms of powered cats vs powerboats, a powered catamaran will typically require less energy to move forward than a monohull of the same sort of hull design (but monohull of course) and thus a cat should, in theory, be able to go faster than a monohull when both are using propulsion that is equal in power. Bibliography
Boating GearTake a look at our Recommended page for a variety of items. Here are some of the things you can expect:
More From Boating Guide Magazine
Return To Home * About Boating Guide * About The Author fakewatches.isShare this post with your friends.
Subscribe to our NewsletterJoin us in our love for all things water. And Adventure. A Guide to Cruising Catamaran Manufacturers In 2022So, you finally decided that a multi-hull will serve you way better than a single-hull but can’t choose which one of the catamaran manufacturers on the market will provide you with your dream vessel. Well, I’ve done a ton of research on the top 13 current manufacturers, so you don’t have to. Leopard Lagoon Fountaine  A Guide To Choosing Your First BoatA Guide To Choosing Your First Boat – A Boating Guide Buyer’s Guide Report for 2023. Would you like to buy your first boat? When you buy a boat for the first time, it is easy to make a mistake due to the lack of experience. Therefore, before making any decision, you must evaluate your  Chasing Dory 5 Thruster Underwater Drone ReviewEvery time you go on a marine or a boat trip, the major issue that arises is preserving memories. It is easy to snap pictures when you’re on the land, but what if you want to capture underwater images? That’s right, in such a scenario, what saves the day is an underwater drone. So, no  The Poseidon 1 Underwater Drone – Best Boating Toy For Adults?Best Boating Toys – The Geneinno Poseidon 1 Underwater Drone Do you love to go out on boating trips? If yes, then an underwater drone is something that’ll be of great use. Not only that, but these drones are ridiculously fun to use with their built-in cameras and clever maneuvering. Believe it or not, but  Before You Buy Guide: Understanding Fish Finders And GPSThere’s nothing more relaxing than a day out on the water. The gentle movement of the boat, the sun, and breeze moving over the water. These things make it hard to want to ever go back to civilization. And catching a few big fish sure would be the icing on the day’s cake. There’s no  How Canoes Are Made (1 Canoe Fabrication Easy Explanation Coming Up!)Want to know how canoes are made? You’ve come to the best place to find out. Canoe fabrication occurs using an incredible variety of materials. Some are made of wood, while others are plastic, and some metals like aluminum. Each material has its benefits. Some are lighter, some are more durable, and others are almost  Boat Information By Type© 2023 Boating.Guide, A Hyperwave Media Group Ltd. Publication. Privacy OverviewWhen Was the Catamaran Invented?Look at how multi-hulled vessels have evolved over the millennia to find out when was the catamaran invented.  Stefan Kristensen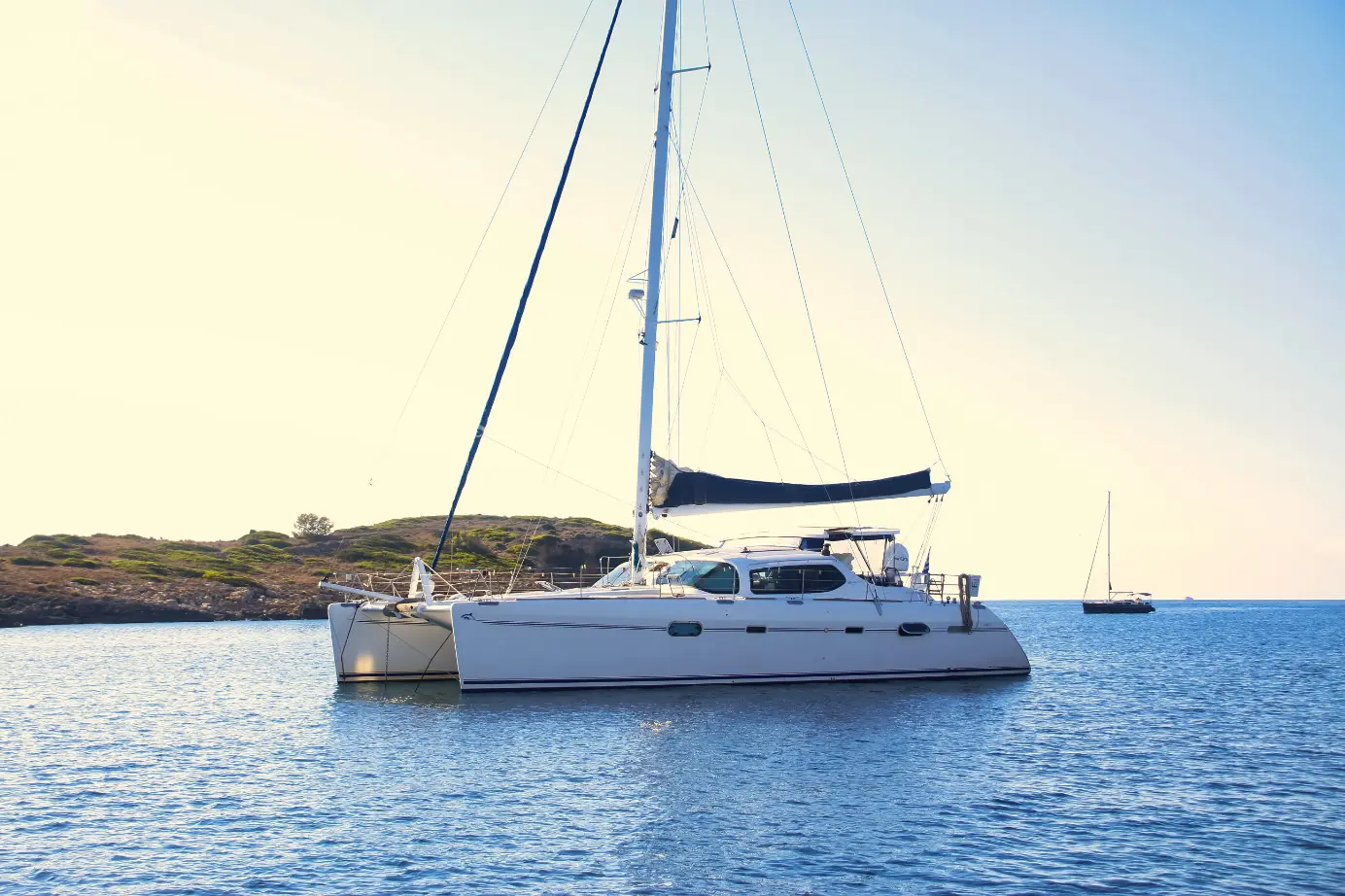 The first modern catamaran was designed and built by Nathanael Herreshoff in 1876 and patented a year later. However, the concept and construction of catamarans and vessels that operate on the same principles date all the way back to the second millennium BCE among the Austronesian people. In the rest of the article, we are going to learn what makes a catamaran different from a traditional boat and explore the long history of the vessel’s gradual development to fully answer the question of when was the catamaran invented. What Is So Special About a Catamaran?Although they are often perceived as a trend or a fad, catamarans actually do have significant structural differences compared to traditional boats. Catamarans have two hulls instead of only one. The two hulls of a catamaran are joined by the bridge deck to form a single vessel. One of the most noticeable practical differences between the catamaran and monohull boats is that catamarans are a lot more stable. This is because the beam is significantly wider than a traditional boat’s, giving the catamaran a greater initial stability, albeit with a poorer secondary stability. This makes the boat less likely to capsize, but more difficult to recover once a capsize has begun. Catamarans also have shallower drafts and displace significantly less water than comparable traditional boats, which means they experience less resistance from the water when moving forward. This, in turn, means that catamarans, whether they are powered by sail or motors, need less energy to move the same mass at the same speed compared to a similarly sized traditional monohull boat. What Is the History of the Catamaran’s Development?When most people think of catamarans, the type of vessel they picture traces its history to Amaryllis , a boat designed and built by American mechanical engineer and naval architect, Nathanael Herreshoff. While only in his 20s, Herreshoff created the modern catamaran design, raced his first one in 1876, and patented it the next year. This kickstarted the modern industry and application of catamarans, but the principles that Herreshoff made use of to design Amaryllis were not all completely new. Similar designs had been trialed by Europeans since the 17th century and used by Austronesians in the Indian and Pacific Oceans going back thousands of years. So then when was the catamaran invented? Early Austronesian OriginsThe history of catamarans among the early Austronesian people is tied to that of outrigger canoes, which are boats that are stabilized through the use of a separate floating device which sits alongside the main hull. There is controversy among academics over whether outrigger canoes developed as scaled down versions of catamarans or catamarans as expanded versions of outrigger canoes. There is history of both types of vessel going back to the second millennium BCE, though the earliest record that Europeans have of them is from 1521, when they were observed by sailors on Ferdinand Magellan’s expedition to circumnavigate the world. Petty, Crisp, and the English PrototypesThe first European prototype of a vessel with two hulls was designed in 1662 by famed English economist, William Petty. Although as with any catamaran, this boat was designed to use less energy, move faster, and navigate shallower waters, the concept was just too experimental for Petty’s contemporaries, and it never took off. A few decades later, toward the end of the 17th century, English navigator and pirate, William Dampier, was on the Indian subcontinent, where he learned of vessels with multiple hulls from the native Tamil speakers. He was the first English speaker to record the word “catamaran” for these, adapting it from the Tamil word “kattumaram.” The first catamaran built by Europeans to see use was designed and built by English captain Mayflower F. Crisp in Burma in the early 19th century. His vessel was called Original , and Crisp documented its exploits and the rationale behind his design himself in his 1849 book, A Treatise on Marine Architecture, Elucidating the Theory of the Resistance of Water . Original remained in service for a number of years, during which it largely navigated the Gulf of Martaban, enabling trade between Southeast Asian ports situated on the gulf. In spite of Original’s success, the work of Captain Crisp did not change sailboat designs among his contemporaries. Herreshoff and the American CatamaranThe final big development in catamaran design came in 1876, when American engineer and naval architect, Nathanael Greene Herreshoff, designed and built his first catamaran, Amaryllis . Herreshoff patented this design in 1877, the year following Amaryllis’ maiden voyage. Whether due to changes in design or the fact that he was the first to formally patent his design, many consider Amaryllis to be the first modern catamaran and therefore Nathanael Herreshoff to be the inventor of the catamaran, as we know it, in 1876. Interestingly, Herreshoff never referred to his design as a catamaran in the patent . The patent itself is simply titled “Improvement in Construction of Sailing-Vessels,” and Herreshoff makes references to “the vessel” and “my invention” but never uses the Tamil word that the English had previously adopted for the design. Catamarans saw a lull in popularity once again after Herreshoff’s design won and was subsequently excluded from a lot of yacht clubs for what was perceived to be unfair competition. The catamaran design saw its final and longest lasting resurgence in the mid-20th century, when its construction and use started getting picked up across the globe. Perhaps the most popular adoption was by American surfing legend, Hobie Alter. Alter’s company, Hobie Cat, manufactured and sold small catamarans bearing the same name. The Hobie Cats have become a world standard, with one vessel, the Hobie 16, having sold more than 100,000 units since manufacturing began. Most people offer Nathanael Herreshoff’s Amaryllis in 1876 as the answer when asked when was the catamaran invented. While it is considered the first modern catamaran, we have learned today about the thousands of years of gradual development across cultures and continents that have shaped the vessel, from early Austronesian rafts to the Hobie Cats of yesteryear. Sign up for more like this. What Is A Catamaran Sailboat? (And What It Looks Like)  Catamarans are increasingly popular for sailing and commercial use, but what sets them apart from monohulls and other multihulls? A catamaran is a twin-hull boat with two equally-sized hulls placed side by side. They’re powered by engines, sails, or both—and they’re known for efficiency and speed. Catamarans are the most common kind of multihull boat. In this article, we’ll go over the characteristics of catamarans and how to differentiate them from other types of boats. Additionally, we’ll cover the advantages and disadvantages of catamarans and compare them to trimarans and monohulls. We’ll also go over the most common types of catamarans and their uses. We sourced the information in this article from marine design guides, boat identification resources, and the online boating community. Table of contents How to Spot a CatamaranSpotting a catamaran is easy. Simply look at the hulls and count them. Catamarans have two hulls side by side and a relatively large gap between them where you can see light on the other end. Catamarans are distinct from trimarans, which have an additional hull between the two outer hulls. How do Catamarans Work?The principle behind the catamaran is simple. You can think of catamarans like cars and monohulls like motorcycles. Catamarans distribute their weight between hulls on either side, whereas monohulls utilize only one hull. Evidently, cars are much more difficult to tip over and can hold much more weight. Additionally, cars are wider, as they have much more contact with the road. Catamarans work in a similar way, as they have a wide stance and contact with the surface on both sides. Obviously, that isn’t the most precise comparison. But the basic principle is the same, and catamarans have a few notable benefits over monohulls. Catamaran Vs MonohullCatamarans are easy to distinguish from monohulls. A monohull is just a regular old boat with a single hull. The vast majority of boats and ships are monohulls. Catamarans have two hulls, which are usually sleek and narrow. Here are some comparisons of catamarans and monohulls, along with the advantages twin-hull designs have over most single hull types. Benefits of CatamaransCatamarans have numerous benefits. The first is speed. Catamarans produce less drag than monohulls and thus can achieve excessive speeds both under sail and power. They don’t need to plane like monohulls to achieve these high speeds, and they use less fuel. Catamarans are also much more stable than monohulls. They have a wide stance and shallow draft, and many waves and swells can travel between the hulls instead of below them. This effectively reduces an entire axis of movement and prevents catamarans from rolling excessively. Drawbacks of CatamaransCatamarans aren’t advantageous in every way, or else we wouldn’t bother building monohulls. The disadvantages of catamarans limit their use to niche commercial applications and high-end yachts. But what are the drawbacks of a twin-hull design? Sailing catamarans don’t follow many of the traditional boat handling rules and characteristics that sailors pass down for generations. Some, such as hull speed limitations, are good to do away with—while others, such as responsiveness, are not. Catamarans aren’t as quick to the helm or responsive as monohulls. There are some exceptions to this rule, but for the most part, you’ll get a lot more feedback from a single-hull vessel. Additionally, the large section of deck between the hulls of a catamaran is prone to pounding in rough seas, which is loud and uncomfortable. Catamarans can sometimes be twice the width of an equivalent monohull sailboat, which can increase mooring fees and limit docking options. The final major drawback of catamarans is a consequence of their stability. Traditional full-keel monohull sailboats have a very low center of gravity, which makes them roll in heavy seas but ensures a recovery. Catamarans have a higher center of gravity, and they can’t right themselves after a knockdown. And though catamarans are less likely to roll, a severe list on a multihull is a much more serious concern than on a ballasted monohull. Catamaran Vs TrimaranCatamarans and trimarans are often lumped together, but they have very different design and performance specifications. Trimarans have three hulls, whereas catamarans have two. Trimarans look a lot like catamarans from the side, but a quick glance at the bow or stern can set them apart. Trimarans are faster than catamarans, as they distribute their weight across three hulls instead of two. This helps them stay centered and reduces interference from pitching and rolling. Catamarans are fast, but they lose out to trimarans when going head to head. However, catamarans are much less expensive to build and maintain and often have roomier cabins due to their larger hulls. Types of CatamaransThere are numerous types of catamarans, and their uses vary widely. The catamaran is one of the oldest and most useful hull types, and some variants have been used for thousands of years. Here are the most common kinds of catamaran boats and their uses. Sailing CatamaranSailing catamarans are probably what you think of when you hear the name. Sailing catamarans are sailboats with two identical hulls connected by a center deck. The largest sailing catamarans are spacious and stable vessels that are capable of serious offshore sailing. Sailing catamarans have a number of notable advantages over monohulls. Monohulls, which are traditional sailboats with a single hull, are limited by a simple concept called hull speed. As the bow and stern wave of a monohull intersect, they cause drag which limits the top speed of the boat. Catamarans are not bound by hull speed limitations, as they have two hulls. Catamarans can go twice or even three times as fast as similar monohulls and achieve excellent travel times. Catamarans are also more stable than monohulls, as their wide stance and shallow draft reduce the effect of rough water. They don’t heel, as the force of the wind is counteracted by the double hulls. Additionally, modern sailing catamarans can ‘wave pierce’ by cutting through swells instead of riding over them. Sailing catamarans come in many shapes and sizes. Small sailing catamarans, such as those used in races and regattas, are known for their speed and relative stability compared to light racing monohulls. Sometimes, they feature a smaller second hull for stability—these are called outriggers. Sailing catamarans have spacious interiors thanks to the large cockpit between the hulls. This cockpit usually contains cooking and eating spaces, a place to sit, and a hallway between the hulls. The hulls usually contain living quarters and often mirror each other. Power CatamaransPower catamarans have an even greater variety than sailing catamarans. These vessels are used for everything from party platforms to ferries and patrol boats. Power catamarans are a recent development, as engineers and marine architects now realize they have numerous hydrodynamic advantages over other hull types. Catamarans are much more efficient than other hull types, as they have less drag relative to their size. Additionally, you can build a much larger catamaran with less material. This makes them popular for car and rail ferries, as builders can construct a very wide vessel with two small hulls rather than a narrower vessel with a large single hull. Military and Commercial CatamaransEven the military has found a use for the catamaran hull shape. The Spearhead class EPF is an expeditionary fast transport vessel designed for carrying capacity and speed. It has two sharp hulls and a huge cargo capacity. The Spearhead class EPF is 337 feet long, which is about the same length as a WW2 escort destroyer. Yet despite having a similar length and displacement, these catamarans can travel more than twice as fast—43 knots, or nearly 50 miles per hour. Their great speed is a direct consequence of their catamaran hull type. Power catamarans are also used as patrol and utility boats on a much smaller scale, with either outboard or inboard motors. The State of Texas uses catamarans to patrol shallow rivers and lakes. Texas Game Wardens utilize state-of-the-art aluminum catamaran patrol boats, which are fast enough to outrun most fishing boats. There’s another form of power catamaran that you may not have considered. Pontoon boats are technically catamarans, and they’re enormously popular on lakes and rivers throughout the country. Pontoon boats aren’t known for speed, but they’re a great platform for a fun and comfortable outing. Catamaran HouseboatsThe final common type of power catamaran is the two-hulled houseboat. Houseboats don’t always use the catamaran hull type, but it’s common enough that most major manufacturers offer it as an option. Catamaran houseboats have a few notable advantages over monohull designs. For one, they’re easier to build—especially when pontoons are chosen. Additionally, they’re better suited for navigating shallow water. These vessels can support more weight across their two hulls, offer increased stability, and they’re also efficient. Why Aren’t Catamarans More Common?With all the advantages listed in this article to consider, it may seem strange that the use of catamarans is still somewhat limited. At the end of the day, it comes down to economics—as monohull boats and ships are simply cheaper to build. Additionally, catamarans have some distinct limitations. Monohulls have lots of storage space in their hulls and can carry thousands of tons of cargo safely in all weather conditions. Catamarans lack this space and low center of gravity, so they’re not ideal for transporting cargo past a certain point. Additionally, monohulls work, and many people are reluctant to experiment with new designs when old designs work just fine. This rule applies to both large and small boats. A large monohull sailboat can be constructed at low cost from stock plans and reliably sail almost anywhere. Very little complex structural engineering is involved, and looser tolerances reduce cost and maintenance requirements. Related Articles Daniel Wade I've personally had thousands of questions about sailing and sailboats over the years. As I learn and experience sailing, and the community, I share the answers that work and make sense to me, here on Life of Sailing. by this author Learn About Sailboats Most Recent What Does "Sailing By The Lee" Mean?October 3, 2023  The Best Sailing Schools And Programs: Reviews & RatingsSeptember 26, 2023 Important Legal Info Lifeofsailing.com is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for sites to earn advertising fees by advertising and linking to Amazon. This site also participates in other affiliate programs and is compensated for referring traffic and business to these companies. Similar Posts Affordable Sailboats You Can Build at HomeSeptember 13, 2023  Best Small Sailboat OrnamentsSeptember 12, 2023  Discover the Magic of Hydrofoil SailboatsDecember 11, 2023 Popular Posts Best Liveaboard Catamaran SailboatsDecember 28, 2023  Can a Novice Sail Around the World?Elizabeth O'Malley June 15, 2022  4 Best Electric Outboard Motors How Long Did It Take The Vikings To Sail To England? 10 Best Sailboat Brands (And Why)December 20, 2023  7 Best Places To Liveaboard A SailboatGet the best sailing content. Top Rated Posts © 2024 Life of Sailing Email: [email protected] Address: 11816 Inwood Rd #3024 Dallas, TX 75244 Disclaimer Privacy Policy From 1964 - the masterpiece that is the Unicorn. Have a read below to see how it started, and how the legend lives on...  Where it startedJohn mazzotti came up with the unique tortured ply construction technique in 1964 that allowed the perfect high strength, light weight hull construction for catamarans. he began his experiments in 1964 on the b class manta and when the iyru laid down the specification for the a class in 1966, mazzotti came up with the mythical beast - the unicorn. she won the rya trials convincingly in 1967 and came close to being selected as the boat of choice by the iyru for the international a class.. The design took the catamaran world by storm. By the end of 1967 the boat had won every major A class event and had proved to be the fastest A class in the UK and the most stable throughout the world in all weathers. By the summer of 1968, there were over 150 boats registered - 70 in the UK, 50 in Canada, 15 in the US, with smaller numbers in Belgium, Sweden, Australia, Germany and South Africa. Trowbridge and Sons became the official builders at the outset, building boats in wood and fibreglass as well as providing kits for home construction. The kit in 1968 was £198-8-0!!! Later, South Midland Marine, South Midlands Laminates and Condor Catamarans Ltd joined those providing ready built boats and kits.  Rarely has a boat been designed so perfectly straight out the box. Over the last forty years the changes have proved to be relatively minor - this design is just outstandingly good for high performance sailing in all weather conditions. In the 80’s, Roger Dewen, an A class specialist, designed a modified hull that was within the class templates. This hull design has more buoyancy in the bow and more rocker. These features allow the boat to be pushed even harder before submarining and allow more efficient tacking. He also experimented very successfully with a ‘knuckle’ on the keel line that allowed the boat to skim over the surface, almost a planing effect. This design (built in hull 1011) won the 1981 A class European Championships and the design has been adopted by Gary Piper in his fine boats. The majority of boats over the years have been home built to varying quality. Unfortunately, this gave a reputation of the boat being fragile. This is so far from the truth for a boat built professionally or to the proper standard. These boats will take the huge rig pressures of a high performance cat and absorb the rough and tumble of capsize, cartwheel and nose diving in their stride.Living on.... Gary Piper, son of a master craftsman woodworker, became fascinated by the wooden boats in the 1980’s. As well as sailing, he began building them to a very high standard. He now builds a new boat most years and will build to order, using the Dewen hull design. If you need to be convinced about the performance of the Unicorn, check out the Rounde om Texel. Dan Jarman, on his first visit to the great event, finished 1st single hander on the water, 2nd on corrected time, 37th overall out of over 700 boats.  Where did the Unicorn get its name?


Stay in the Know with World Cat" * " indicates required fields Where You Do Your BoatingOur history, true to our name, you’ll find our boats on virtually every ocean and lake in the world.. Over 80,000 customers across the globe can be found enjoying our catamarans. They’ve chosen our boats because World Cat delivers a smoother, more stable, more enjoyable experience from entertaining at the dock to navigating the deepest waters. The origin of World Cat can be traced back over a quarter of a century to the beginning of our Glacier Bay Edition boats in America’s Pacific Northwest. Today, World Cat is the largest maker of power catamarans in the world. Located in Tarboro, North Carolina, our boats are precision crafted in a state-of-the-art 140,000 square foot facility. While we build an array of boats in different sizes and configurations, each is a reflection of our mission to deliver the smoothest ride on water – making boating more enjoyable and giving boaters the comfort and confidence to cruise, fish, dive, and explore the water world around them. From the South Pacific to Siberia, World Cats have safely carried thousands of boaters over tens of thousands of miles. Shouldn’t you share in that experience?  The first World Cat is built in Greenville, NC with a new mold and new hull. By fall of 1998, the World Cat brand is launched with three models: the 246 Sport Fisherman (SF), 266 Sport Cuddy (SC), and 266 Sport Fisherman (SF). The 246DC Dual Console launches. A World Cat wins the Bermuda Challenge – a run from Norfolk, VA to Bermuda. The acquisition and renovation of a new facility is the start of transitioning production to Tarboro, NC. Chris Peters sets the World Record Maco Shark in a 246SF.  World Cat launches the 33’ TE Center Console, an innovative performance boat. At the time, it was the largest outboard boat in production and the first outboard boat to feature the new Suzuki 300HP 4-stroke engines, an absolute game changer.  World Cat introduces a truly complex and innovative design with the 320EC, featuring World Cat’s first hull with a cabin and separate head. World Cat secures its staying power by acquiring Glacier Bay and Livingston Catamaran Boats, while reinforcing its commitment to A Better Way To Boat™.  World Cat launches its first family fish friendly hull and deck design with the new 320CC Center Console. World Cat officially enters the inshore audience with the launch of the 230CC and 230DC. For the first time, World Cat launches a boat that does not focus on fishing first with the 230SD, featuring a refined family and cruising boating experience.  World Cat launches the largest dual console outboard boat on the market with the 320DC.  The 280CC-X and 280DC-X is launched, featuring a new hull style line, designed to deliver a refined look at top speeds.  The new flagship 40’ hull emerges with the launch of the 400DC-X, becoming the largest dual console catamaran to ever hit the market. Quickly following was the 400CC-X Center Console featuring the innovative Cat-Track™ seating.  World Cat celebrates their 25th Anniversary year.  World Cat introduces the all-new 260CC-X.  World Cat introduces the all-new 260DC-X.  A catamaran ( / ˌ k æ t ə m ə ˈ r æ n / ) (informally, a "cat") is a watercraft with two parallel hulls of equal size. The distance between a catamaran's hulls imparts resistance to rolling and overturning. Catamarans typically have less hull volume, smaller displacement , and shallower draft (draught) than monohulls of comparable length. The two hulls combined also often have a smaller hydrodynamic resistance than comparable monohulls, requiring less propulsive power from either sails or motors. The catamaran's wider stance on the water can reduce both heeling and wave-induced motion, as compared with a monohull, and can give reduced wakes. Development in AustronesiaTraditional catamarans, western development of sailing catamarans, performance, swath and wave-piercing designs, applications, passenger transport, further reading. Catamarans were invented by the Austronesian peoples , and enabled their expansion to the islands of the Indian and Pacific Oceans . [1] Catamarans range in size from small sailing or rowing vessels to large naval ships and roll-on/roll-off car ferries. The structure connecting a catamaran's two hulls ranges from a simple frame strung with webbing to support the crew to a bridging superstructure incorporating extensive cabin and/or cargo space.  Catamarans from Oceania and Maritime Southeast Asia became the inspiration for modern catamarans. Until the 20th century catamaran development focused primarily on sail-driven concepts. The word "catamaran" is derived from the Tamil word, kattumaram (கட்டுமரம்), which means "logs bound together" and is a type of single-hulled raft made of three to seven tree trunks lashed together. The term has evolved in English usage to refer to unrelated twin-hulled vessels. [2] [3] [4]  Catamaran-type vessels were an early technology of the Austronesian peoples . Early researchers like Heine-Geldern (1932) and Hornell (1943) once believed that catamarans evolved from outrigger canoes , but modern authors specializing in Austronesian cultures like Doran (1981) and Mahdi (1988) now believe it to be the opposite. [5] [6] [1]  Two canoes bound together developed directly from minimal raft technologies of two logs tied together. Over time, the twin-hulled canoe form developed into the asymmetric double canoe, where one hull is smaller than the other. Eventually the smaller hull became the prototype outrigger , giving way to the single outrigger canoe, then to the reversible single outrigger canoe. Finally, the single outrigger types developed into the double outrigger canoe (or trimarans ). [5] [6] [1] This would also explain why older Austronesian populations in Island Southeast Asia tend to favor double outrigger canoes, as it keeps the boats stable when tacking . But they still have small regions where catamarans and single-outrigger canoes are still used. In contrast, more distant outlying descendant populations in Oceania , Madagascar , and the Comoros , retained the twin-hull and the single outrigger canoe types, but the technology for double outriggers never reached them (although it exists in western Melanesia ). To deal with the problem of the instability of the boat when the outrigger faces leeward when tacking, they instead developed the shunting technique in sailing, in conjunction with reversible single-outriggers. [5] [6] [1] [7] [8] Despite their being the more "primitive form" of outrigger canoes, they were nonetheless effective, allowing seafaring Polynesians to voyage to distant Pacific islands . [9] The following is a list of traditional Austronesian catamarans:
The first documented example of twin-hulled sailing craft in Europe was designed by William Petty in 1662 to sail faster, in shallower waters, in lighter wind, and with fewer crew than other vessels of the time. However, the unusual design met with skepticism and was not a commercial success. [10] [11]  The design remained relatively unused in the West for almost 160 years until the early 19th-century, when the Englishman Mayflower F. Crisp built a two-hulled merchant ship in Rangoon, Burma . The ship was christened Original . Crisp described it as "a fast sailing fine sea boat; she traded during the monsoon between Rangoon and the Tenasserim Provinces for several years". [12] [13] Later that century, the American Nathanael Herreshoff constructed a twin-hulled sailing boat of his own design (US Pat. No. 189,459). [14] The craft, Amaryllis , raced at her maiden regatta on June 22, 1876, and performed exceedingly well. Her debut demonstrated the distinct performance advantages afforded to catamarans over the standard monohulls. It was as a result of this event, the Centennial Regatta of the New York Yacht Club, that catamarans were barred from regular sailing classes, and this remained the case until the 1970s. [15] On June 6, 1882, three catamarans from the Southern Yacht Club of New Orleans raced a 15 nm course on Lake Pontchartrain and the winning boat in the catamaran class, Nip and Tuck , beat the fastest sloop's time by over five minutes. [16] [17] In 1916, Leonardo Torres Quevedo patented a multihull steel vessel named Binave (Twin Ship), a new type of catamaran which was constructed and tested in Bilbao ( Spain ) in 1918. The innovative design included two 30 HP Hispano-Suiza marine engines and could modify its configuration when sailing , positioning two rudders at the stern of each float, with the propellers also placed aft . [18] [19] [20] In 1936, Eric de Bisschop built a Polynesian "double canoe" in Hawaii and sailed it home to a hero's welcome in France. In 1939, he published his experiences in a book, Kaimiloa , which was translated into English in 1940. [21] Roland and Francis Prout experimented with catamarans in 1949 and converted their 1935 boat factory in Canvey Island , Essex (England), to catamaran production in 1954. Their Shearwater catamarans easily won races against monohulls. Yellow Bird, a 1956-built Shearwater III , raced successfully by Francis Prout in the 1960s, is in the collection of the National Maritime Museum Cornwall . [22] Prout Catamarans , Ltd. designed a mast aft rig with the mast aft of midships to support an enlarged jib—more than twice the size of the design's reduced mainsail; it was produced as the Snowgoose model. [23] The claimed advantage of this sail plan was to diminish any tendency for the bows of the vessel to dig in. [24] [25]  In the mid-twentieth century, beachcats became a widespread category of sailing catamarans, owing to their ease of launching and mass production. In California, a maker of surfboards , Hobie Alter , produced the 250-pound (110 kg) Hobie 14 in 1967, and two years later the larger and even more successful Hobie 16 . As of 2016, the Hobie 16 was still being produced with more than 100,000 having been manufactured. [26] Catamarans were introduced to Olympic sailing in 1976. The two-handed Tornado catamaran was selected for the multihull discipline in the Olympic Games from 1976 through 2008. It was redesigned in 2000. [27] The foiling Nacra 17 was used in the Tokyo 2020 Olympics, which were held in 2021; [28] [29] after the 2015 adoption of the Nacra 15 as a Youth World Championships class and as a new class for the Youth Olympic Games. [30] [31]  Catamarans have two distinct primary performance characteristics that distinguish them from displacement monohull vessels: lower resistance to passage through the water and greater stability (initial resistance to capsize). Choosing between a monohull and catamaran configuration includes considerations of carrying capacity, speed, and efficiency. At low to moderate speeds, a lightweight catamaran hull experiences resistance to passage through water that is approximately proportional to its speed. A displacement monohull has the same relationship at low speed since resistance is almost entirely due to surface friction. When boat speed increases and waves are generated the resistance is dependant on several design factors, particularly hull displacment to length and hull separation to length ratio, it is a non trivial resistance curve with many small peaks as wave trains at various speeds combine and cancel [32] . [33] For powered catamarans, this implies smaller power plants (although two are typically required). For sailing catamarans, low forward resistance [34] allows the sails to derive power from attached flow , [35] their most efficient mode—analogous to a wing—leading to the use of wingsails in racing craft. [36] Catamarans rely primarily on form stability to resist heeling and capsize. [33] Comparison of heeling stability of a rectangular-cross section monohull of beam, B , compared with two catamaran hulls of width B /2, separated by a distance, 2× B , determines that the catamaran has an initial resistance to heeling that is seven times that of the monohull. [37] Compared with a monohull, a cruising catamaran sailboat has a high initial resistance to heeling and capsize—a fifty-footer requires four times the force to initiate a capsize than an equivalent monohull. [38]  One measure of the trade-off between speed and carrying capacity is the displacement Froude number (Fn V ) , [39] compared with calm water transportation efficiency . [40] Fn V applies when the waterline length is too speed-dependent to be meaningful—as with a planing hull. [41] It uses a reference length, the cubic root of the volumetric displacement of the hull, V , where u is the relative flow velocity between the sea and ship, and g is acceleration due to gravity :  Calm water transportation efficiency of a vessel is proportional to the full-load displacement and the maximum calm-water speed, divided by the corresponding power required. [42] Large merchant vessels have a Fn V between one and zero, whereas higher-performance powered catamarans may approach 2.5, denoting a higher speed per unit volume for catamarans. Each type of vessel has a corresponding calm water transportation efficiency, with large transport ships being in the range of 100–1,000, compared with 11-18 for transport catamarans, denoting a higher efficiency per unit of payload for monohulls. [40]  Two advances over the traditional catamaran are the small-waterplane-area twin hull (SWATH) and the wave-piercing configuration—the latter having become a widely favored design. SWATH reduces wave-generating resistance by moving displacement volume below the waterline, using a pair of tubular, submarine-like hulls, connected by pylons to the bridge deck with a narrow waterline cross-section. The submerged hulls are minimally affected by waves. [43] The SWATH form was invented by Canadian Frederick G. Creed , who presented his idea in 1938 and was later awarded a British patent for it in 1946. It was first used in the 1960s and 1970s as an evolution of catamaran design for use as oceanographic research vessels or submarine rescue ships. [44] In 1990, the US Navy commissioned the construction of a SWATH ship to test the configuration. [45] SWATH vessels compare with conventional powered catamarans of equivalent size, as follows: [43]
 Wave-piercing catamarans (strictly speaking they are trimarans , with a central hull and two outriggers) employ a low-buoyancy bow on each hull that is pointed at the water line and rises aft, up to a level, to allow each hull to pierce waves, rather than ride over them. This allows higher speeds through waves than for a conventional catamaran. They are distinguished from SWATH catamarans, in that the buoyant part of the hull is not tubular. The spanning bridge deck may be configured with some of the characteristics of a normal V-hull, which allows it to penetrate the crests of waves. [46] Wave-piercing catamaran designs have been employed for yachts, [47] passenger ferries, [48] and military vessels. [49]  A catamaran configuration fills a niche where speed and sea-kindliness is favored over bulk capacity. In larger vessels, this niche favors car ferries and military vessels for patrol or operation in the littoral zone.  Recreational and sport catamarans typically are designed to have a crew of two and be launched and landed from a beach. Most have a trampoline on the bridging structure, a rotating mast and full-length battens on the mainsail. Performance versions often have trapezes to allow the crew to hike out and counterbalance capsize forces during strong winds on certain points of sail. [50] For the 33rd America's Cup , both the defender and the challenger built 90-foot (27 m) long multihulls. Société Nautique de Genève , defending with team Alinghi , sailed a catamaran. The challenger, BMW Oracle Racing, used a trimaran, replacing its soft sail rig with a towering wing sail —the largest sailing wing ever built. In the waters off Valencia , Spain in February 2010, the BMW Oracle Racing trimaran with its powerful wing sail proved to be superior. This represented a break from the traditional monohulls that had always been sailed in previous America's Cup series. [51] On San Francisco Bay, the 2013 America's Cup was sailed in 72-foot (22 m) long AC72 catamarans (craft set by the rules for the 2013 America's Cup). Each yacht employed hydrofoils and a wing sail. The regatta was won 9–8 by Oracle Team USA against the challenger, Emirates Team New Zealand , in fifteen matches because Oracle Team USA had started the regatta with a two-point penalty. [52] [53] Yachting has seen the development of multihulls over 100 feet (30 m) in length. " The Race " helped precipitate this trend; it was a circumnavigation challenge which departed from Barcelona, Spain, on New Year's Eve, 2000. Because of the prize money and prestige associated with this event, four new catamarans (and two highly modified ones) over 100 feet (30 m) in length were built to compete. The largest, PlayStation , owned by Steve Fossett , was 125 feet (38 m) long and had a mast which was 147 feet (45 m) above the water. Virtually all of the new mega-cats were built of pre-preg carbon fiber for strength and the lowest possible weight. The top speeds of these boats can approach 50 knots (58 mph; 93 km/h) . The Race was won by the 33.50 m (109.9 ft) -long catamaran Club Med skippered by Grant Dalton . It went round the globe in 62 days at an average speed of 18 knots (21 mph; 33 km/h) . [54]  Whitewater catamaran—sometimes called "cata-rafts"—for whitewater sports are widely spread in post-Soviet countries . They consists of two inflatable hulls connected with a lattice scaffold. The frame of the tourist catamaran can be made of both aluminum (duralumin) pipes and from felled tree trunks. The inflatable part has two layers—an airtight balloon with inflation holes and a shell made of dense tissue, protecting the balloon from mechanical damage. Advantages of such catamarans are light weight, compactness and convenience in transportation (the whole product is packed in one pack-backpack, suitable for air traffic standards) and the speed of assembly (10–15 minutes for the inflation). [55] All-inflatable models are available in North America. [56] A cata-raft design has been used on the Colorado River to handle heavy whitewater, yet maintain a good speed through the water. [57]  Cruising sailors must make trade-offs among volume, useful load, speed, and cost in choosing a boat. Choosing a catamaran offers increased speed at the expense of reduced load per unit of cost. Howard and Doane describe the following tradeoffs between cruising monohulls and catamarans: [38] A long-distance, offshore cruising monohull may be as short as 30 feet (9.1 m) for a given crew complement and supporting supplies, whereas a cruising catamaran would need to be 40 feet (12 m) to achieve the same capacity. In addition to greater speed, catamarans draw less water than do monohulls— as little as 3 feet (0.91 m) —and are easier to beach. Catamarans are harder to tack and take up more space in a marina. Cruising catamarans entail added expense for having two engines and two rudders. Tarjan adds that cruising catamarans boats can maintain a comfortable 300 nautical miles (350 mi; 560 km) per day passage, with the racing versions recording well over 400 nautical miles (460 mi; 740 km) per day. In addition, they do not heel more than 10-12 degrees, even at full speed on a reach. [58] Powered cruising catamarans share many of the amenities found in a sail cruising catamaran. The saloon typically spans two hulls wherein are found the staterooms and engine compartments. As with sailing catamarans, this configuration minimizes boat motion in a seaway. [59] The Swiss-registered wave-piercing catamaran, Tûranor PlanetSolar , which was launched in March 2010, is the world's largest solar powered boat. It completed a circumnavigation of the globe in 2012. [60]  The 1970s saw the introduction of catamarans as high-speed ferries , as pioneered by Westermoen Hydrofoil in Mandal , Norway, which launched the Westamaran design in 1973. [61] The Stena Voyager was an example of a large, fast ferry, typically traveling at a speed of 46 miles per hour (74 km/h) , although it was capable of over 70 miles per hour (110 km/h) . [62] The Australian island Tasmania became the site of builders of large transport catamarans— Incat in 1977 [63] and Austal in 1988 [64] —each building civilian ferries and naval vessels. Incat built HSC Francisco , a High-Speed trimaran that, at 58 knots, is (as of 2014) the fastest passenger ship in service. [65]  The first warship to be propelled by a steam engine, named Demologos or Fulton and built in the United States during the War of 1812 , was a catamaran with a paddle wheel between her hulls. In the early 20th Century several catamarans were built as submarine salvage ships: SMS Vulkan and SMS Cyclop of Germany , Kommuna of Russia , and Kanguro of Spain , all designed to lift stricken submarines by means of huge cranes above a moon pool between the hulls. Two Cold War-era submarine rescue ships , USS Pigeon and USS Ortolan of the US Navy , were also catamarans, but did not have the moon pool feature. The use of catamarans as high-speed naval transport was pioneered by HMAS Jervis Bay , which was in service with the Royal Australian Navy between 1999 and 2001. The US Military Sealift Command now operates several Expeditionary Fast Transport catamarans owned by the US Navy; [66] they are used for high speed transport of military cargo, and to get into shallow ports. The Makar -class is a class of two large catamaran-hull survey ships built for the Indian Navy . As of 2012, one vessel, INS Makar (J31) , was in service and the second was under construction. [67] First launched in 2004 at Shanghai, the Houbei class missile boat of the People's Liberation Army Navy (PLAN) has a catamaran design to accommodate the vessel's stealth features. [68] The Tuo Chiang-class corvette is a class of Taiwanese -designed fast and stealthy multi-mission wave-piercing catamaran corvettes [69] first launched in 2014 for the Republic of China (Taiwan) Navy .
Related Research Articles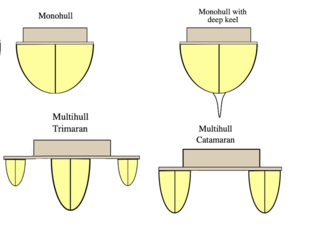 A multihull is a boat or ship with more than one hull, whereas a vessel with a single hull is a monohull. The most common multihulls are catamarans, and trimarans. There are other types, with four or more hulls, but such examples are very rare and tend to be specialised for particular functions.  A yacht is a sail- or motor-propelled watercraft made for pleasure, cruising, or racing. There is no standard definition, though the term generally applies to vessels with a cabin intended for overnight use. To be termed a yacht , as opposed to a boat , such a pleasure vessel is likely to be at least 33 feet (10 m) in length and may have been judged to have good aesthetic qualities. A sailboat or sailing boat is a boat propelled partly or entirely by sails and is smaller than a sailing ship. Distinctions in what constitutes a sailing boat and ship vary by region and maritime culture.  A trimaran is a multihull boat that comprises a main hull and two smaller outrigger hulls which are attached to the main hull with lateral beams. Most modern trimarans are sailing yachts designed for recreation or racing; others are ferries or warships. They originated from the traditional double-outrigger hulls of the Austronesian cultures of Maritime Southeast Asia; particularly in the Philippines and Eastern Indonesia, where it remains the dominant hull design of traditional fishing boats. Double-outriggers are derived from the older catamaran and single-outrigger boat designs.  An outrigger is a projecting structure on a boat, with specific meaning depending on types of vessel. Outriggers may also refer to legs on a wheeled vehicle that are folded out when it needs stabilization, for example on a crane that lifts heavy loads. A monohull is a type of boat having only one hull, unlike multihulled boats which can have two or more individual hulls connected to one another.  Outrigger boats are various watercraft featuring one or more lateral support floats known as outriggers, which are fastened to one or both sides of the main hull. They can range from small dugout canoes to large plank-built vessels. Outrigger boats can also vary in their configuration, from the ancestral double-hull configuration (catamarans), to single-outrigger vessels prevalent in the Pacific Islands and Madagascar, to the double-outrigger vessels (trimarans) prevalent in Island Southeast Asia. They are traditionally fitted with Austronesian sails, like the crab claw sails and tanja sails, but in modern times are often fitted with petrol engines.  Proas are various types of multi-hull outrigger sailboats of the Austronesian peoples. The terms were used for native Austronesian ships in European records during the Colonial era indiscriminately, and thus can confusingly refer to the double-ended single-outrigger boats of Oceania, the double-outrigger boats of Island Southeast Asia, and sometimes ships with no outriggers or sails at all. A small waterplane area twin hull , better known by the acronym SWATH , is a catamaran design that minimizes hull cross section area at the sea's surface. Minimizing the ship's volume near the surface area of the sea, where wave energy is located, minimizes a vessel's response to sea state, even in high seas and at high speeds. The bulk of the displacement necessary to keep the ship afloat is located beneath the waves, where it is less affected by wave action. Wave excitation drops exponentially as depth increases, so wave action normally does not affect a submerged submarine at all. Placing the majority of a ship's displacement under the waves is similar in concept to creating a ship that rides atop twin submarines.  Hobie Cat is a company that manufactures watercraft and other products as the Hobie Cat Company. "Hobie Cat" can also refer to specific products of the company, notably its sailing catamarans. Its fiberglass catamaran models range in nominal length between 14 feet (4.3 m) and 18 feet (5.5 m). Rotomolded catamaran models range in length between 12 feet (3.7 m) and 17 feet (5.2 m). Other sailing vessels in the Hobie Cat lineup include, monocats, dinghies, and trimarans, ranging in length between 9 feet (2.7 m) and 20 feet (6.1 m). Its largest product was the Hobie 33, 33 feet (10 m) in length. The company's non-sailing product line includes surfboards, kayaks, stand-up paddle boards, pedalboards, eyeware, and e-bikes. It was founded in 1961 by Hobart (Hobie) Alter, who originally manufactured surfboards. The term beachcat is an informal name for one of the most common types of small recreational sailboats, minimalist 14 to 20 foot catamarans, almost always with a cloth "trampoline" stretched between the two hulls, typically made of fiberglass or more recently rotomolded plastic. The name comes from the fact that they are designed to be sailed directly off a sand beach, unlike most other small boats which are launched from a ramp. The average 8 foot width of the beachcat means it can also sit upright on the sand and is quite stable in this position, unlike a monohull of the same size. The Hobie 14 and Hobie 16 are two of the earliest boats of this type that achieved widespread popularity, and popularized the term as well as created the template for this type of boat.  A wave-piercing boat hull has a very fine bow, with reduced buoyancy in the forward portions. When a wave is encountered, the lack of buoyancy means the hull pierces through the water rather than riding over the top, resulting in a smoother ride than traditional designs, and in diminished mechanical stress on the vessel. It also reduces a boat's wave-making resistance.  A sailing hydrofoil , hydrofoil sailboat , or hydrosail is a sailboat with wing-like foils mounted under the hull. As the craft increases its speed the hydrofoils lift the hull up and out of the water, greatly reducing wetted area, resulting in decreased drag and increased speed. A sailing hydrofoil can achieve speeds exceeding double and in some cases triple the wind speed.  A sailing yacht , is a leisure craft that uses sails as its primary means of propulsion. A yacht may be a sail or power vessel used for pleasure, cruising, or racing. There is no standard definition, so the term applies here to sailing vessels that have a cabin with amenities that accommodate overnight use. To be termed a "yacht", as opposed to a "boat", such a vessel is likely to be at least 33 feet (10 m) in length and have been judged to have good aesthetic qualities. Sailboats that do not accommodate overnight use or are smaller than 30 feet (9.1 m) are not universally called yachts. Sailing yachts in excess of 130 feet (40 m) are generally considered to be superyachts. VPLP design is a French-based naval architectural firm founded by Marc Van Peteghem and Vincent Lauriot-Prévost, responsible for designing some of the world's most innovative racing boats. Their designs presently hold many of the World Speed Sailing records. James Wharram was a British multihull pioneer and designer of catamarans. The Ocean Bird is a class of trimaran sailboat designed by John Westell and produced by Honnor Marine Ltd. at Totnes, Teignmouth in the 1970s, featuring fold-in lateral floats on a webless steel-beam frame chosen to provide stability against heeling, yet allow a compact footprint in harbour.  Kaep is a traditional type of double-ended Proa sailboat native to Palau. Some of the essential design elements have also been adopted as a modern smaller multihull prototype variant.  Polynesian multihull terminology , such as "ama", "aka" and "vaka" are multihull terms that have been widely adopted beyond the South Pacific where these terms originated. This Polynesian terminology is in common use in the Americas and the Pacific but is almost unknown in Europe, where the English terms "hull" and "outrigger" form normal parlance. Outriggers, catamarans, and outrigger boats are a common heritage of all Austronesian peoples and predate the Micronesian and Polynesian expansion into the Pacific. They are also the dominant forms of traditional ships in Island Southeast Asian and Malagasy Austronesian cultures, where local terms are used.  Austronesian vessels are the traditional seafaring vessels of the Austronesian peoples of Taiwan, Maritime Southeast Asia, Micronesia, coastal New Guinea, Island Melanesia, Polynesia, and Madagascar. They also include indigenous ethnic minorities in Vietnam, Cambodia, Myanmar, Thailand, Hainan, the Comoros, and the Torres Strait Islands.

Did You Know That We Offer Contract to Closing Services? Click Here to Find Out More. Need Marine Financing? Apply Here With Our Partner, First Approval Source
Catalac Catamaran History
 Following the successful development with Bill O’Brien of the Bobcat Catamaran in the 1960s, Tom Lack Catamarans LTD specialized in building these early cruising catamarans. In fact, they built hundreds of Bobcat Catamarans. It was 1970 when they came to the decision to end building O’Brien’s Bobcat and working with boat designer John Winterbotham, created their own design, the Catalac 9M. This marked the beginning of the Catalac line of cruising catamarans.  The Catalac 9M was formally introduced in 1970, followed by the Catalac 8M in 1975, 12M and then the 10M. The boats had a stellar reputation for build quality and seaworthiness. Close to 1000 cruising catamarans were built by the Lack family, 600 of them were Catalacs, making them a cruising catamaran success story as well as one of the pioneers in multihulls. A related footnote is that boat builder Tony Smith of Performance Cruising Inc. (Gemini Catamarans) also worked for O’Brien at that time. It’s no coincidence that the layout of Gemini’s and Catalacs are very similar. “Another interesting bit of history. One of the Catalac rivals in the early 1970’s was the Aristocat. It failed to sell as it wasn’t as good a boat as the Catalac. Years later Tony Smith got the Aristocat moulds and it became the first Gemini. Which maybe gives an indication as to how good the Catalac actually is.” Richard Woods of Woods Designs www.sailingcatamarans.com There was at least one “official” upgrade of the Catalac 8M’s and 9M’s, which was the Mk II about 1980. The company directly addressed the windward performance complaints received, and introduced a newly designed skeg hung rudder system. This modification was a success and greatly improved the windward performance of the boats. The new design was applied to all boat designs going forward.  It is believed that there were some additional improvements as well: modifying the mould to include steps on the forward cabin between the windows for easy access to the cabin top, a square window replaced the round one in head and aft cabin/storage area. There had also been different engines mounted over the years but those are not structural. Production of Catalac Catamarans made by the Lack family ceased around 1985, after Tom Lack was seriously injured in an auto accident. Family tragedies usually come at a poor time and this was no exception. The introduction of the 12 meter Catalac at this time put unusual financial strains on the company, as the boat was a huge success at American boat shows. Alas, the company did not survive the combination of these events. After 1985 production becomes confused with some boat repair boats finished and sold by Lacks sons and or builders associated with them. Additional boats were made/sold by several builders including Catalac Catamarans LTD (not related to the Lack family), which appears to have been the most successful making 10M’s until 1989. After the demise of CCC, John Lack (Tom’s son) was to finish two 10M’s for owners who had boats that had been started but not finished by CCC, and was producing Catalac 8M’s through at least 1990. The Next EvolutionSometime around 1995 the British boat builder Hythe Marine Services LTD of Southampton, started making the Catalac 11M, a updated 10M with “stern scoops” which increased LOA by some 1.5 ft (.6 meters), and rerouted all sail control lines to the cockpit. They also featured handcrafted interior joinery and plush upholstery. While the boat received great reviews and from all reports was well made, sailed and motored better than the Catalac 10M, it was not a sales success. I have a letter sent to a 10M owner where they were exploring an upgrade, and have added the Catalac 11M data to the menu bar.  During this same time period Blue Water Catalacs Ltd, bought the 8m/9M moulds and a “new” 9M came on the market, renamed the Catalac 900. The boat was modified by eliminating the main hatch and extending the ‘doghouse’ into a completely sealed cabin with cockpit entry door. Unfortunately, it was less than a sales success story, in that only 26 boats were manufactured during the company’s existence over 10 years.  I received an email from Nibby David, who lives in Seaton, East Devon, UK concerning the Catalac moulds. He has personally seen the moulds for the 12 meter Catalac at Burnham-on-Sea boatyard, Somerset, Bristol Channel west coast UK, and is fairly certain John Lack still has the 8M moulds, He also reports that the 9M moulds were bought by Blue Water Catalacs and moved to Piddlehinton in Dorset. This was the basis for the Catalac 900. As a side note, Blue Water Catalacs also moulded a few of the Solaris range of cats. However, John Lack disagrees. He told me that he doesn’t have the 8M moulds. John Lack also told me that he believes the 10m Catalac moulds used once by a Company in Hythe, near Southampton, following the demise of Catalac Catamarans, were cut up and discarded. John confirmed the 12m Catalac moulds were last known to be in the Weston Super Mare area of the West Country in the UK.  Owner of a Catalac 8M and Catamaransite webmaster. 9 replies on “Catalac Catamaran History”Great article on Catalac history. Does this mean that the 10M is not of the same high quality as the original 8/9M? “After 1985 production becomes confused with some boat repair boats finished and sold by Lacks sons and or builders associated with them. Additional boats were made/sold by several builders including Catalac Catamarans LTD (not related to the Lack family), which appears to have been the most successful making 10M’s until 1989.’ I’m not sure how to answer a question about what happened 35 years ago. Let me say this. There is a story that the firm awarded the contract to design the Catalac 10M assigned the task to a recent university graduate. His roommate at the time, told me the story. His design was done in Metric which was little understood at the time. In converting metric to imperial, they made errors. When building the 10Ms, they used twice as much fiberglass as needed making them twice as strong as designed. I personally installed a windlass on a 10M and saw this for myself. The foredeck was 3 inches thick. These boats are fine. — Rick Hello Rick, my name is Philippe Honorat (French). I have a question; do you know the hull number of the two catalac 900 with two helms. Thank you very much for your response and this very helpful CatamaranSite!! Regards Philippe Thank you for your technicle dilligence…Facts versus fiction my desire…Is it true the 9 and 8 M boats with optional inboard vs outboard engines retaining or disgarding the prop shapht seal as a form of excess maintainence expence what is the dry dock experinece two that end…?…Does that same option appear on the 12,10 M ect…I am not a sailer but within a previous life i think. Its my goal two atain ownership what is a fine boat bi all acounts but as a new comer i have found sailing isnt the point and shoot afair it seams two be…Many a newcomer has learned the hidden expence what appears two be a vacation enviroment…Thusly my interest in the maintainence aspect of what would be my first boat…Seems two me the less time in dry dock the beter…Enamored…Eric… I think you’re asking if the additional maintenance required by inboard diesel engines, is worth the cost? The answer is, it depends. Longshaft outboards work just fine, but have limitations. First, the outboards have tiny alternators which recharge batteries much slower than inboards do. Then there is the outboard cavitation issue in moderate seas as the propeller can actually leave the water instead of propelling the boat. Cruising range under power can be more than 1000 Kilometers with diesel engines, and a fraction of that with outboards. Lastly the twin throttles of the inboards allow for incredible maneuvering within marinas. So, there are benefits to having the inboards, but it depends if any of this is important to you. Indeed…i didnt think about the charging of bateries relation two alternator i stand corrected on that front…I think that is due two my inexperience as i rely upon my info from what i research there has been nothing on that differnce untill now…Manuvering i understand asweell the rough seas what would be prop out of water but you know marco polo…hahaha…Thankyou for your wizdom and experince fair winds and glassy sea… Hello What an excellent forum. I was glad to stumble on all this information and positive comments about the Catalac. In 1969 I was an apprentice working for M.G.Duff and partners Ltd. Tom Lack invited John to design the Cat that Lacks Nothing and John (bravely) asked me to do the styling. He had done all the clever work so all I had to do was design it’s appearance. This was really exciting opportunity and I was given a free hand. I wanted to give the craft a distinctive profile, which explains the broken sheer and what I hoped would be an elegant bow. To my surprise, John was happy with my styling and I was lucky enough to be on the Stand with a scale model later on at The Boat Show. Those were great days, especially for a 17 year old. Safe seas and happy sailing. Nick, I’m happy you discovered our website. Please post more about your Catalac experiences. – Rick What an interesting site. I’m the proud owner of 9/183. A mark 2, 9M Catalac on which I have lived for the past two years. Leave a Reply Cancel replyYour email address will not be published. Required fields are marked * Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment. How It All StartedA letter from the founder. To understand Aspen Power Catamaran’s goals and philosophy, you need a little history. My dad, Dave Graf, introduced me to boating and instilled in me a love of the outdoors. Throughout my youth we spent our summer vacations exploring, fishing, camping, and hiking in and around the San Juan Islands, the Washington Coast and Puget Sound. Our first boat trips were done in an 18-foot, plywood fiberglass cruiser that Dad built. Later, we moved up to a 24-footer, then a 26, and finally, to a 42-footer. The boats were our vehicles, and the fun was in the places we went and the things we did together. I remember getting up before sunrise to catch the morning bite, seeing the sun roll around and break through to melt the fog, hauling in salmon almost as big as me, and exploring small islands on a warm sunny day. These are the memories that last and shape my views of fun to this day. At the age of 32, I realized that the entrepreneur in me had to escape. As a design engineer, I had developed more than 75 innovative consumer products for a variety of companies in the automotive, powerboat, and quality fitness equipment industries. My passion for engineering really took off in 1980 when I was studying at Western Washington University and joined the Viking Car Program where we designed and built aerodynamic cars that achieve fuel economy upwards of 100mpg, winning competitions around the country. All the books I had read on starting a company said to do it in an area in which you feel great passion. Deciding that boating was the field was easy, I had owned 17 boats myself by this point! Creating a new, special niche was more work. My underlying goal and thought process was that a better mousetrap was needed. I thought that if I could bring the ride, stability, and comfort of larger boats into a smaller, trailerable boat, that boaters would beat a path to my door. Starting with a fresh outlook to solve the ride and comfort issues, the displacement, catamaran hull concept evolved. It was developed and tested over a six-month period with scale models in 1987. A full-scale engineering test boat was built in 1988 and the first Glacier Bay production catamarans were introduced in 1990 to a boating world that had no idea what it was. Through the years of Glacier Bay, 1990 – 2007, the company grew to building 358 boats a year with 205 employees. We became the world’s largest cat builder with 35 dealers, and sales in 7 different countries globally. In the fall of 2007, I began developing the next line of exceptionally efficient cruisers, “Aspen”. The design stemmed from the ability to operate Glacier Bays off one engine, but with slight counter steering. The concept of designing an asymmetrical hull shape then evolved, to correct for the offset thrust. I suspected that if I could design a full displacement catamaran that operated under one diesel inboard engine that the fuel efficiency would be unparalleled. In the spring of 2008, I began constructing the first prototype with my son Nick. Like the first Glacier Bay prototype, this began in a small shop alongside my house. After months of development, we tested the first prototype with sea trials in September of 2008. The performance results of that first sea trial were astounding and surpassed what I initially thought was possible. By February 2009 we had dialed in the final details of the prototype hull and took the boat to the Miami International Boat Show. Two years later we would return and win the award for Innovation of the Year, competing against the world’s largest companies. By January 2010 we had developed the first Aspen C90 Cruiser and displayed it at the Seattle Boat Show where we pre-sold 8 boats. Over the following three years we built 19 C90s in the 4,000 square foot shop alongside my house in Snohomish, Washington with a team of 7 employees. During this time, we partnered with Nordic Tugs out of Burlington, Washington for the fiberglass construction. After listening to our customers express a desire for a larger cockpit and larger engine, we began developing the 32’ Aspen C100 in 2012. In January 2013 we debuted the C100 at the Seattle Boat Show where sales were amazing. The C100 offered a cockpit that was 4’ longer than the C90, higher tunnel clearance for a slightly softer ride, and a Volvo D3 220hp engine that provided higher cruise speeds. It was also in 2012 that the design of the 40’ Aspen C120 began. Starting with drawings, and then eventually a full-size chipboard mockup. In June 2014 my son Nick, friend Dave Boner and I embarked on the Pacific Challenge put on by Pacific Yachting magazine. On this trip we circumnavigated Vancouver Island non-stop traversing 557 miles, in 47 hours and 5 minutes, consuming only 267 gallons of diesel. To this day we hold the record. At this stage, in 2014, the company had outgrown that 4,000 square foot shop alongside my house, so we moved production into Nordic Tug’s facilities in Burlington, Washington. It was also at this time that we began development and tooling on the next big step for Aspen, the 40’ Aspen C120. This 40’x14’ yacht hit the water in the spring of 2015. To our delight, we proved that the patented proa hull design scales beautifully, and in fact only gets better. As of the summer of 2022 there are 23 C120’s cruising the waters around the United States. It was in the fall of 2015 that Aspen moved out of Nordic Tugs facilities after acquiring two new facilities of our own in Burlington, Washington with a total of 33,000 square feet at that time. This included both assembly and our own lamination building. By early 2016 the facilities were fully up and running. Always having a thirst for adventure, from May 2017 to October 2018 we partnered with a new C120 owner to journey 10,502 miles from the Pacific Northwest to Annapolis, Maryland on an expedition we called the Aspen 10,000 Mile Tour. This voyage included cruising North to the glaciers of Alaska, before heading down the Pacific Coast, around the Baja Peninsula into the Sea of Cortez Mexico. The C120 was then portaged by truck to Texas where the journey continued across the Gulf of Mexico, through the Florida Keys, and up the eastern seaboard to arrive in Annapolis, Maryland for the 2018 Annapolis Boat Show. We averaged 19.5mph, getting an average fuel economy of 1.48mpg, and a top speed of 32mph surfing down the California coast (per the Garmin chartplotter). In 2018 we won the Family Business Award for Innovation from Seattle Business Magazine. This was a really cool award… maybe the coolest. As an engineer in the innovation category, I don’t know if it gets any better than receiving an award for working with your family that you love. Today I work with my son Nick, Aspen’s Sales Director, my son Steve, the Financial Controller, and my son-in-law Brandon, the Service Manager. Putting my engineering and design hat back on, we followed the market and Aspen’s first asymmetrical outboard powered hull launched in June 2018. This new design featured dissimilar powered outboards to match the asymmetrical hulls, with a 70hp on port and a 200hp on starboard. This new outboard design was applied to the C100, and the 34’ C107 was introduced the fall of 2018. To prove the capabilities of this new outboard design I thought up a new, albeit crazy adventure. We decided to take the outboard prototype boat down the Mackenzie River in Canada to the Arctic Ocean in July 2019 in a promotion we called Aspen’s Arctic Adventure. This was an epic journey through the untamed Canadian wilderness, down an uncharted river 1,120 miles to the Arctic Ocean, and then back up the river to return to where we launched. In the summer of 2020, we expanded operations even further, acquiring a 17,400 square foot building to be home for Aspen’s Service Department and a second lamination facility for the C120 line. By fall of 2021 we acquired another 5,000 square foot building for sub-assembly, across the street from our main assembly building. Today, Aspen builds 7 models in a modern 48,000 square foot campus in the Pacific Northwest with a team of more than 44 skilled boat builders. The company has become quite successful, and I am very proud of our products, and our team including my family. I am also confident that if you have, or will be purchasing an Aspen Power Catamaran, you will be proud to own one of the most advanced and innovative boats available. Larry Graf, Founder / Designer Glacier Bay RootsEngineering development begins on high-speed, displacement cat hull shapes. A series of one-eighth scale, tow tank models are built to develop and then refine a new hull shape that runs at high speeds with the express goal of NOT planing. A great deal was learned with the scale models about what shapes performed, which ones didn’t and why. Construction begins on a full-scale 22-foot engineering prototype (tongue and groove cedar strips with fiberglass-epoxy covering). It was constructed alongside Larry Graf’s home after hours, weekends and holidays. Engineering prototype is ready for the water after more than 2,000 hours of “after hours” assembly. Launching of the first hull. Spring 1988-1989Testing of full-scale prototype. After refinements, the 2,200-pound boat ran 22mph with a single 60hp outboard. It was tested in Puget Sound, the Straits of Juan de Fuca, the Pacific Ocean, and the Canadian Gulf Islands. Introduction of the first tooled production model a Glacier Bay 248 at the Seattle International Boat Show. It was powered by a single 90hp outboard and included an aft head compartment and a queen size cuddy cabin berth. First twin engine GB 248T introduced. Production moves to Arlington, WA. 3,000 sq. ft. facility w/ 8 employees. Glacier Bay 252 Explorer Cuddy Cabin introduced. They were popular in Hawaii. Introduced the Glacier Bay 220 Center Console, 90hp engines, top speeds of 38mph. The GB 260 Canyon Runner series is introduced with additional hull refinements for enhanced tracking, stability and heavy-load carrying performance – sold 56 at first show, market leader in FL. In 1996, this model was the first outboard-powered boat in history to run at speed from Norfolk, Virginia, to Bermuda – 728 miles nonstop – to win Boating’s Bermuda Challenge! The 2670 Isle Runner Cuddy Cabin was introduced. Additional 8,000 sq. ft. leased facilities, team grows to 55. Completed 1,378-mile delivery trip in 7-days from Oahu to Midway Island with a 260 Canyon Runner and a 2680 Coastal Runner with one refueling stop at Turn Island. Spring/SummerThe 2680-90 Coastal Runners make their debut and complete two, incredible Alaskan adventures. One was a 2,700-mile run up the Pacific Coast to Prince William Sound and then across the Gulf of Alaska to Homer. A second adventure trip ran from Nome across the Bering Strait to Russia-Siberia and back. the GB 2640 Renegade is introduced – the first GB, dual console, family sport-boat cat. The 2240 dual console, family sport-boat with easily accessible head compartment and extra-large swim platform. Sales Zoom! The 3470-80 Ocean Runner sedan express cruiser twin diesel is introduced with an 8,400-mile Grand Americas Trip from Seattle to Portland, Maine. Production team grows to 150. Sold 74 Ocean Runners over the following 18-months. Glacier Bay purchases new 7-acre complex. The new building design incorporates the latest technology into every aspect of the facility. With lamination combined facilities totals 128,000 sq. ft. The first diesel inboard boat launched at Miami International Boat Show. the 3065 Canyon Runner joins the fleet with new Quantum hull, and amazing blue water fishing features. Company books 358 boats for 2007 model year, 205 employees, 35 dealers, and sales in 7 countries around the world. Becomes largest cat builder in the world. Aspen Key MilestonesLarry transitions to start new proa cat company – “Aspen”. Engineering and design of the Aspen hull form begins. Construction of the first Aspen prototype begins in a shop alongside Larry’s house. First sea trials of the Aspen prototype. Results surpass expectations, measuring 4.8mpg running at 17.5mph. Prototype is debuted at the Miami International Boat Show. The 28’ C90 is introduced at the Seattle Boat Show where 8 are pre-sold. Assembly team grows to 7, and partnership with Nordic Tugs is established for manufacturing of the fiberglass parts. The C90 is debuted at the Miami International Boat Show where the award for Innovation of the Year is won, competing against the world’s largest companies. Tooling of the 32’ C100 begins, lengthening the cockpit of the C90 by 4’ and housing a larger 220hp engine. The design and development of the 40’ C120 begins. The C100 is introduced at the Seattle Boat Show where sales were amazing. Also at the show was a full-size chipboard mockup of the interior of the Aspen C120. Production moves to Burlington, Washington where Aspen leases 50% of Nordic Tugs facilities. Tooling of the C120 begins. Team grows to 15 employees. The Pacific Challenge is won with a C100, circumnavigating Vancouver Island non-stop, 557 miles in 47 hours and 5 minutes, consuming only 267 gallons of diesel. The C120 is launched for sea trials with minimal adjustments needed, proving that the patented proa hull design scales beautifully, and in fact only gets better. Aspen leaves Nordic Tugs facilities, acquiring an assembly and lamination building in Burlington, Washington for a total of 33,000 square feet. Aspen begins laminating their own fiberglass parts. New facilities are fully updated and operational. Production of C90s, C100s, and C120s are all underway. Team grows to 25 employees. May 2017 – October 2018Aspen partners with new C120 owners for the 10,000 Mile Tour, journeying 10,502 miles from the Pacific Northwest to the glaciers of Alaska, down the Pacific Coast, around the Baja Peninsula into the Sea of Cortez Mexico. After a truck portage to Texas the journey continues across and through the Gulf of Mexico, through the Florida Keys, and up the eastern seaboard to arrive in Annapolis, Maryland for the 2018 Annapolis Boat Show. The average speed was 19.5mph, getting an average fuel economy of 1.48mpg, and a top speed of 32mph surfing down the California coast (per the Garmin chartplotter). The first asymmetrically L107 outboard powered Aspen prototype is launched. An Aspen C100 being towed to California is involved in a freeway crash where the boat takes on a concrete jersey barrier, and wins. On seen cleanup crews said highway boat accidents typically involve sweeping up the pieces of the vessel but the Aspen is completely intact. The boat is refurbished and cruises Puget Sound today. The 34’ C107 is introduced. This is the sister ship of the C100, with the same interior configurations but powered by outboards. Aspen is awarded the Family Business Award for Innovation from Seattle Business Magazine. Aspen wins Manufacturer of the Year Award in the small company category from Seattle Business Magazine. This is one of Washington state’s most acclaimed manufacturing industry tributes. Arctic Adventure trip with the Aspen L107 outboard prototype. 1,120 miles down the uncharted Mackenzie River to the Arctic Ocean through untamed Canadian wilderness and back. Design and development of the 35’ outboard powered C108 begins. The first C108 is delivered. On the owner’s first ride they were slicing through 3-4 footers at 21mph and “high fiving” with delight in how she ran. Operations are expanded further with a 17,400 square foot building for the Service Department and a second lamination facility for the C120 line. Team grows to 35 employees. 5,000 square foot sub-assembly building is acquired across the street from the main assembly building. Patent No. US 8,109,221 B2 Stay Up to Date with Aspen Sign up to receive our enewsletter. 11656 Knudson Rd. Burlington, WA 98233 Privacy Policy Tell us your Aspen Story . © Copyright 2012 - 2024 | Aspen Power Catamarans (360) 668-4347 EMAIL US  | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A Formula 16 beachable catamaran Powered catamaran passenger ferry at Salem, Massachusetts, United States. A catamaran (/ ˌ k æ t ə m ə ˈ r æ n /) (informally, a "cat") is a watercraft with two parallel hulls of equal size. The distance between a catamaran's hulls imparts resistance to rolling and overturning. Catamarans typically have less hull volume, smaller displacement, and ...
catamaran, twin-hulled sailing and powered boat developed for sport and recreation in the second half of the 20th century. Its design is based on a raft of two logs bridged by planks that had earlier been used by peoples in the Indonesian archipelago and throughout Polynesia and Micronesia. Early catamarans were up to 21.3 metres (70 feet) long ...
Catamarans: A Complete Guide to Multihull Boats. Catamarans have been a part of sailing history for centuries and continue to be popular for their stability, spaciousness, and performance. Developed by various cultures around the world, the principles of catamaran design have evolved over time to become optimized for both pleasure cruising and racing. . This complete guide will help you ...
August 23, 2024. Catamarans are boats with two connected hulls that are joined by a bridge. Because they are faster, more stable, and capable of carrying larger cargo than their monohull counterparts, catamarans are growing in popularity. Contents show.
A catamaran (from Tamil kattumaram) is a type of multihulled boat or ship consisting of two hulls, or Vakas, joined by a frame, formed of Akas.Catamarans can be sail- or engine-powered. The catamaran was first discovered being used by the paravas, a fishing community in the southern coast of Tamil Nadu, India.Catamarans were used by the ancient Tamil Chola dynasty as early as the fifth century ...
Learn the catamaran history, from ancient roots to modern sailing, and discover why a Charleston catamaran charter is an experience you don't want to miss. 843-973-0761 ... catamarans served a similar purpose. Fishermen relied on these sturdy boats to venture into the ocean, while traders used them to transport goods along the coast. The Tamil ...
A History Of The Catamaran. It is believed that the first people to use a catamaran design were those living in Australasia. ... Building A Boat - Basics Of Catamaran Construction. A boat is usually thought of as being a single-hulled vessel that travels along the surface of the water. It can have multiple types, shapes, and designs of the hull.
The history of catamarans among the early Austronesian people is tied to that of outrigger canoes, which are boats that are stabilized through the use of a separate floating device which sits alongside the main hull. ... Although as with any catamaran, this boat was designed to use less energy, move faster, and navigate shallower waters, the ...
A catamaran is a twin-hull boat with two equally-sized hulls placed side by side. They're powered by engines, sails, or both—and they're known for efficiency and speed. Catamarans are the most common kind of multihull boat. In this article, we'll go over the characteristics of catamarans and how to differentiate them from other types of ...
She was Porsche-like—low, sleek, and souped-up—a genuine firebreather with literally thousands of horsepower, a top speed of 120 miles per hour, and a set of knife-like sponsons that were asymmetrical, meaning curvaceous outside, slab-sided inside. Normally, Impresia throttled the boat for the famous driver, Stuart Hayim.
Some people think of any multihull boat as a catamaran, but in strict terms a catamaran is a boat with two hulls. A boat with one hull is a monohull and a boat with three hulls is a trimaran. Pontoon boats can be either catamarans or trimarans (sometimes called tri-toons), but can be differentiated from most other multihulls in that their hulls ...
A catamaran is a boat with two hulls and a bridge between them. Catamarans can be designed as sailboats or motorboats. A catamaran stays stable since it has a wide base, it does not have a deep keel as on a monohull. Cats are known for not heeling, increased comfort, more space, and faster speeds. In this article, we will explore everything you ...
Generally, brand new sailing catamarans and power catamarans will have a price tag in the range of $200,000 to over $1 million. Whereas used catamarans on the brokerage market can be found for around $500,000 and under. Of course, these are general guidelines and will depend on the age of the catamaran, the length of the boat, and the condition ...
He began his experiments in 1964 on the B class Manta and when the IYRU laid down the specification for the A class in 1966, Mazzotti came up with the mythical beast - the Unicorn. She won the RYA trials convincingly in 1967 and came close to being selected as the boat of choice by the IYRU for the International A class.
The origin of World Cat can be traced back over a quarter of a century to the beginning of our Glacier Bay Edition boats in America's Pacific Northwest. Today, World Cat is the largest maker of power catamarans in the world. Located in Tarboro, North Carolina, our boats are precision crafted in a state-of-the-art 140,000 square foot facility.
History Succession of forms in the development of the Austronesian boat (Mahdi, 1999). Catamarans from Oceania and Maritime Southeast Asia became the inspiration for modern catamarans. Until the 20th century catamaran development focused primarily on sail-driven concepts.
The Catalac 9M was formally introduced in 1970, followed by the Catalac 8M in 1975, 12M and then the 10M. The boats had a stellar reputation for build quality and seaworthiness. Close to 1000 cruising catamarans were built by the Lack family, 600 of them were Catalacs, making them a cruising catamaran success story as well as one of the ...
Through the years of Glacier Bay, 1990 - 2007, the company grew to building 358 boats a year with 205 employees. We became the world's largest cat builder with 35 dealers, and sales in 7 different countries globally. In the fall of 2007, I began developing the next line of exceptionally efficient cruisers, "Aspen".